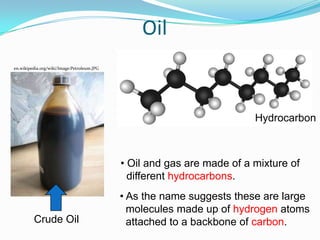
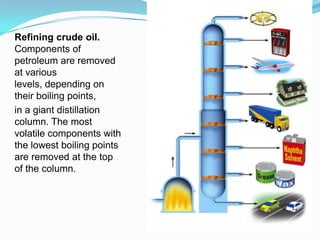
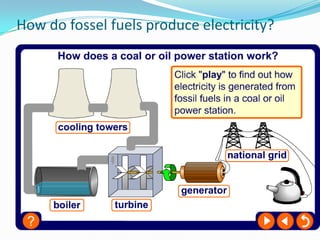
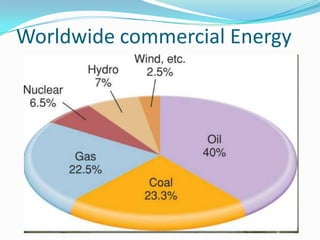
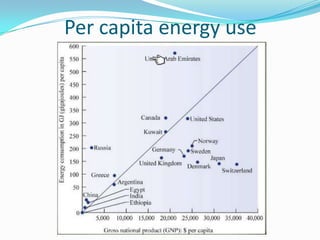
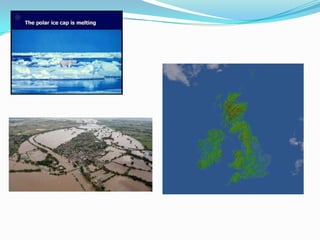
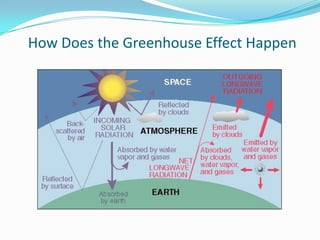
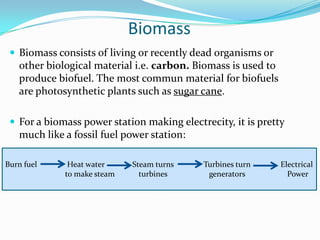
The document outlines an exploration of renewable and non-renewable energy sources, discussing the greenhouse effect and its relation to global warming as well as the environmental impacts of fossil fuels. It identifies examples of both energy types, such as coal and oil for non-renewables, and wind and solar for renewables, while also highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it emphasizes the growing importance of renewable energy to reduce climate change and reliance on fossil fuels.