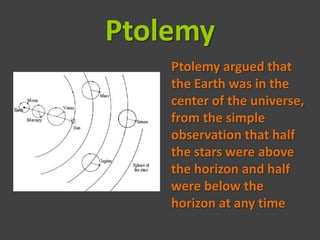
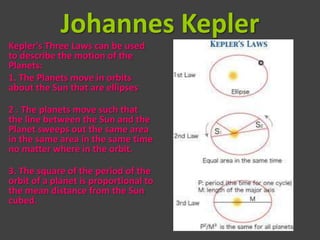
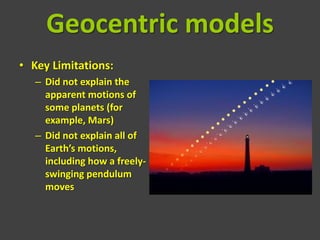
The document discusses the Age of Enlightenment, highlighting the shift from geocentric to heliocentric models of the universe through key figures like Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and Newton. It details how the Enlightenment challenged traditional beliefs upheld by the Catholic Church, ultimately leading to a heightened understanding of astronomy and the rejection of superstition. The document concludes with the eventual acknowledgment by the Church of the heliocentric theory as correct, long after Galileo’s death.