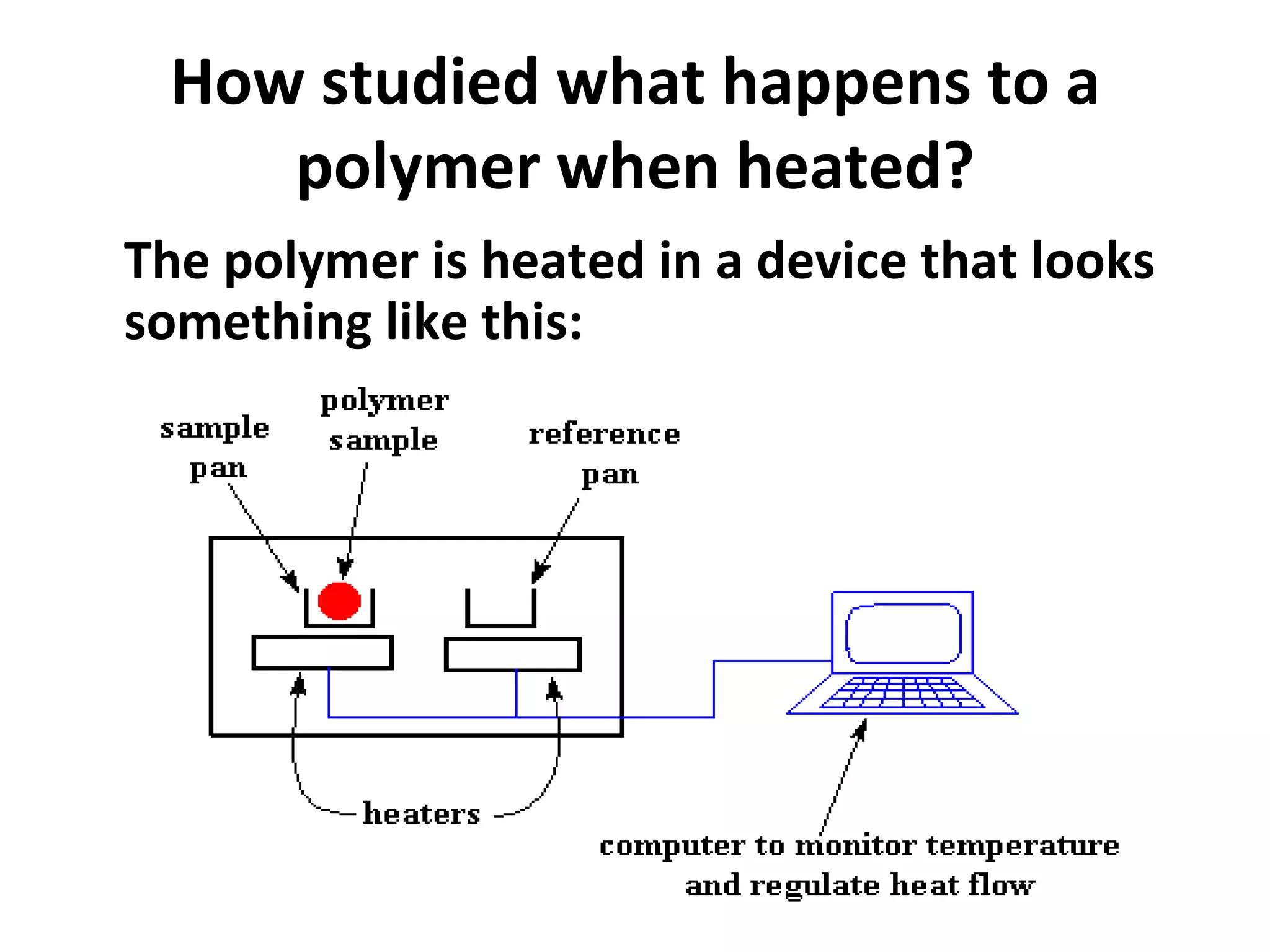
