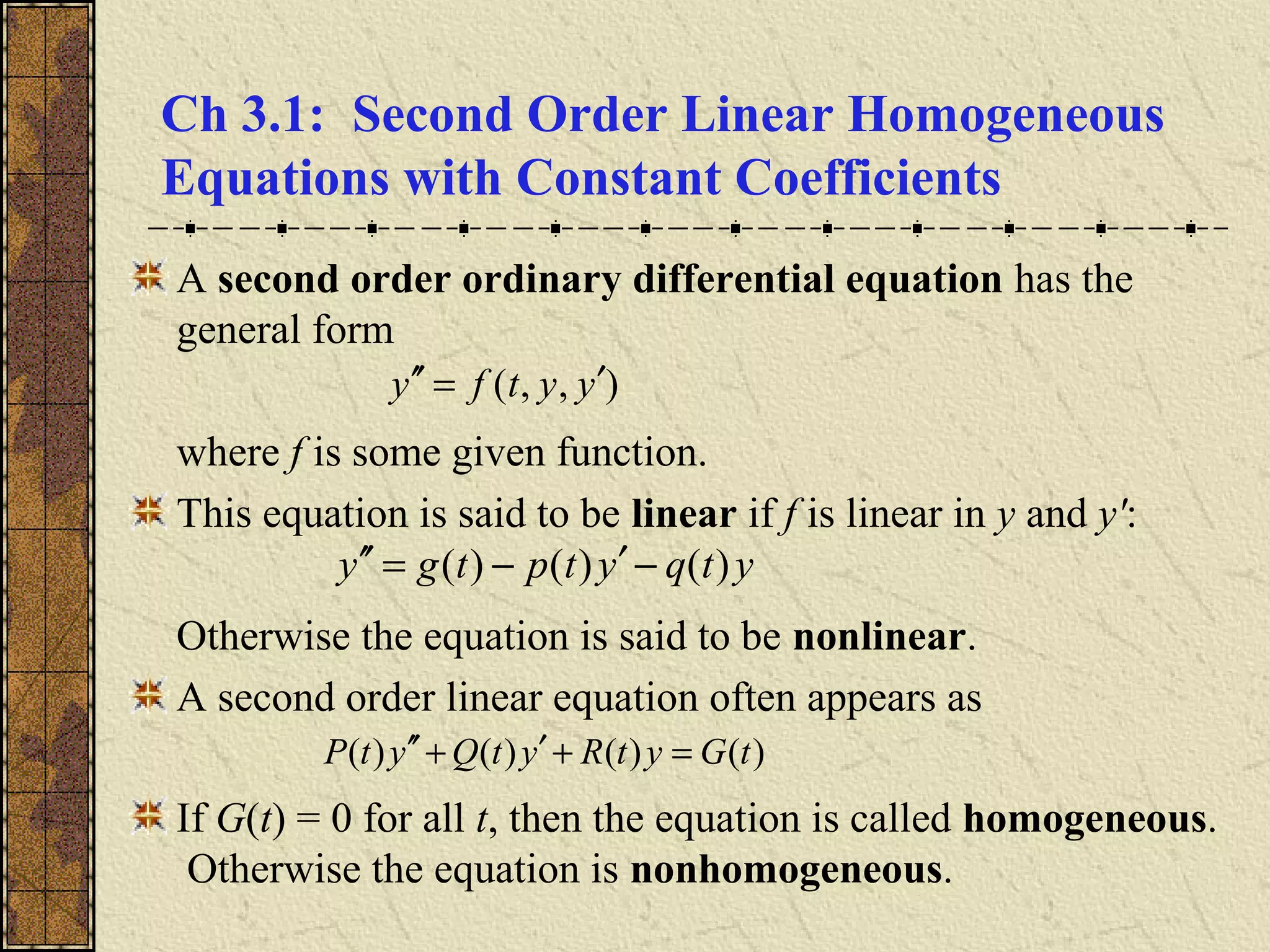
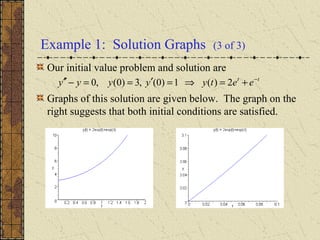
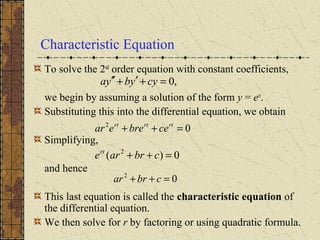
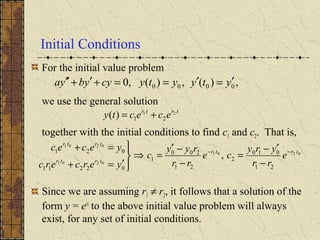
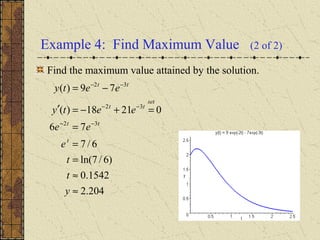
The document discusses solving second order linear homogeneous differential equations with constant coefficients. It explains that the characteristic equation is obtained by substituting an exponential solution into the differential equation. The roots of the characteristic equation determine the general solution, which is a linear combination of exponential terms. Initial value problems can then be solved for the coefficients by applying the initial conditions to the general solution. Several examples illustrate these steps to solve initial value problems for different differential equations.