This document discusses the Z-transform, which converts a discrete-time signal into a complex frequency domain representation. Some key points:
- The Z-transform provides a technique for analyzing and designing discrete time signals and systems, representing them in the complex Z-plane. It has advantages over other transforms like allowing stability analysis.
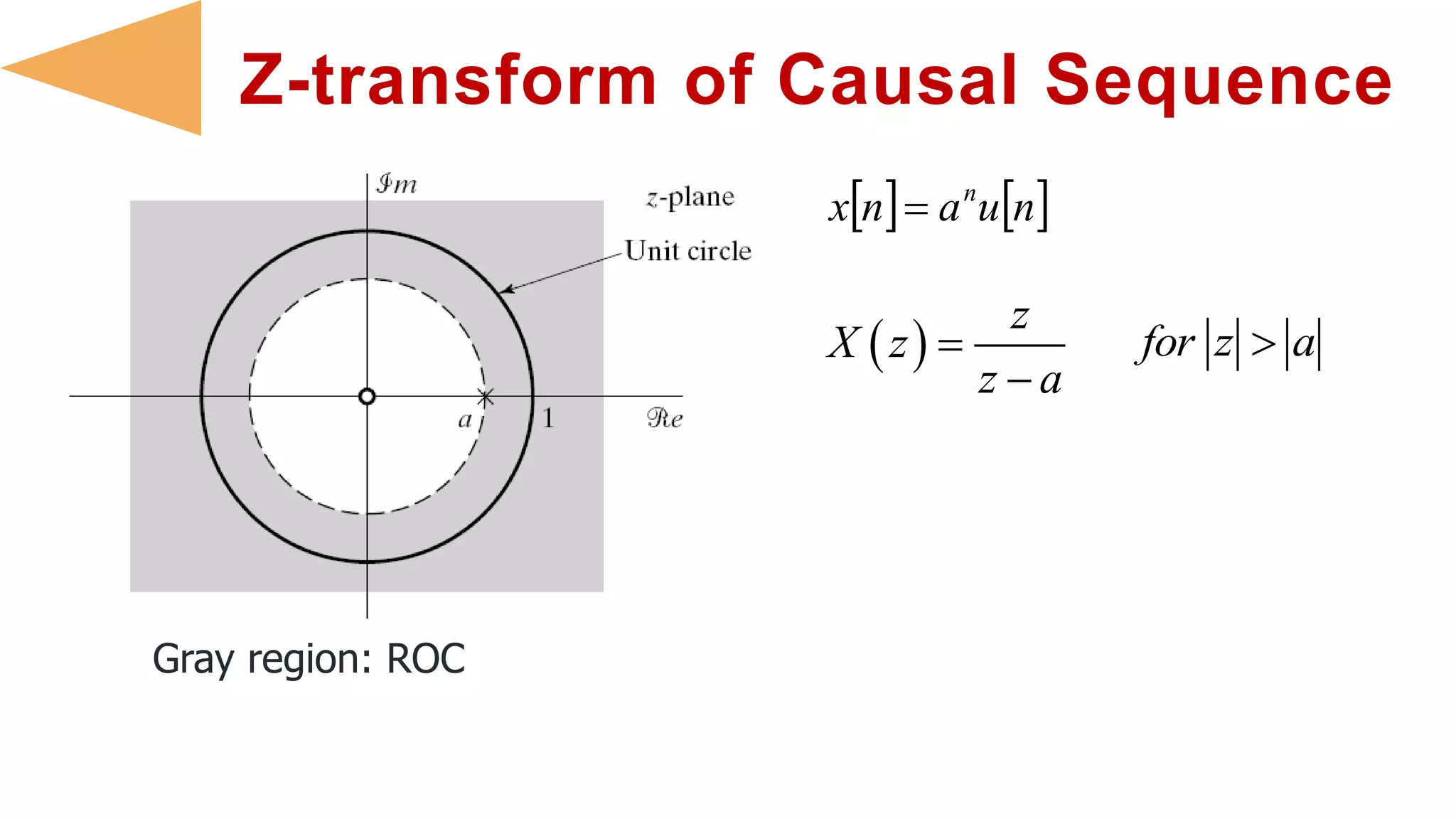
- The region of convergence (ROC) is the set of Z-plane values where the Z-transform is finite. ROCs cannot contain poles and must be connected. Causal sequences have an exterior ROC, anti-causal an interior one.