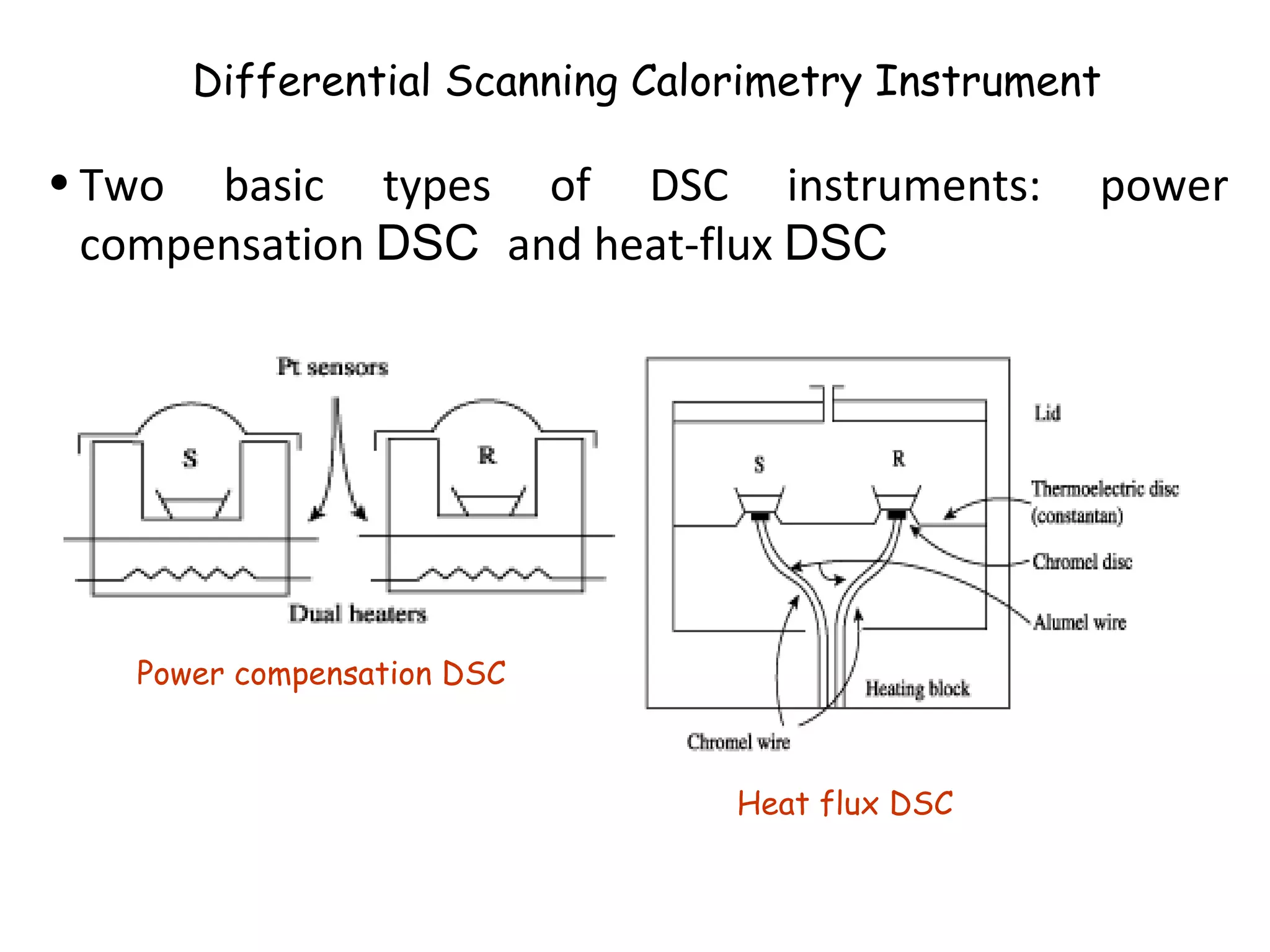
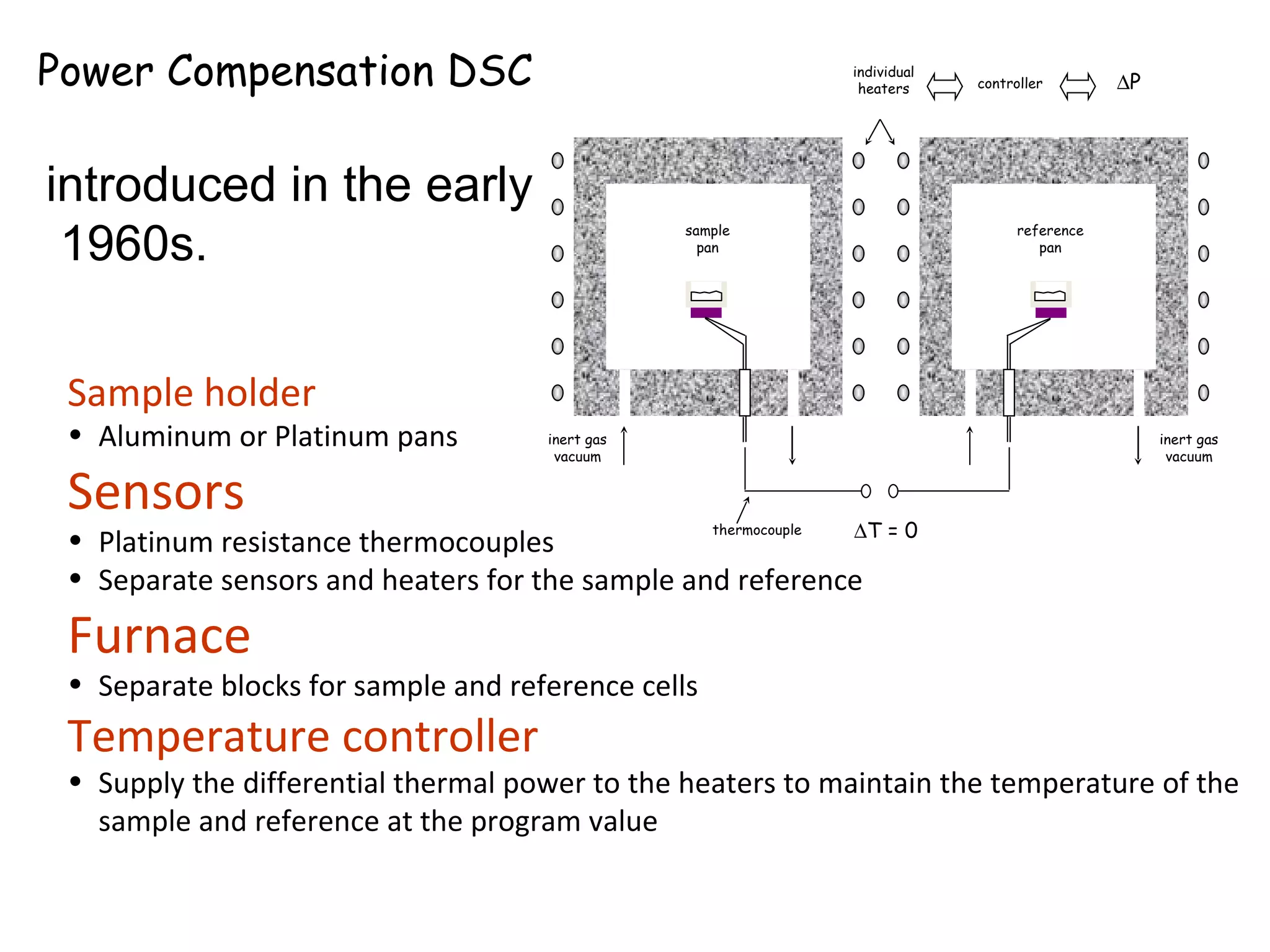
