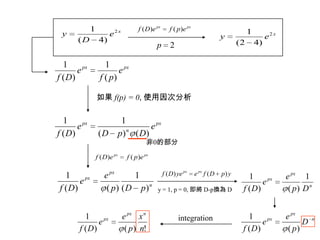
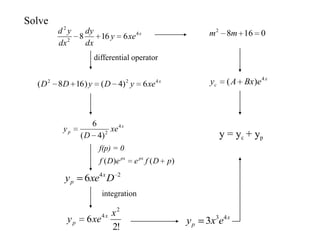
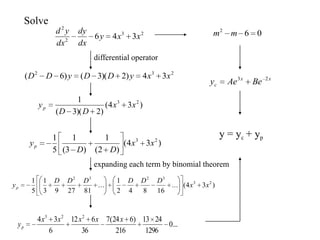
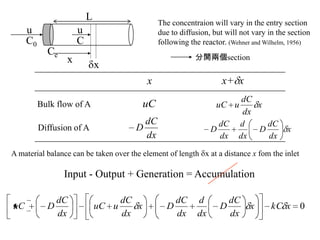
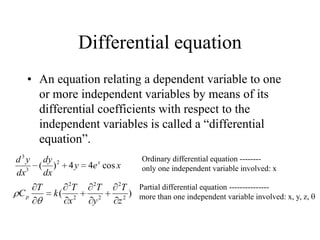
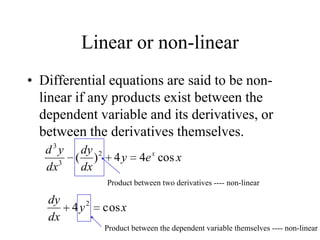
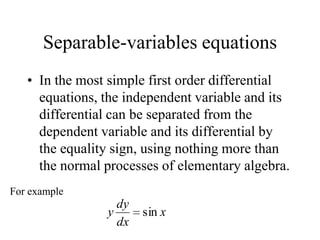
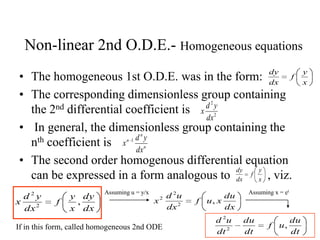
1) Ordinary differential equations relate a dependent variable to one or more independent variables by means of differential coefficients. They can be classified based on order, degree, whether they are linear or non-linear, and type (exact, separable variables, homogeneous).
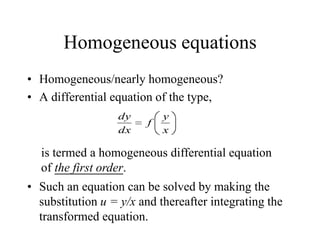
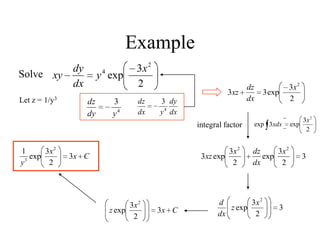
2) First order differential equations can sometimes be solved by separation of variables, or by finding an integrating factor. Homogeneous equations can be transformed by substitution.
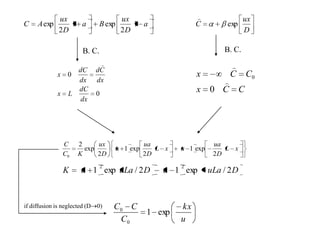
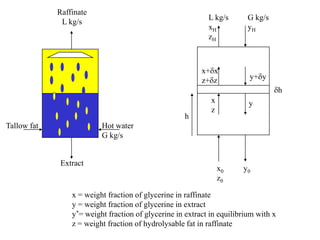
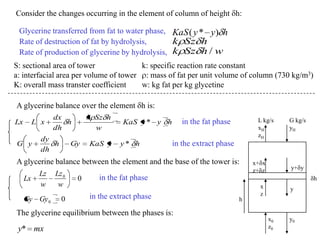
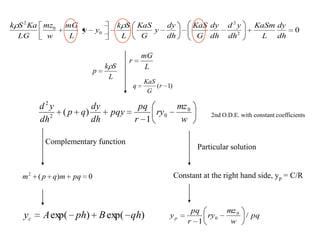
