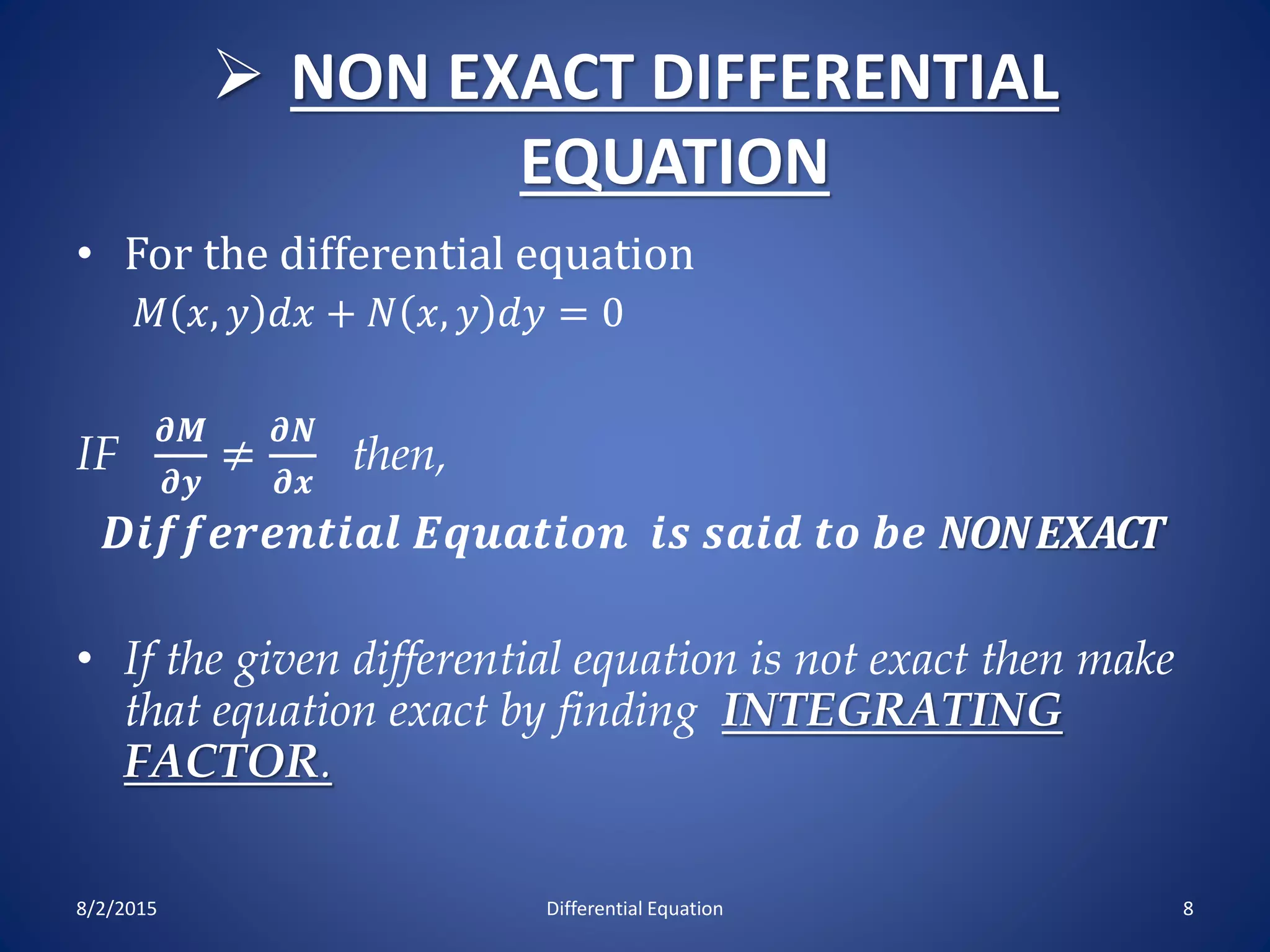
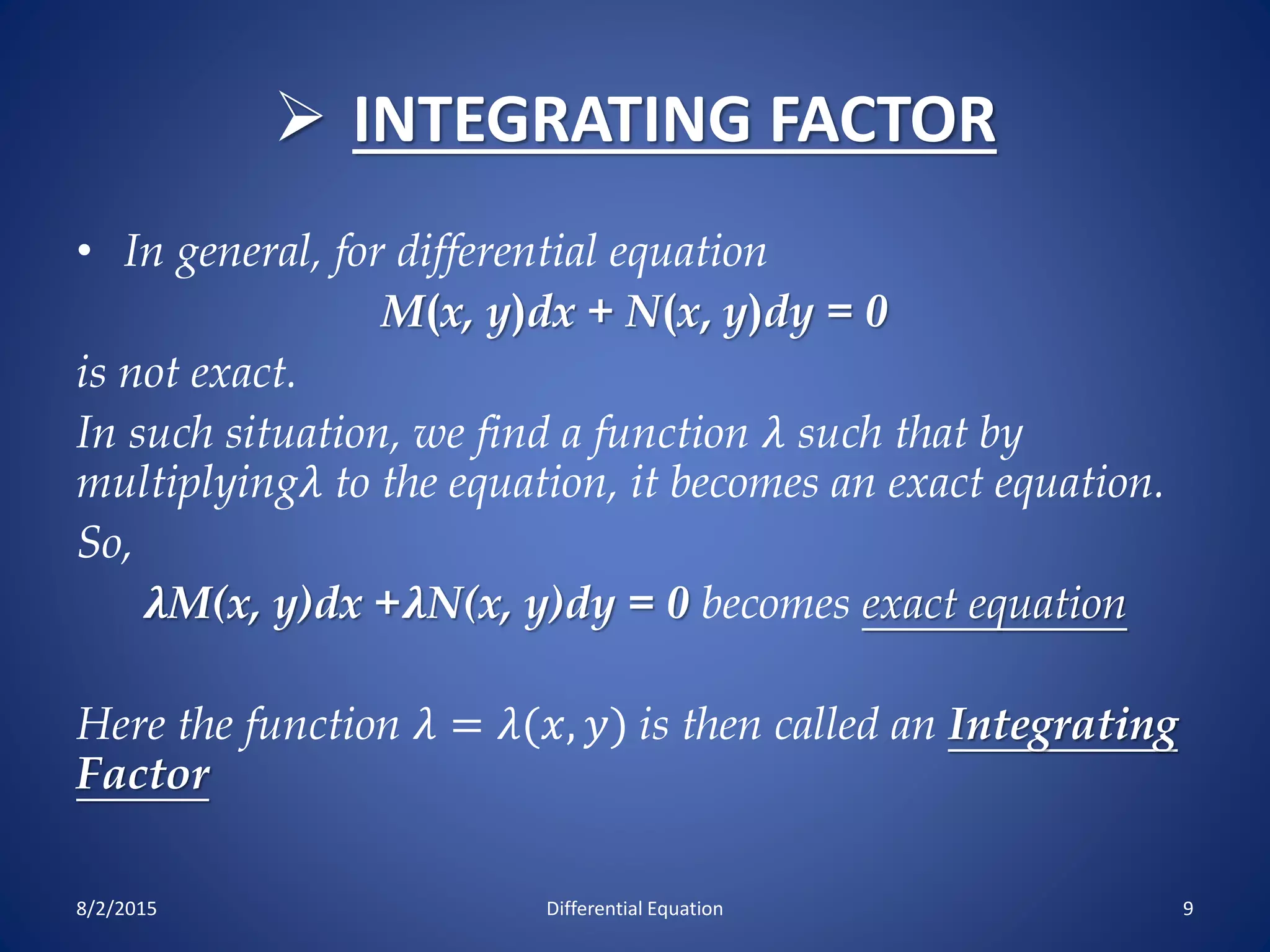
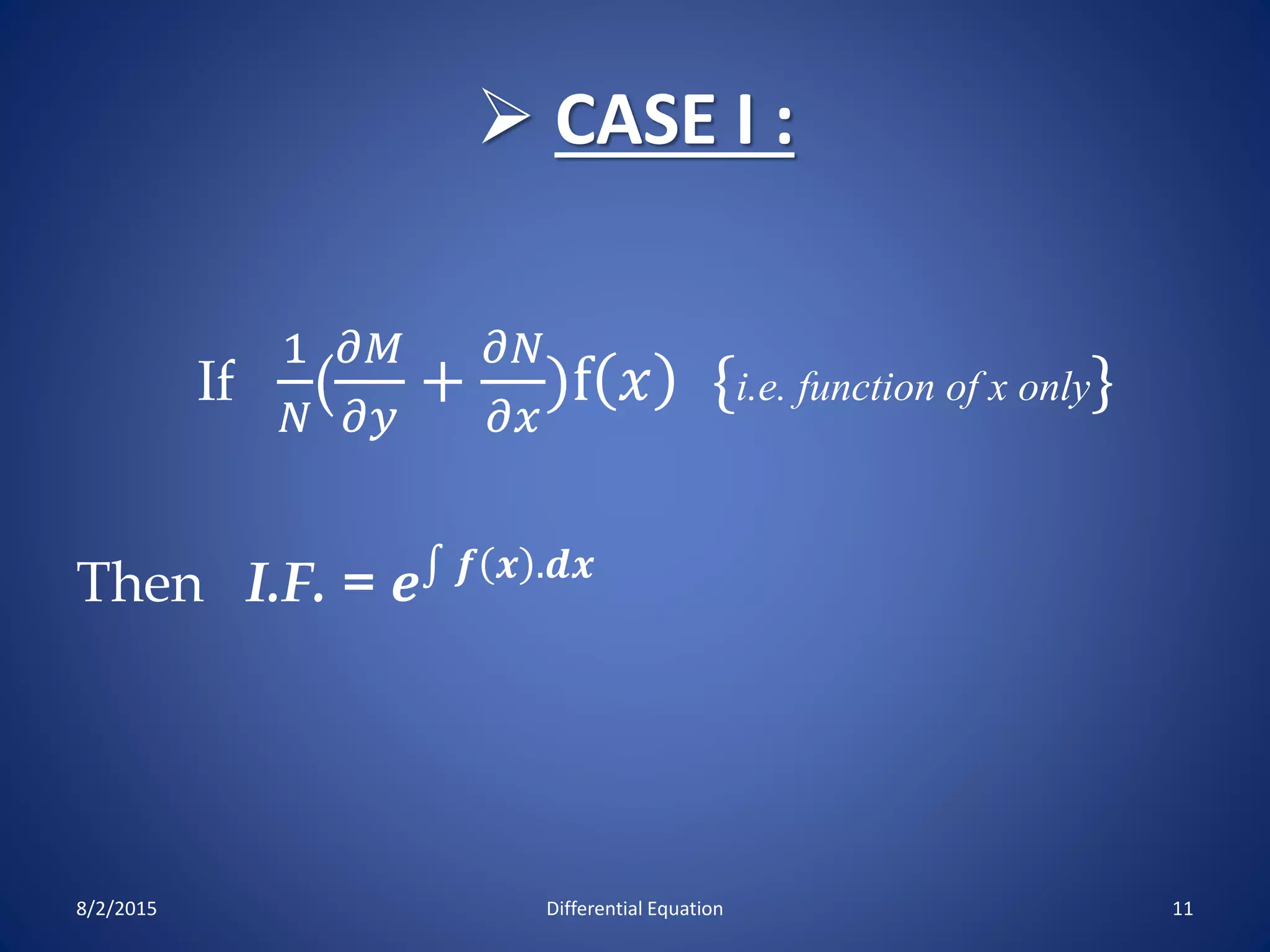
The document discusses exact and non-exact differential equations. It defines an exact differential equation as one where the partial derivatives of M and N with respect to y and x respectively are equal. The solution to an exact differential equation involves finding a constant such that the integral of Mdx + terms of N not containing x dy is equal to that constant. A non-exact differential equation has unequal partial derivatives, requiring an integrating factor to make the equation exact. Several methods for finding an integrating factor are presented, including cases where it is a function of x or y alone or where the equation is homogeneous. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts.