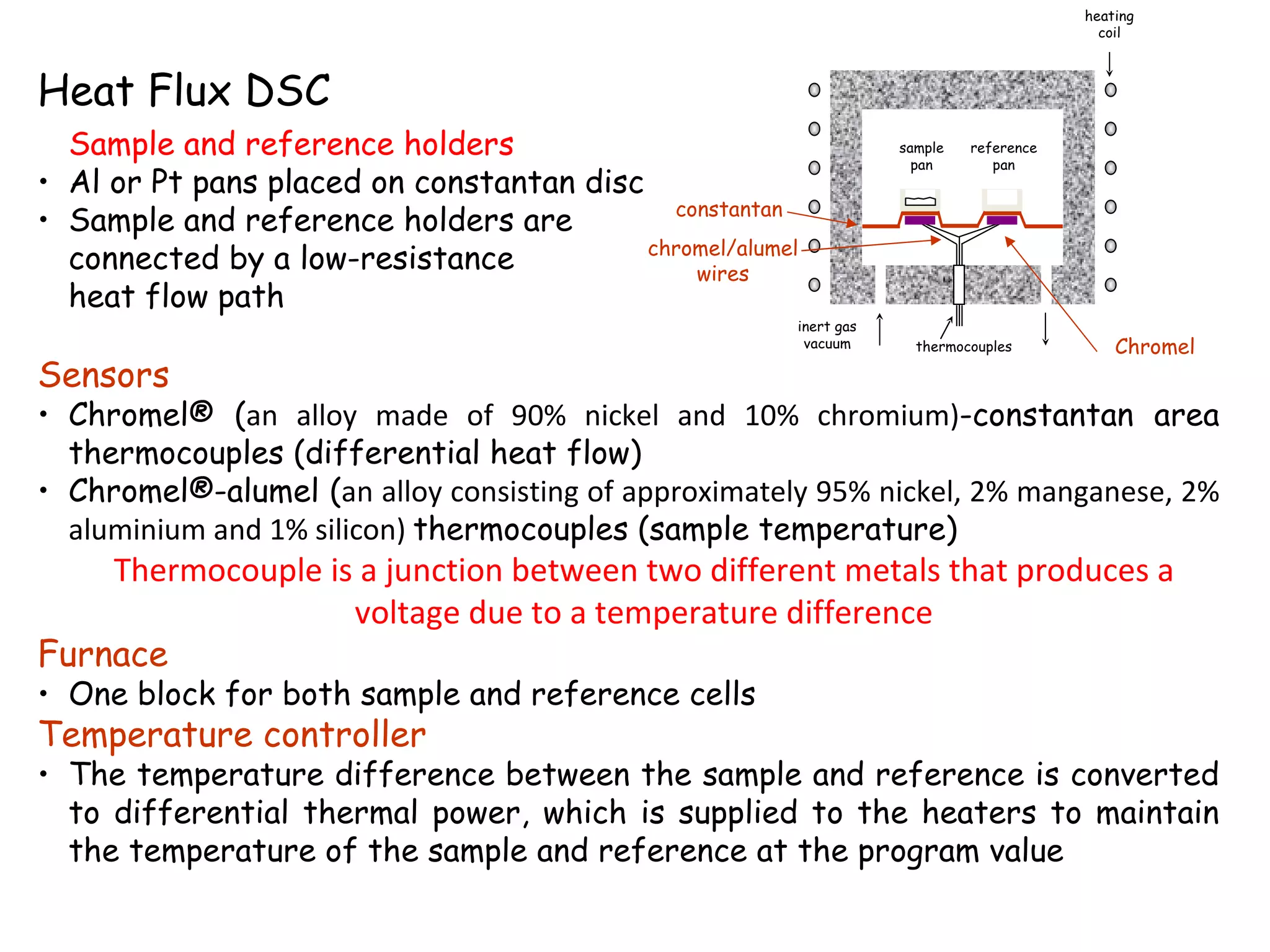