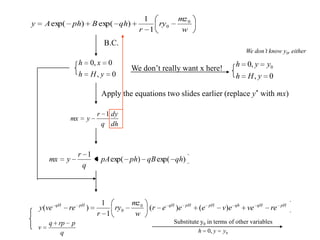
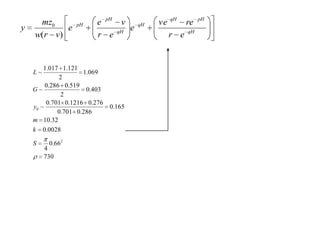
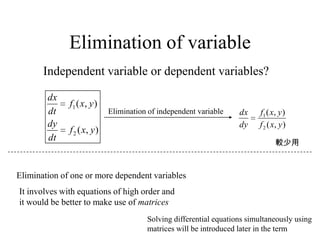
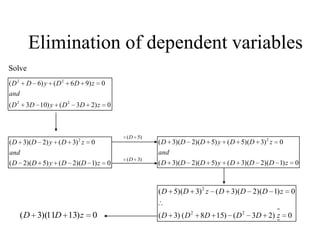
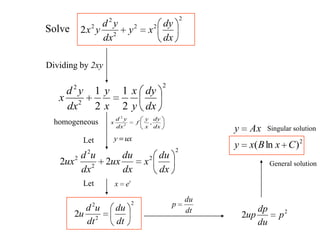
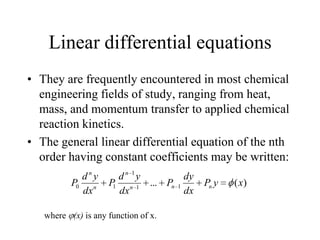
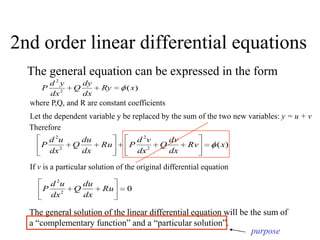
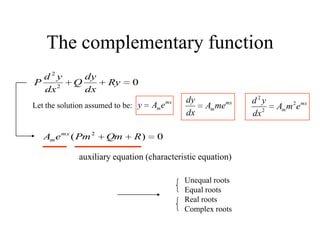
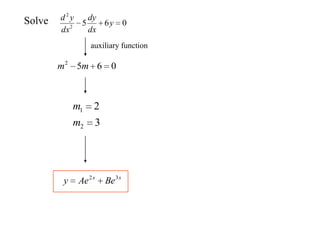
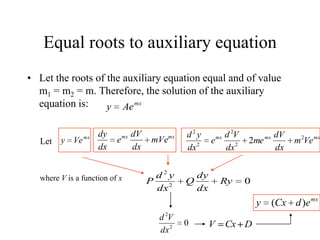
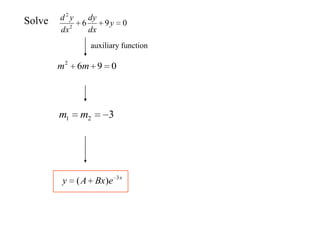
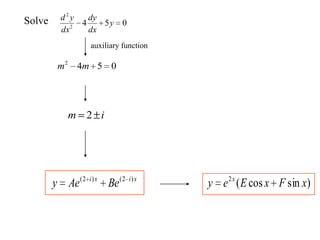
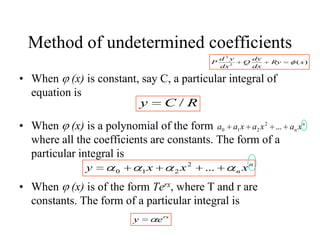
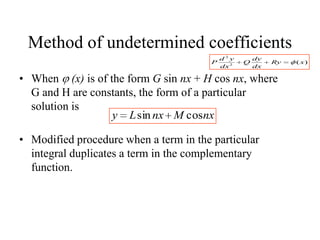
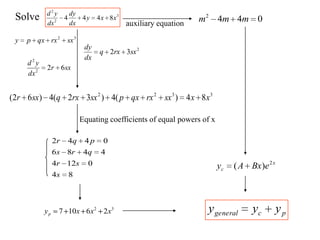
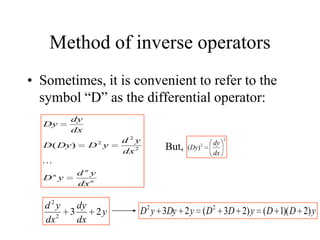
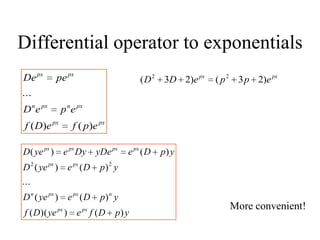
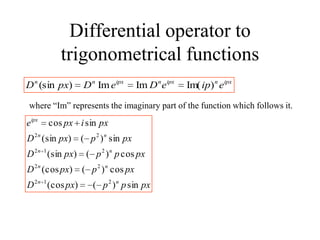
3) Second order linear differential equations can be reduced to a system of two first order equations. The complementary function and particular solutions combine to form the general solution. Unequal or equal roots of the characteristic equation determine the form of the complementary function.



