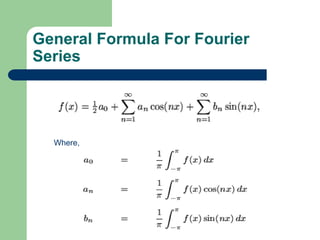
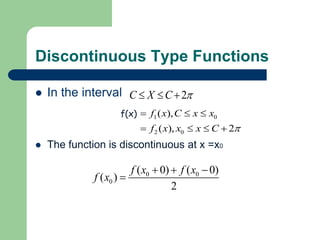
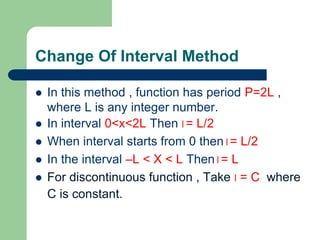
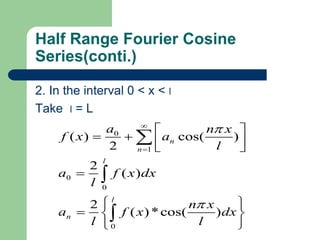
This document provides an overview of Fourier series and related concepts. It defines a Fourier series as an expansion of a periodic function in terms of an infinite sum of sines and cosines. It also describes formulas for general Fourier series, solving examples, discontinuous functions, the change of interval method, even and odd functions, and half range Fourier cosine and sine series.