1. The document discusses Fourier series and orthogonal functions. It defines orthogonal functions and provides examples of orthogonal function sets, such as cosine and sine functions.
2. The chief advantage of orthogonal functions is that they allow functions to be represented as generalized Fourier series expansions. The orthogonality of the functions helps determine the Fourier coefficients in a simple way using integrals.
3. Euler's formulae give the expressions for calculating the Fourier coefficients a0, an, and bn of a periodic function f(x) from its values over one period using integrals of f(x) multiplied by cosine and sine terms.


![3
ii)
2 2
1
cos cos [cos( ) cos( ) ]
2
mx nxdx m n x m n x dx
2
1 1 1
sin( ) sin( )
2
m n x m n x
m n m n
= 0, m n.
iii)
2
cos sin 0
mx nxdx
iv)
2 2
2 2
cos ( ) sin ( ) , 0
nx dx nx dx n
2 2
2
2 1 cos(2 ) 1 1
cos ( ) sin 2
2 2 2
nx
nx dx dx x x
n
a
a 2
2
1
In addition to these properties of integrals involving sine and cosine functions, we often need the
following trigonometric functions for particular arguments.
i)
n
n
n )
1
(
cos
2
)
1
2
sin(
and (ii) ,
0
2
)
1
2
cos(
sin
n
n n = 1, 2,
Theorem : (Euler’s Formulae): The Fourier coefficients in
1
0
sin
cos
2
)
(
n
n
n nx
b
nx
a
a
x
f are given by
2 2
0
1 1
( ) , ( )cos
n
a f x dx a f x nxdx
and
2
1
( )sin
n
b f x nxdx
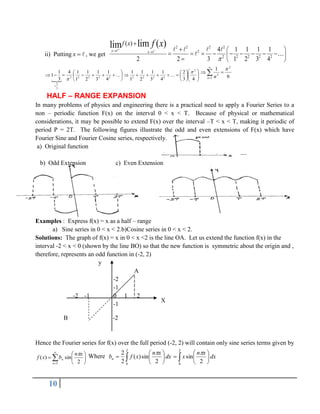
Corollary : 1. If = 0, the interval becomes 0 < x < 2 , and Euler’s formulae are given by:
2
0
0 )
(
1
dx
x
f
a ,
2
0
cos
)
(
1
nxdx
x
f
an
,
2
0
sin
)
(
1
nxdx
x
f
bn .
2. If = - , then the interval becomes -< x < , and the Euler’s Formulae and given by:
dx
x
f
a )
(
1
0 ,
nxdx
x
f
a cos
)
(
1
0 ,
nxdx
x
f
bn sin
)
(
1
.
Examples If
2
2
)
(
x
x
f
in the range (0, 2), show that
1
2
2
cos
12
)
(
n n
nx
x
f
.
Solution: The Fourier serves for f in (0, 2) is
1
0
sin
cos
2
)
(
n
n
n nx
b
nx
a
a
x
f , where
2
0
2
2
2
2
2
0
0 )
2
(
4
1
2
1
)
(
1
dx
x
x
dx
x
dx
x
f
a
6
3
1
4
1 2
2
0
3
2
2
x
x
x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/math1102-ch-3-lecturenotefourierseries-220924014049-1bcc3d60/85/Math-1102-ch-3-lecture-note-Fourier-Series-pdf-3-320.jpg)