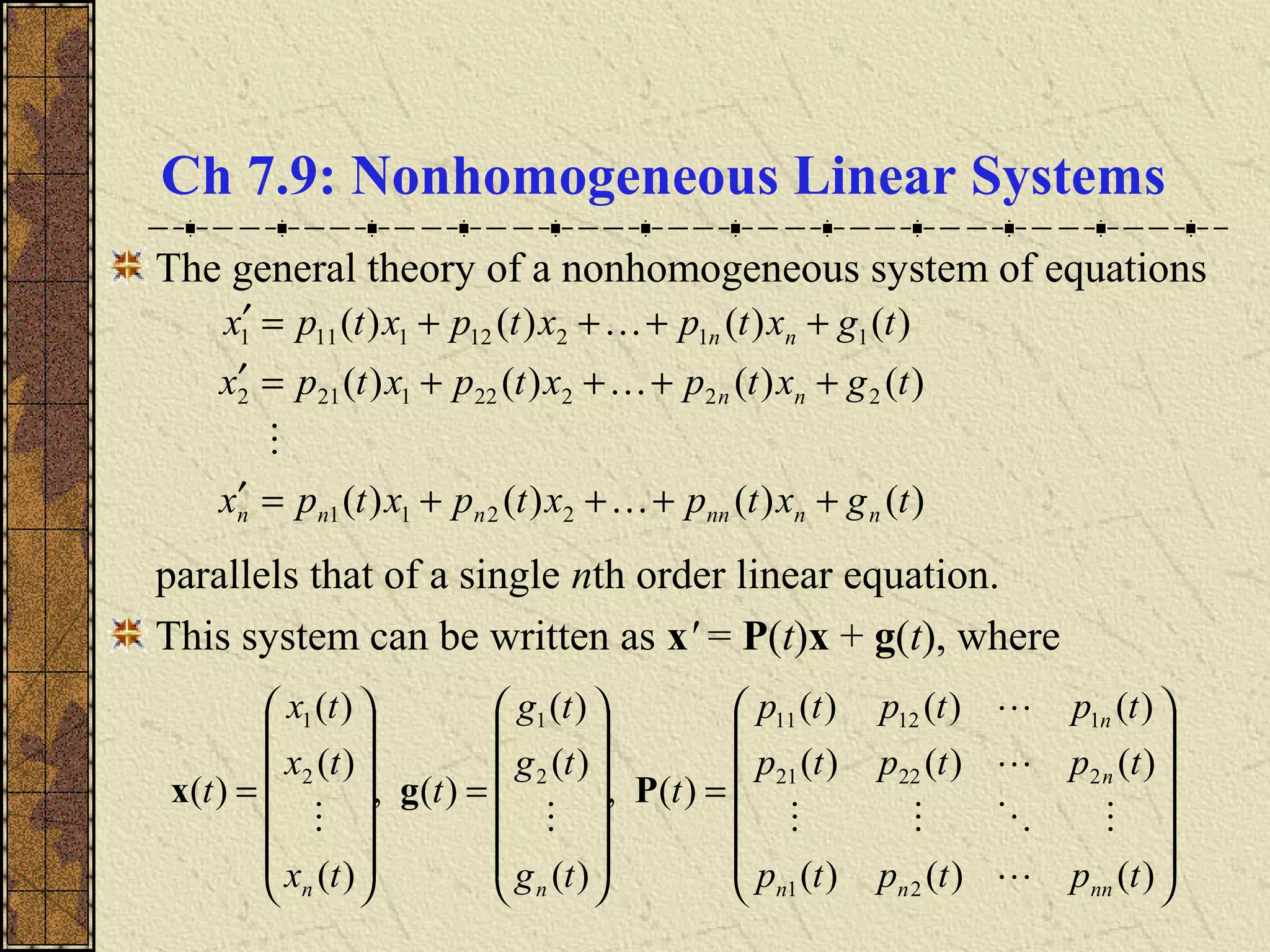
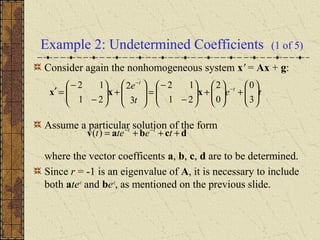
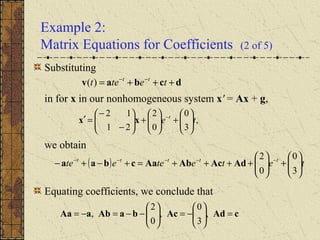
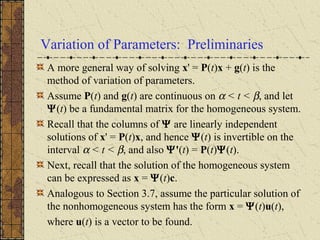
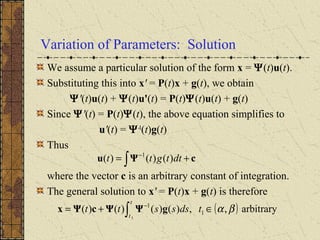
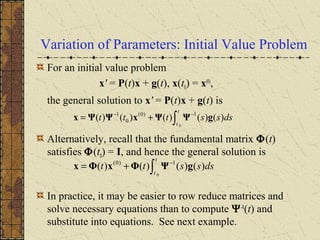
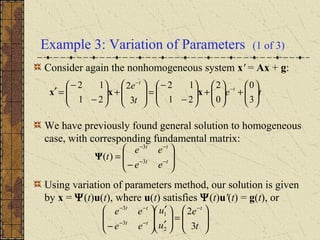
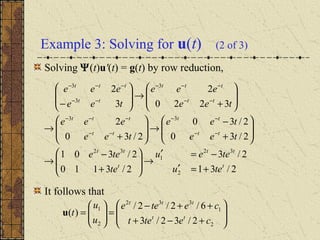
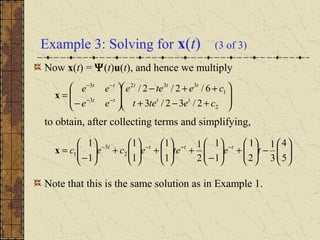
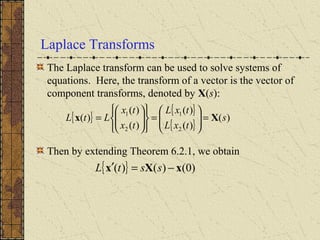
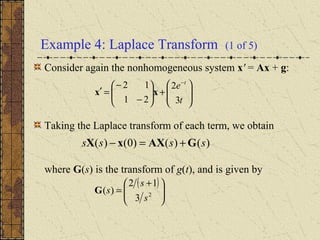
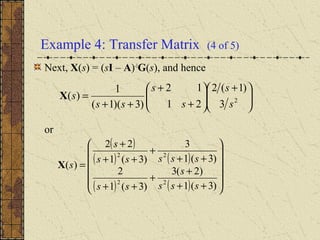
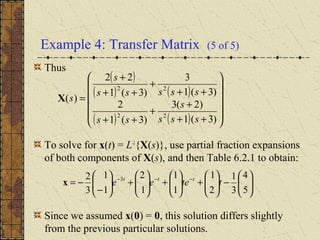
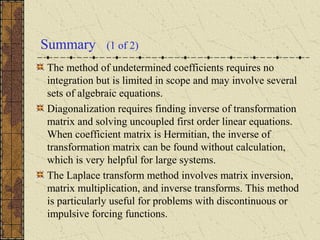
1) Nonhomogeneous linear systems generalize the theory of single nth order linear equations. They can be written in the form x' = P(t)x + g(t).