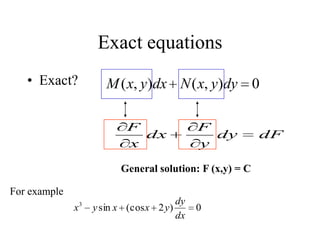





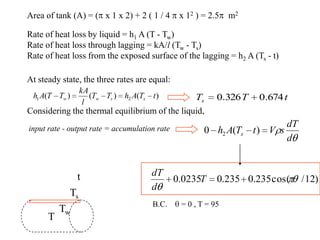


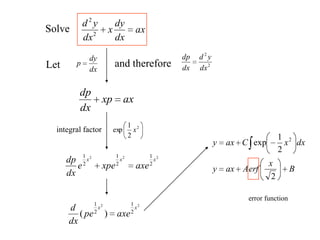

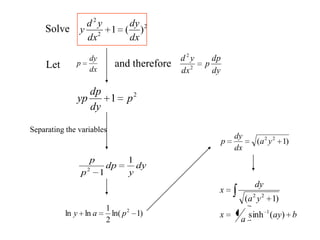
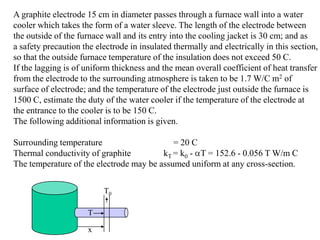
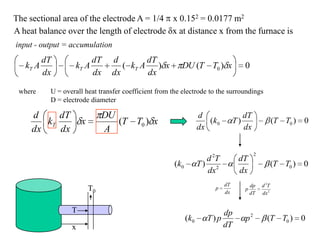
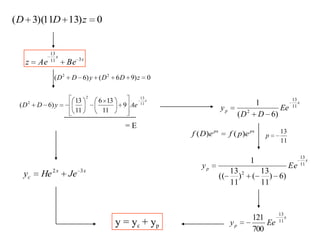
![0)()( 0
2
0 TTp
dT
dp
pTk
zp2
)( 0TTy
022])[( 0 yz
dy
dz
yTk
Integrating factor 2
00
00
2
exp yTk
yTk
dy
])(32))(([
)(
3
0
2
00
0
TTTTTkC
dTTk
x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-140401055554-phpapp02/85/Higher-Differential-Equation-25-320.jpg)




![Solve x
ey
dx
dy 2
4
differential operator
x
eyD 2
)4(
x
e
D
y 2
)4(
1
1...])
4
1
()
4
1
()
4
1
(1[
4
1 322
DDDey x
binomial expansion
=2
x
ey 2
2
1
pxpx
epfeDf )()(
x
e
D
y 2
)
4
1
1(4
1
2p
x
ey 2
)42(
1
...])
2
1
()
2
1
()
2
1
(1[
4
1 322x
ey](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-140401055554-phpapp02/85/Higher-Differential-Equation-43-320.jpg)