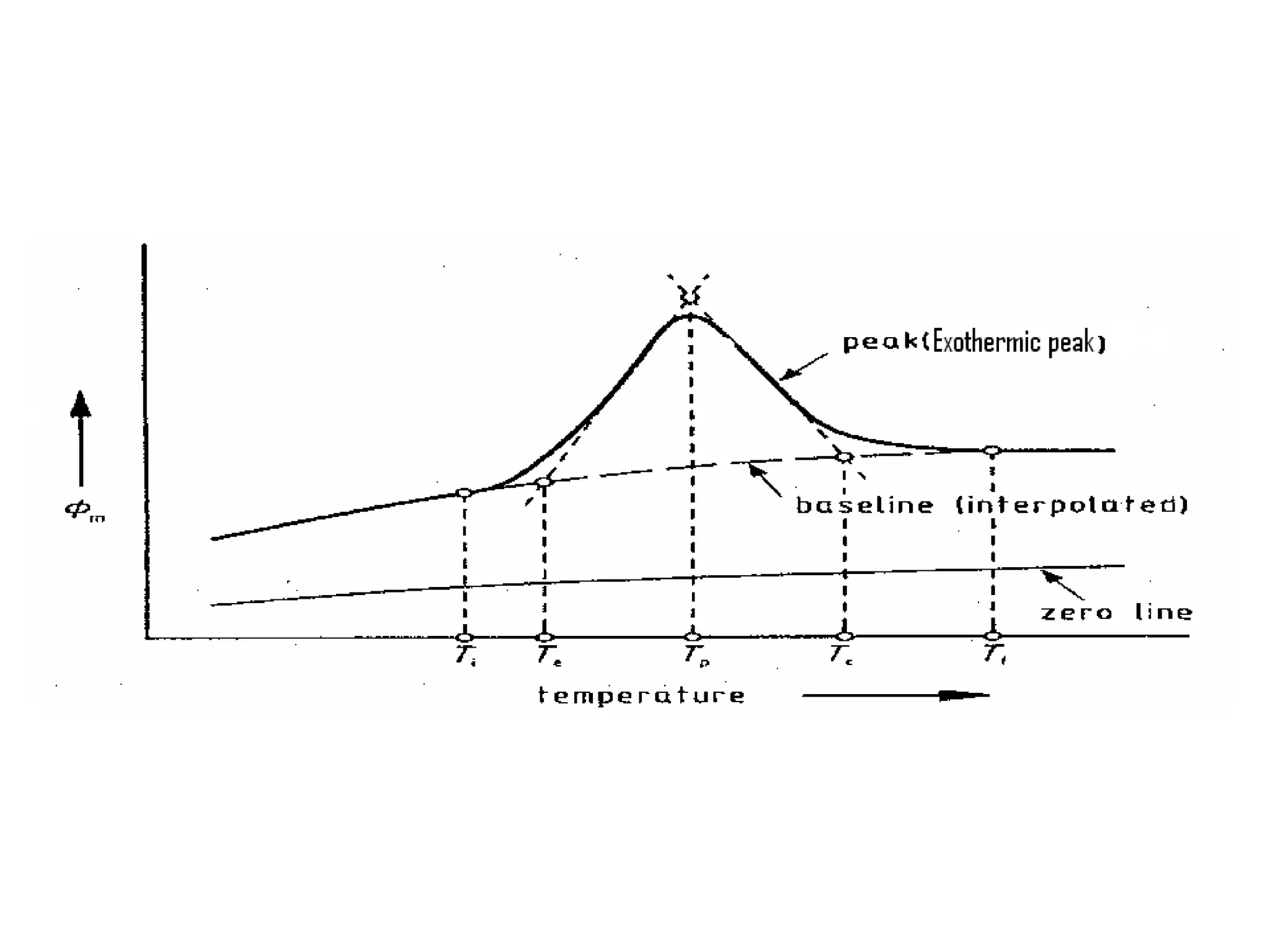
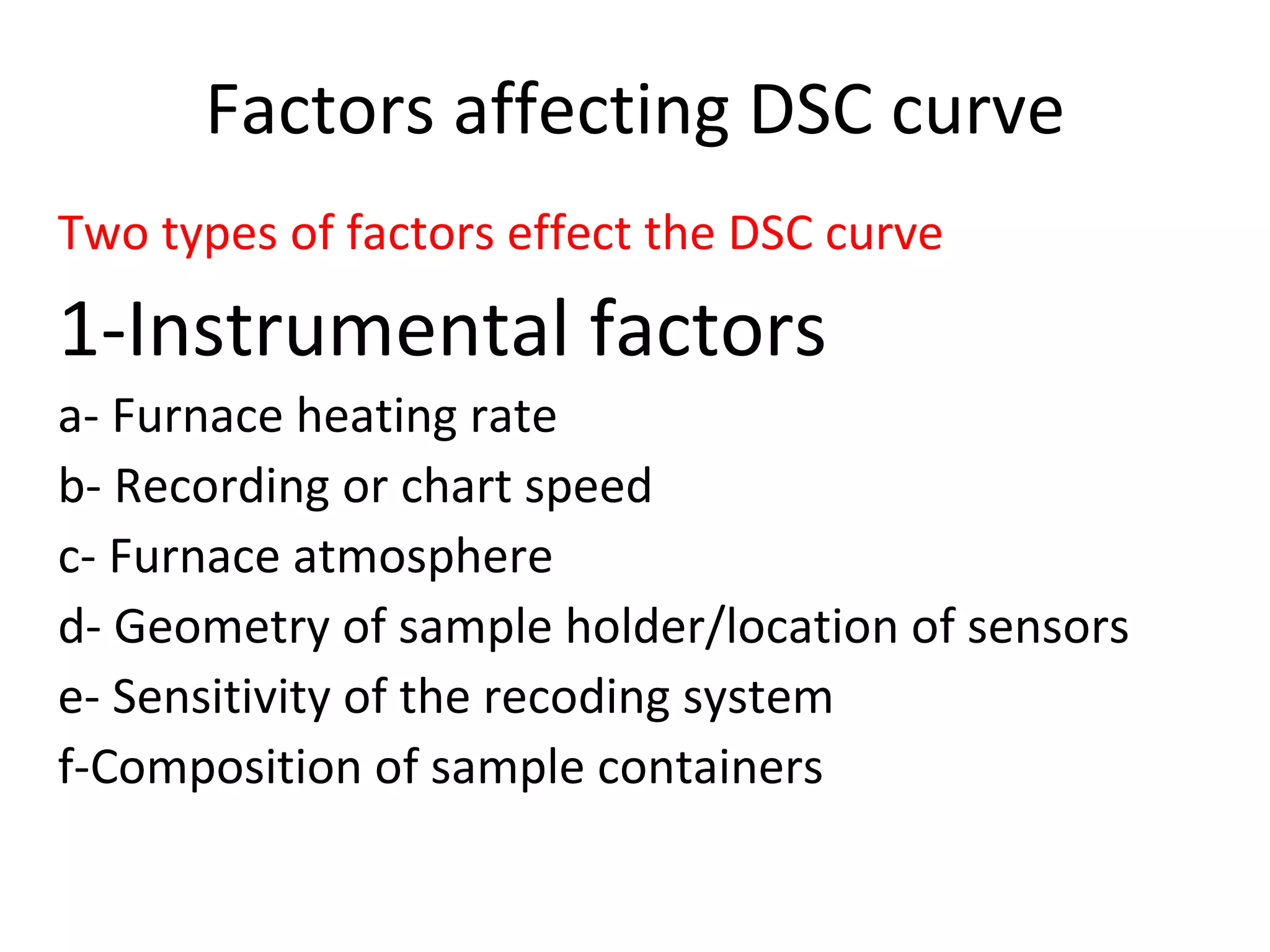
