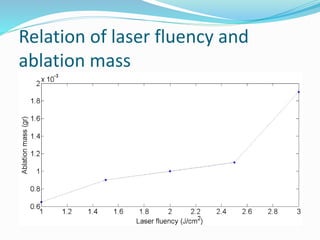
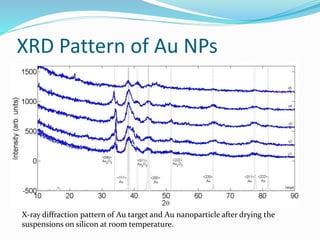
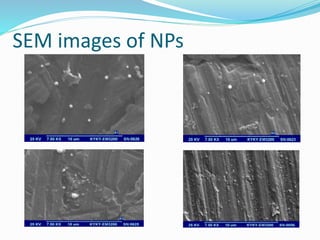
This document provides an overview of nanotechnology, specifically focusing on gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) produced by laser ablation methods. It discusses the properties and applications of noble and base metals, the production process of Au NPs, and the effects of laser fluence on their size and morphology. Key findings indicate that laser fluence significantly influences nanoparticle characteristics, and the generated nanoparticles exhibit structures closely related to their bulk counterparts.