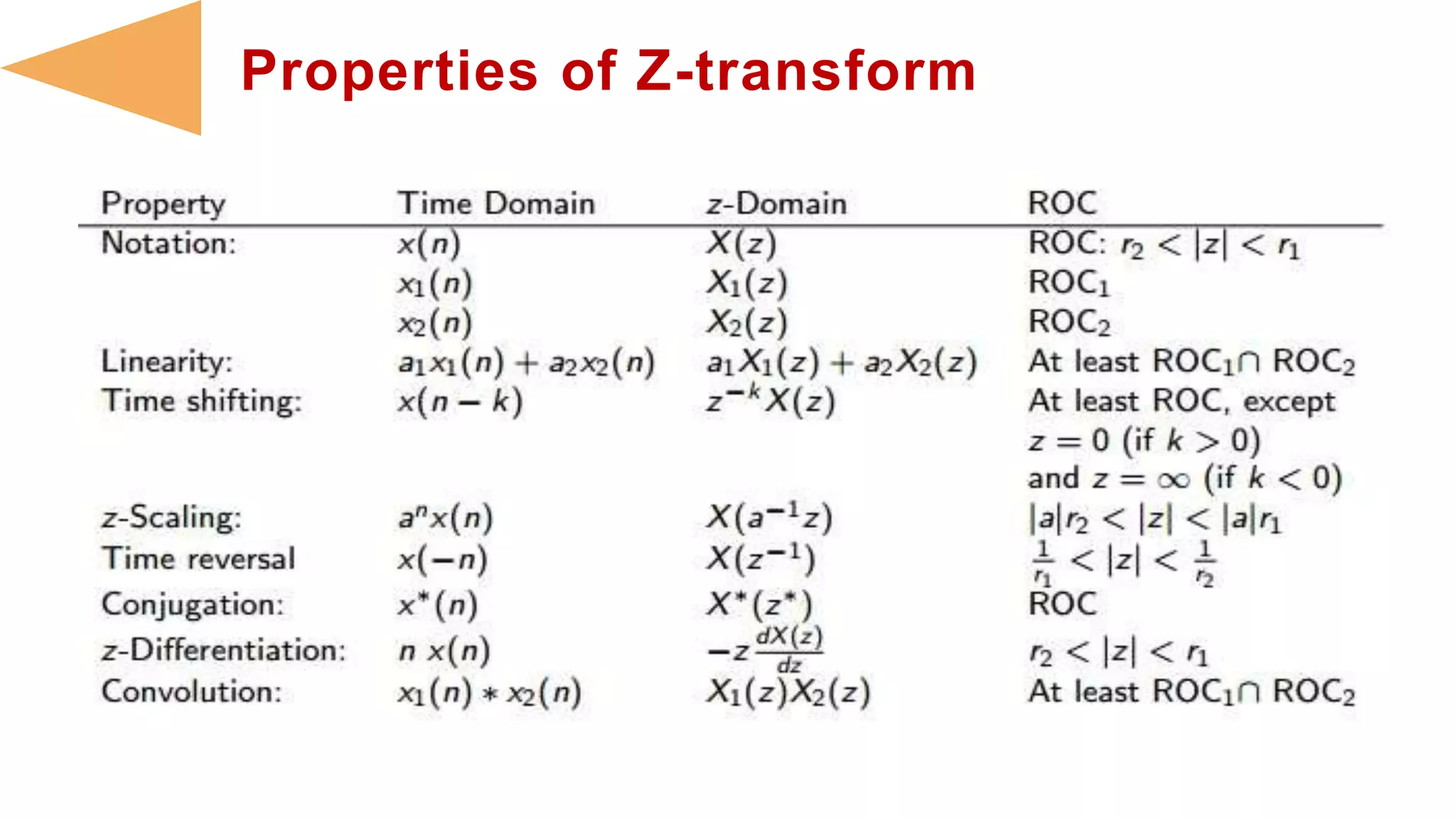
- Z-transforms characterize discrete time signals and linear time-invariant systems completely. Properties include how ROCs restrict poles, and transformations