The document defines the Laplace transform and provides examples of its use.
The Laplace transform converts a function f(t) into another function F(s) through an integral transform. This allows problems involving discontinuous functions to be solved more easily. The transform is particularly useful for linear differential equations with constant coefficients. Examples show how to take the Laplace transform of basic functions like 1, e^at, and sin(at) and how the transform is linear.
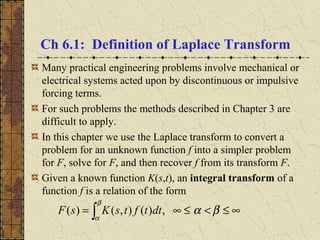


![Example 2
Consider the following improper integral.
We can evaluate this integral using integration by parts:
Since this limit diverges, so does the original integral.
[ ]
( )[ ]1cossinlim
cossinlim
sinsinlim
coslimcos
00
00
00
−+=
+=
−=
=
∞→
∞→
∞→
∞→
∞
∫
∫∫
bsbsb
tstst
tdtstst
tdtsttdtst
b
bb
b
bb
b
b
b
∫
∞
0
costdtst](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch061-150731094730-lva1-app6891/85/Ch06-1-4-320.jpg)
![Piecewise Continuous Functions
A function f is piecewise continuous on an interval [a, b] if
this interval can be partitioned by a finite number of points
a = t0 < t1 < … < tn = b such that
(1) f is continuous on each (tk, tk+1)
In other words, f is piecewise continuous on [a, b] if it is
continuous there except for a finite number of jump
discontinuities.
nktf
nktf
k
k
tt
tt
,,1,)(lim)3(
1,,0,)(lim)2(
1
=∞<
−=∞<
−
+
+
→
→](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch061-150731094730-lva1-app6891/85/Ch06-1-5-320.jpg)
![Example 3
Consider the following piecewise-defined function f.
From this definition of f, and from the graph of f below, we
see that f is piecewise continuous on [0, 3].
≤<+
≤<−
≤≤
=
321
21,3
10,
)(
2
tt
tt
tt
tf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch061-150731094730-lva1-app6891/85/Ch06-1-6-320.jpg)
![Example 4
Consider the following piecewise-defined function f.
From this definition of f, and from the graph of f below, we
see that f is not piecewise continuous on [0, 3].
( )
≤<
≤<−
≤≤+
=
−
32,4
21,2
10,1
)(
1
2
t
tt
tt
tf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch061-150731094730-lva1-app6891/85/Ch06-1-7-320.jpg)
![Theorem 6.1.2
Suppose that f is a function for which the following hold:
(1) f is piecewise continuous on [0, b] for all b > 0.
(2) | f(t) | ≤ Keat
when t ≥ M, for constants a, K, M, with K, M > 0.
Then the Laplace Transform of f exists for s > a.
Note: A function f that satisfies the conditions specified above
is said to to have exponential order as t → ∞.
{ } finite)()()(
0∫
∞
−
== dttfesFtfL st](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch061-150731094730-lva1-app6891/85/Ch06-1-8-320.jpg)



![Linearity of the Laplace Transform
Suppose f and g are functions whose Laplace transforms exist
for s > a1 and s > a2, respectively.
Then, for s greater than the maximum of a1 and a2, the Laplace
transform of c1f (t) + c2g(t) exists. That is,
with
{ } [ ] finiteis)()()()(
0
2121 ∫
∞
−
+=+ dttgctfcetgctfcL st
{ }
{ } { })()(
)()()()(
21
0
2
0
121
tgLctfLc
dttgecdttfectgctfcL stst
+=
+=+ ∫∫
∞
−
∞
−](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch061-150731094730-lva1-app6891/85/Ch06-1-12-320.jpg)