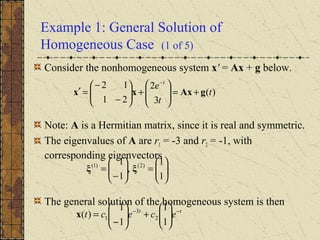
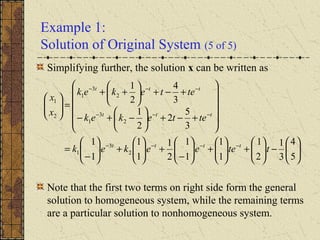
2) The general solution is the sum of the general solution to the homogeneous system x' = P(t)x and a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous system.
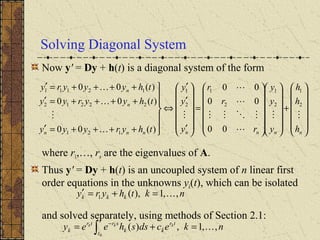
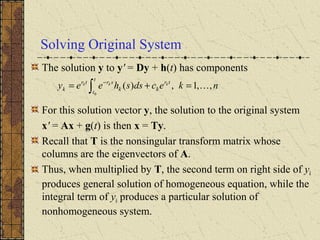
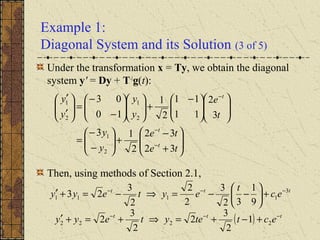
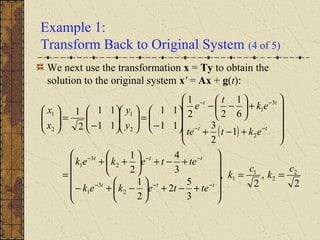
3) If the matrix P is constant and diagonalizable, the system can be transformed to uncoupled equations y' = Dy + h(t) via diagonalization, whose solutions give the solution to the original system.