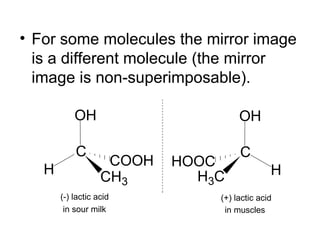
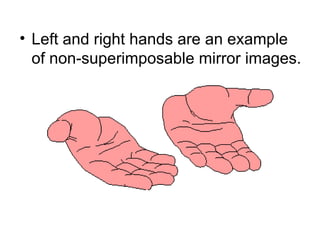
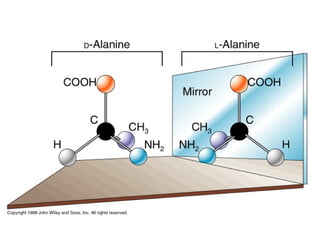
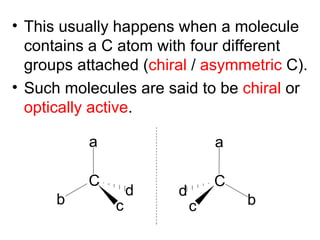
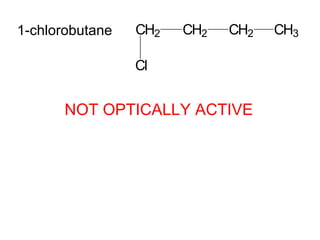
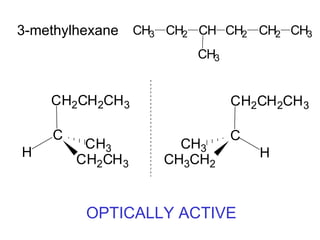
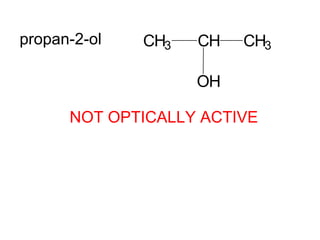
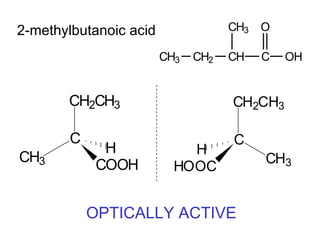
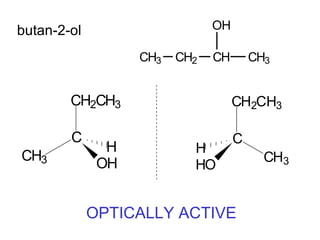
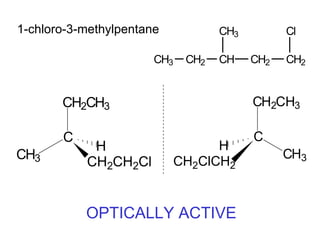
1) Optical isomers, also known as enantiomers, are non-superimposable mirror images of chiral molecules that contain an asymmetric carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
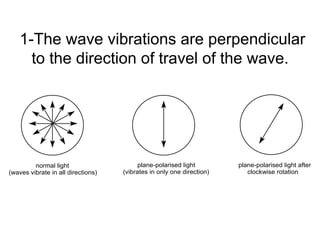
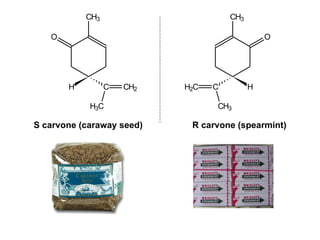
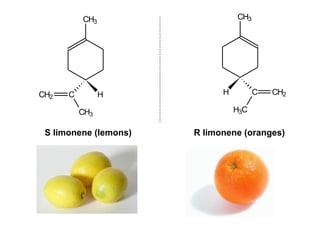
2) Enantiomers rotate polarized light in opposite directions and often react differently with other chiral molecules.
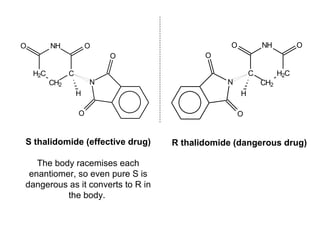
3) Many drugs, amino acids, and other biological molecules exist as enantiomers but only one "handedness" is active in the body, with the other sometimes being harmful. Thalidomide caused birth defects because the inactive enantiomer converted to the active form in the body.