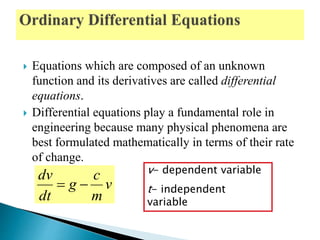
- Differential equations relate an unknown function and its derivatives, and are classified as ordinary (ODE) or partial (PDE) depending on the number of independent variables. Higher order equations can be reduced to systems of first order equations.
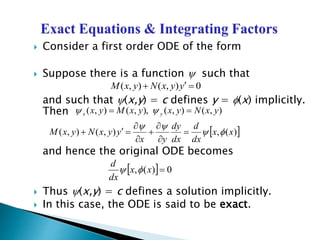
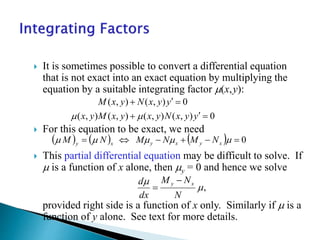
- Exact differential equations can be written as the total differential of a function, while non-exact equations may require an integrating factor to convert them to exact form.
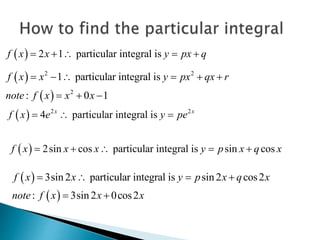
- The general solution to a non-homogeneous second order differential equation is the sum of the complementary function (solution to the homogeneous equation) and a particular integral similar to the non-homogeneous term.