![Multiply both side by I.F. (i.e.
1
𝒙 𝟐), we get
1
𝑥2
(𝑥2
+ 𝑦2
+ 3)𝑑𝑥 − 2𝑥𝑦. 𝑑𝑦 = 0
[( 1 +
𝑦2
𝑥2
+
3
𝑥2
)𝑑𝑥 − 2𝑥𝑦. 𝑑𝑦] = 0
8/2/2015 Differential Equation 14
Example : 2 (cont.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exactnondifferentialequation-150802123533-lva1-app6892/75/Exact-non-differential-equation-14-2048.jpg)

![ Example : 2 (cont.)
[( 1 +
𝑦2
𝑥2 +
3
𝑥2)𝑑𝑥 − 2𝑥𝑦. 𝑑𝑦] = 0,
which is exact differential equation.
It’s solution is :
𝑦=𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡 𝑎 𝑛𝑡
𝑀𝑑𝑥 + 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑠𝑜𝑓𝑁𝑛𝑜𝑡𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑖 𝑛𝑖 𝑛 𝑔𝑥 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑐
𝑦=𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡 𝑎 𝑛𝑡
1 +
𝑦2
𝑥2
+
3
𝑥2
)𝑑𝑥+ (0)𝑑𝑦 = 𝑐
8/2/2015 Differential Equation 16
x −
𝑦2
𝑥
−
3
𝑥
= 𝑐](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exactnondifferentialequation-150802123533-lva1-app6892/75/Exact-non-differential-equation-16-2048.jpg)












![ Example : 4 (cont.)
Now,
𝑀𝑥 − 𝑁𝑦 = 𝑥2
𝑦2
+ 2 𝑦𝑥 + 2 − 𝑥2
𝑦2
𝑥𝑦
=𝑥3 𝑦3 + 2𝑥𝑦 − 2𝑥𝑦 + 𝑥3 𝑦3
=2𝑥3
𝑦3
So, I.F.=
1
𝑀𝑥−𝑁𝑦
=
1
2𝑥3 𝑦3
Multiplying the given equation by
1
2𝑥3 𝑦3 , we have
1
2𝑥3 𝑦3
[ 𝑥2 + 2 𝑦𝑑𝑥 + 2 − 𝑥2 𝑦2 𝑥𝑑𝑦]
308/2/2015 Differential Equation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exactnondifferentialequation-150802123533-lva1-app6892/75/Exact-non-differential-equation-30-2048.jpg)


