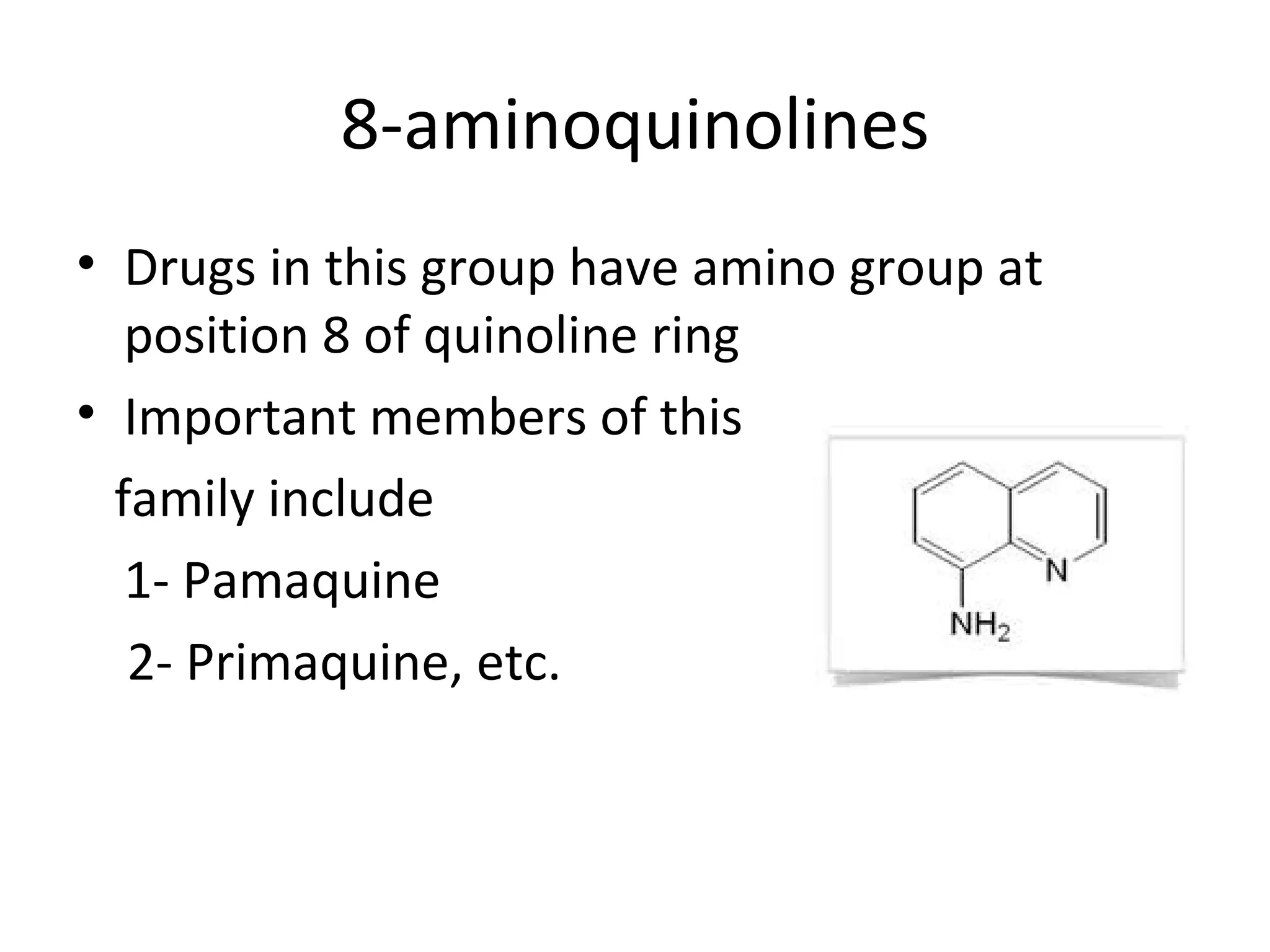
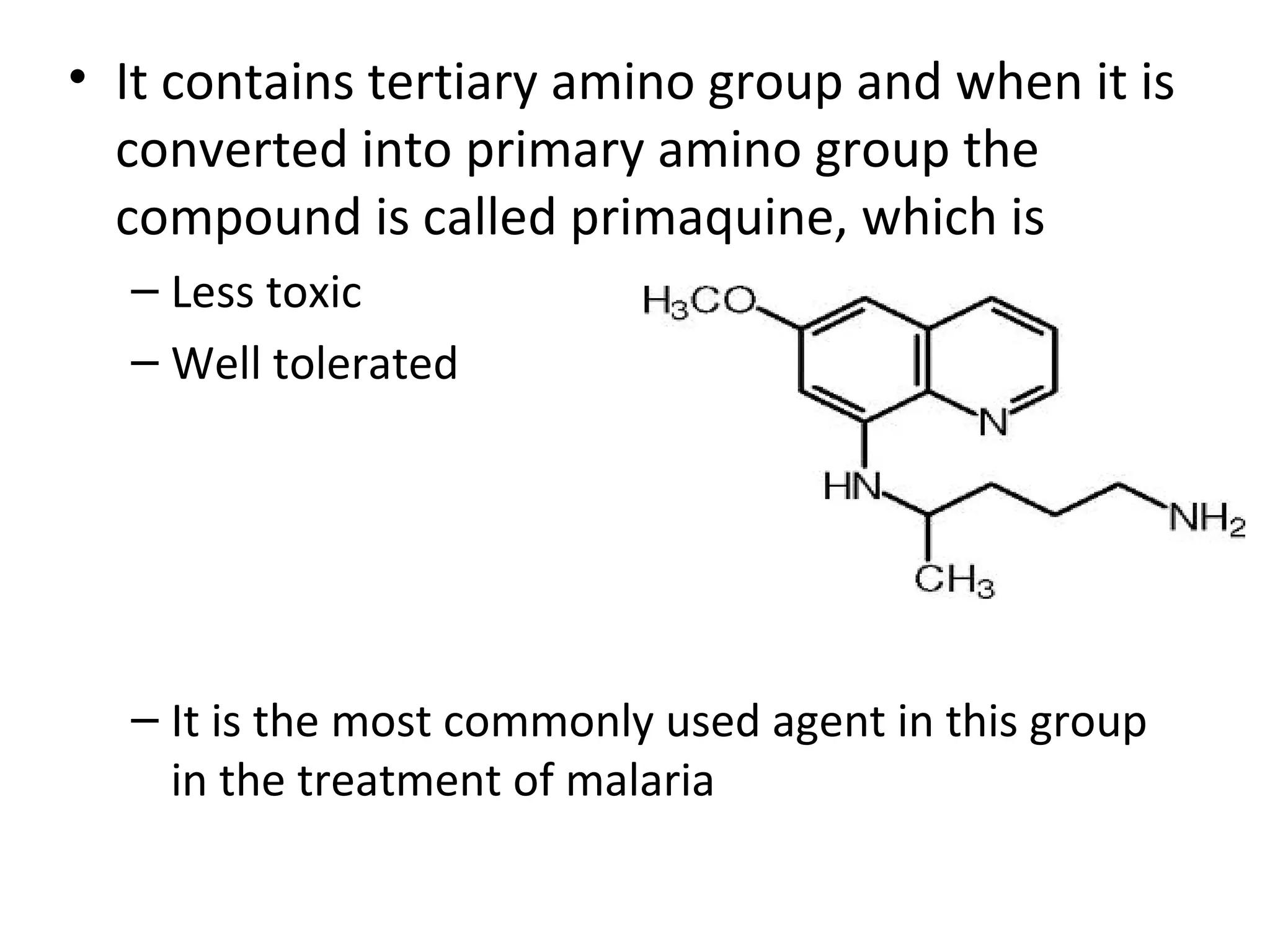
8-aminoquinolines are a class of antimalarial drugs containing an amino group at the 8 position of the quinoline ring. Important members include pamaquine and primaquine. Pamaquine has enhanced antimalarial activity due to its diethyl amino pentyl side chain, but also causes hemolysis. Primaquine is less toxic and better tolerated as it contains a primary amino group. It is commonly used to treat malaria and provides radical cure of the hepatic stages of P. vivax and P. ovale.