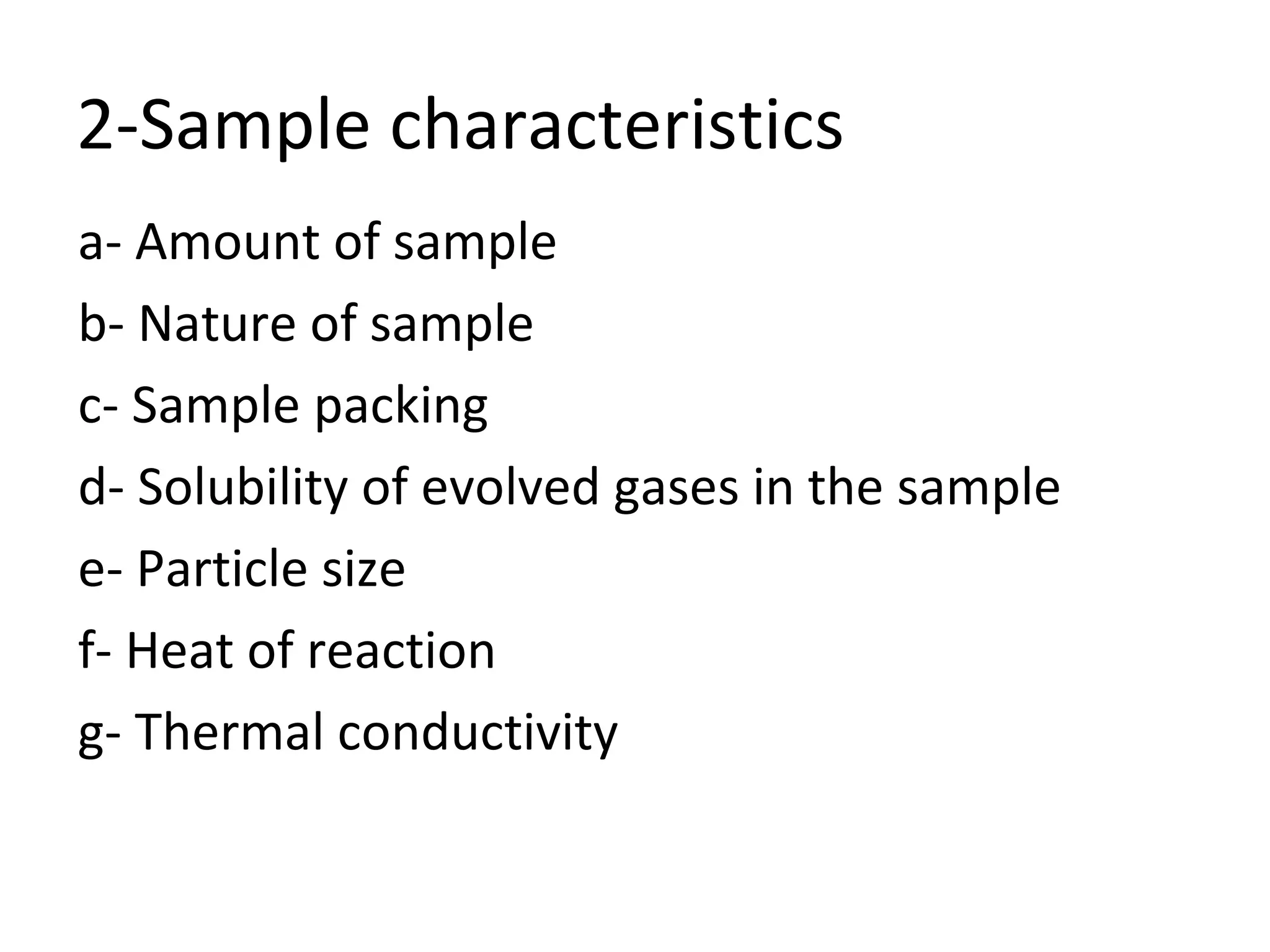
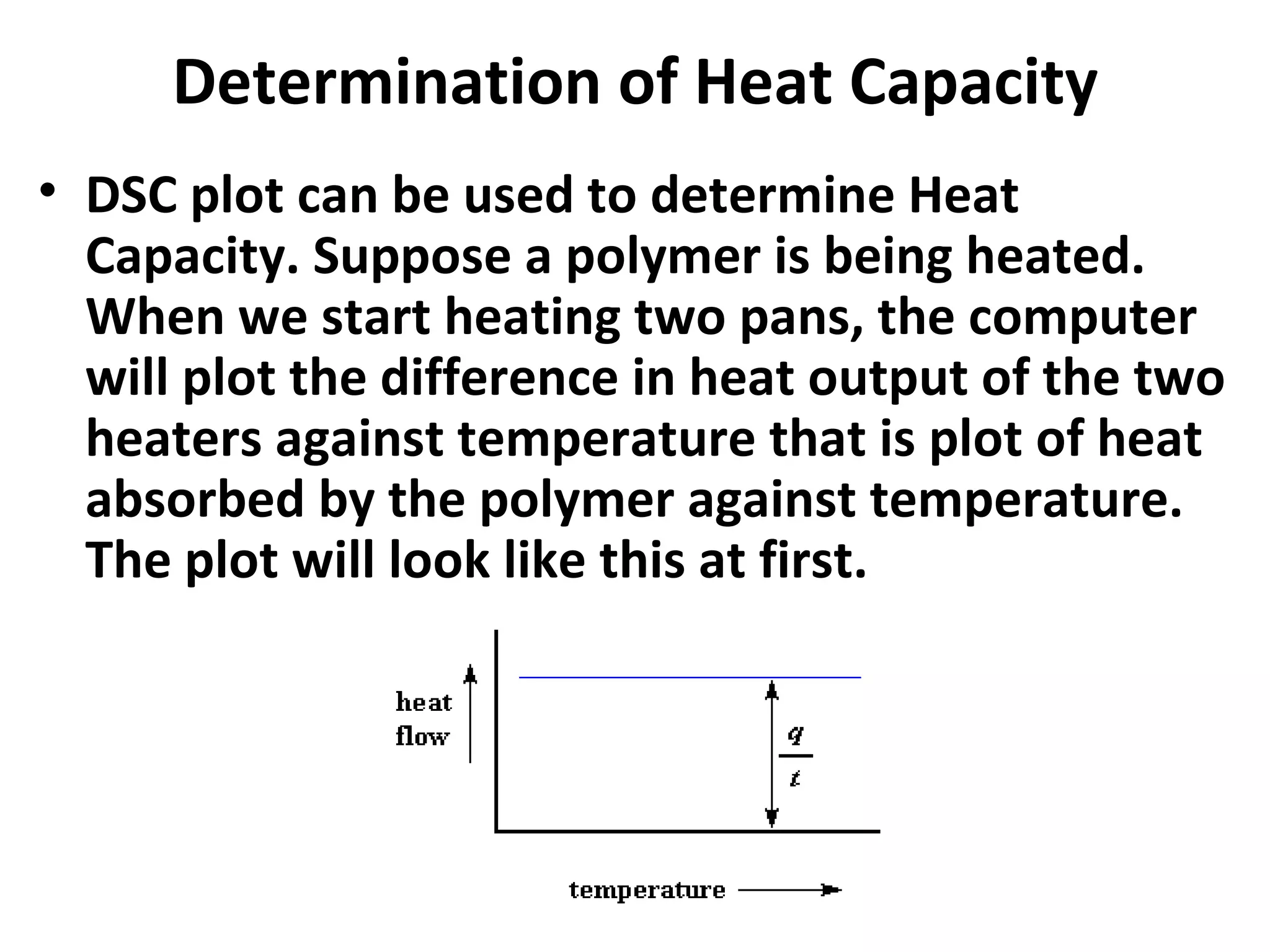
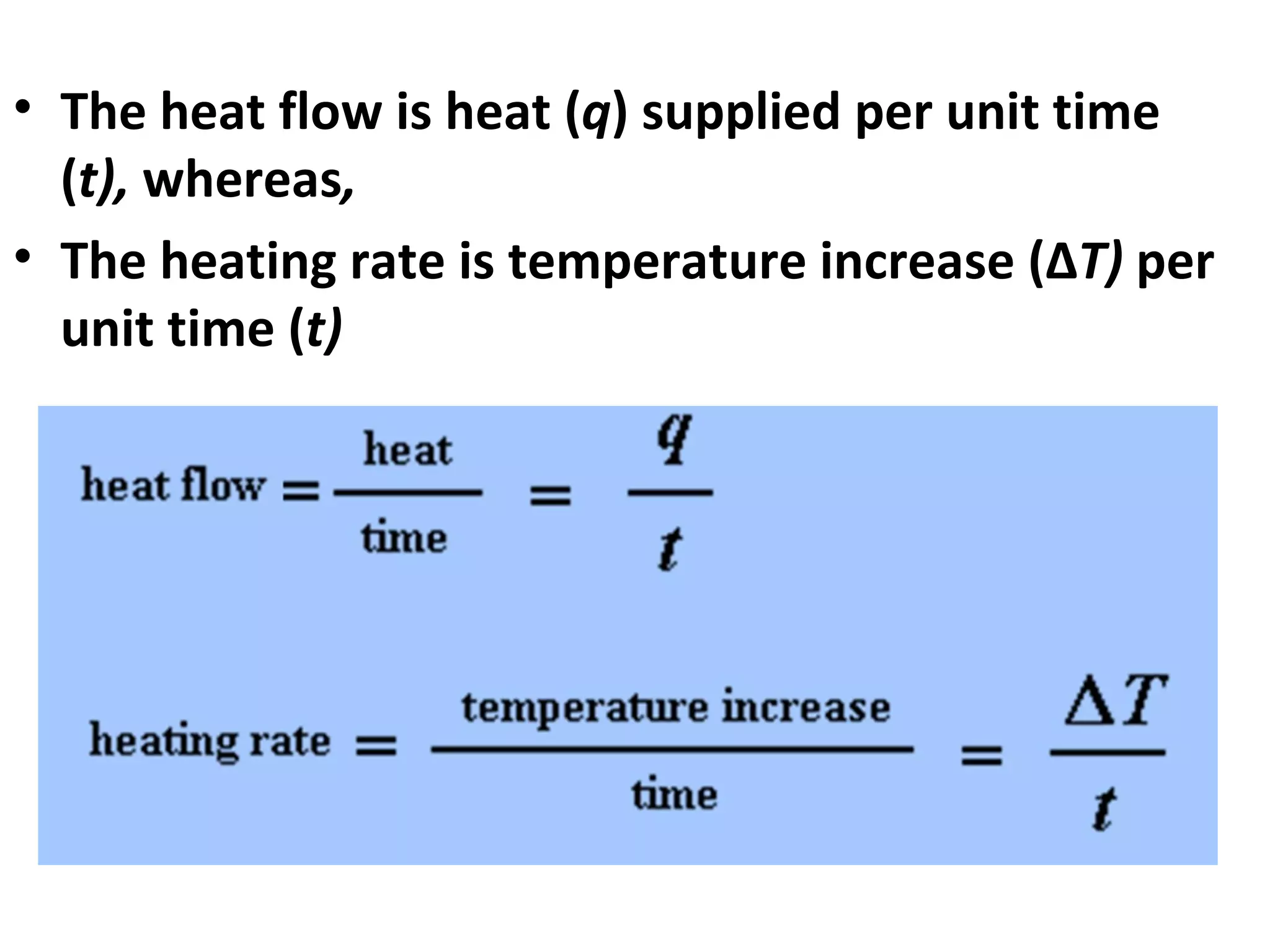
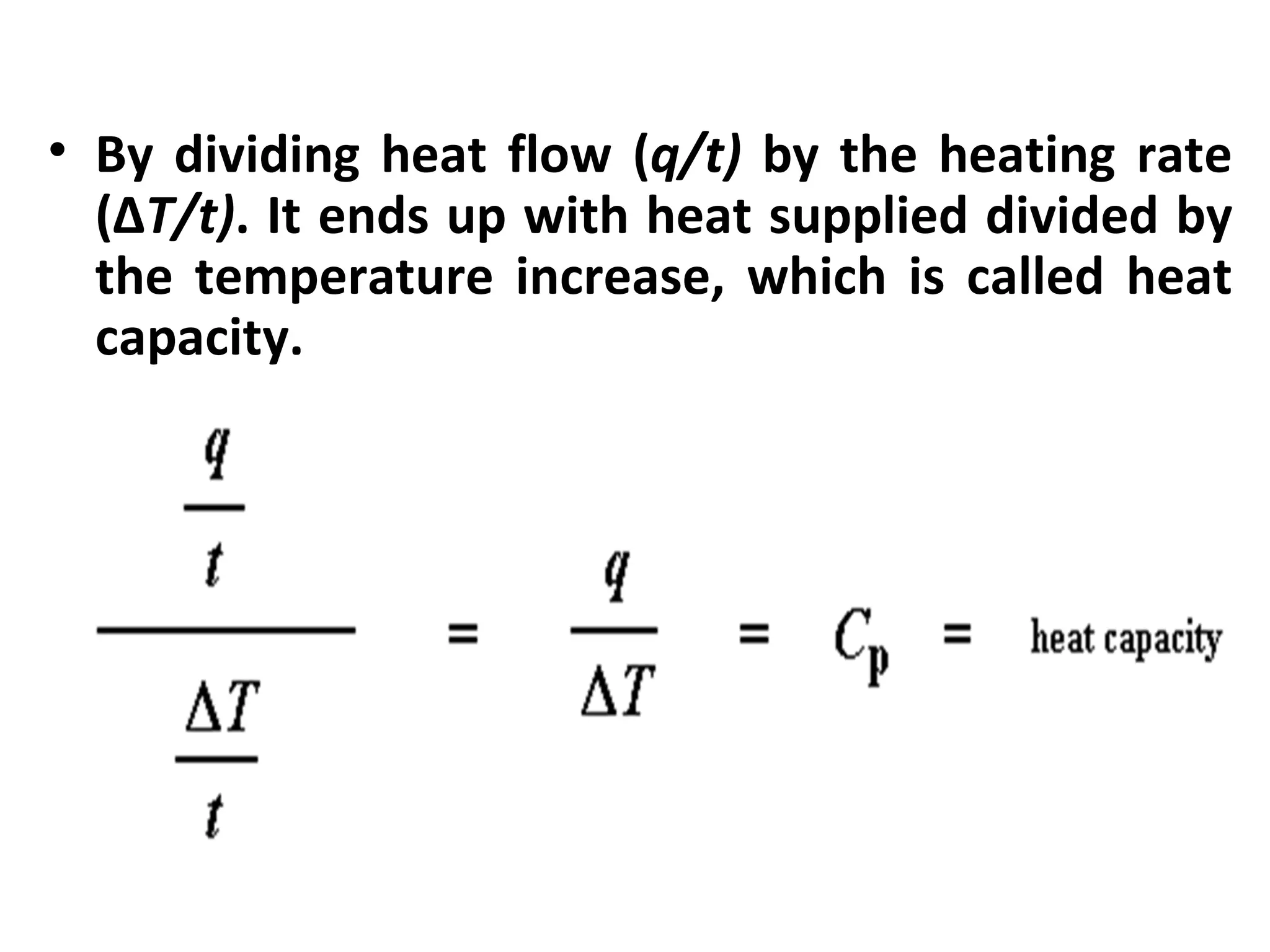
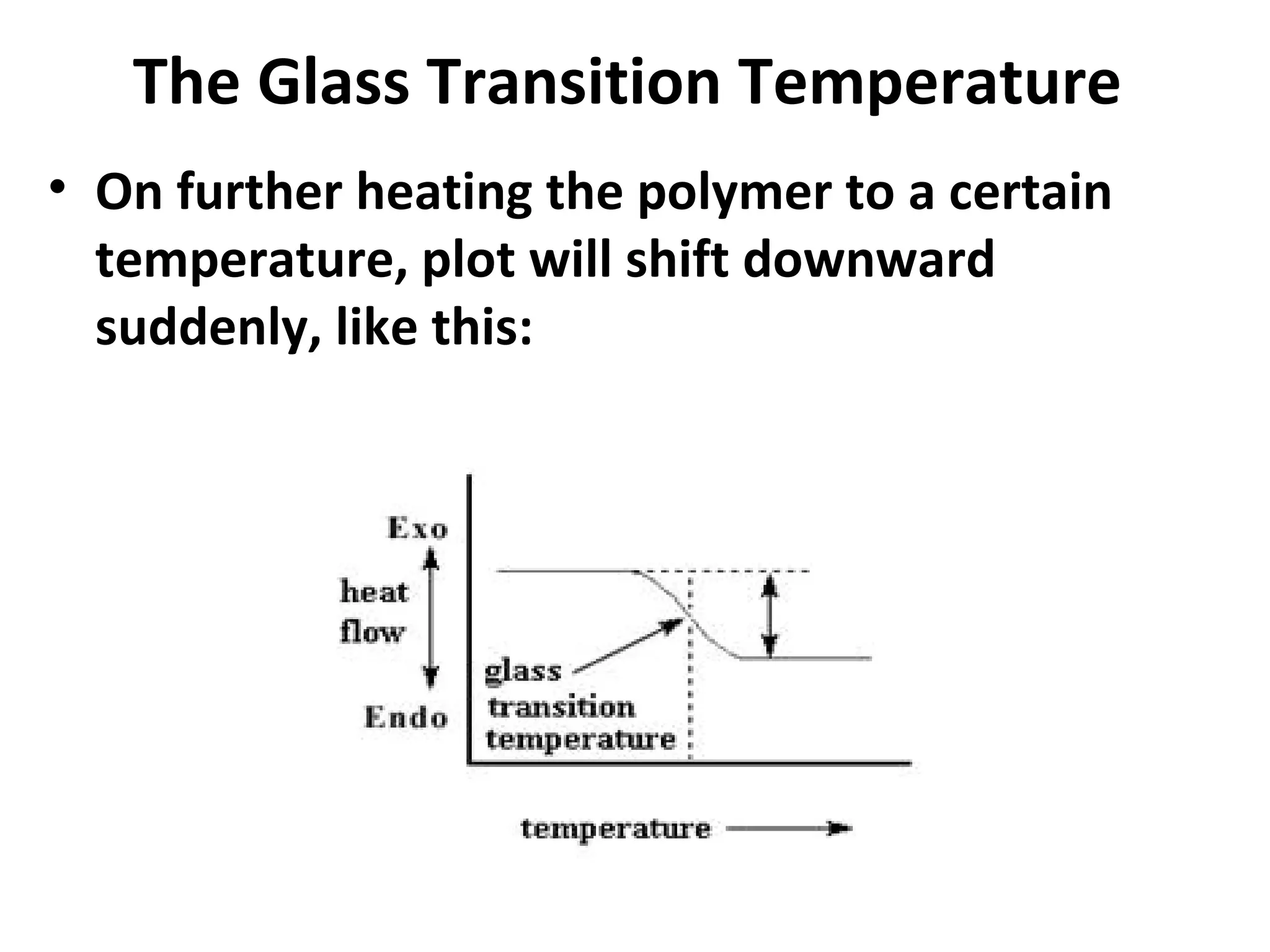
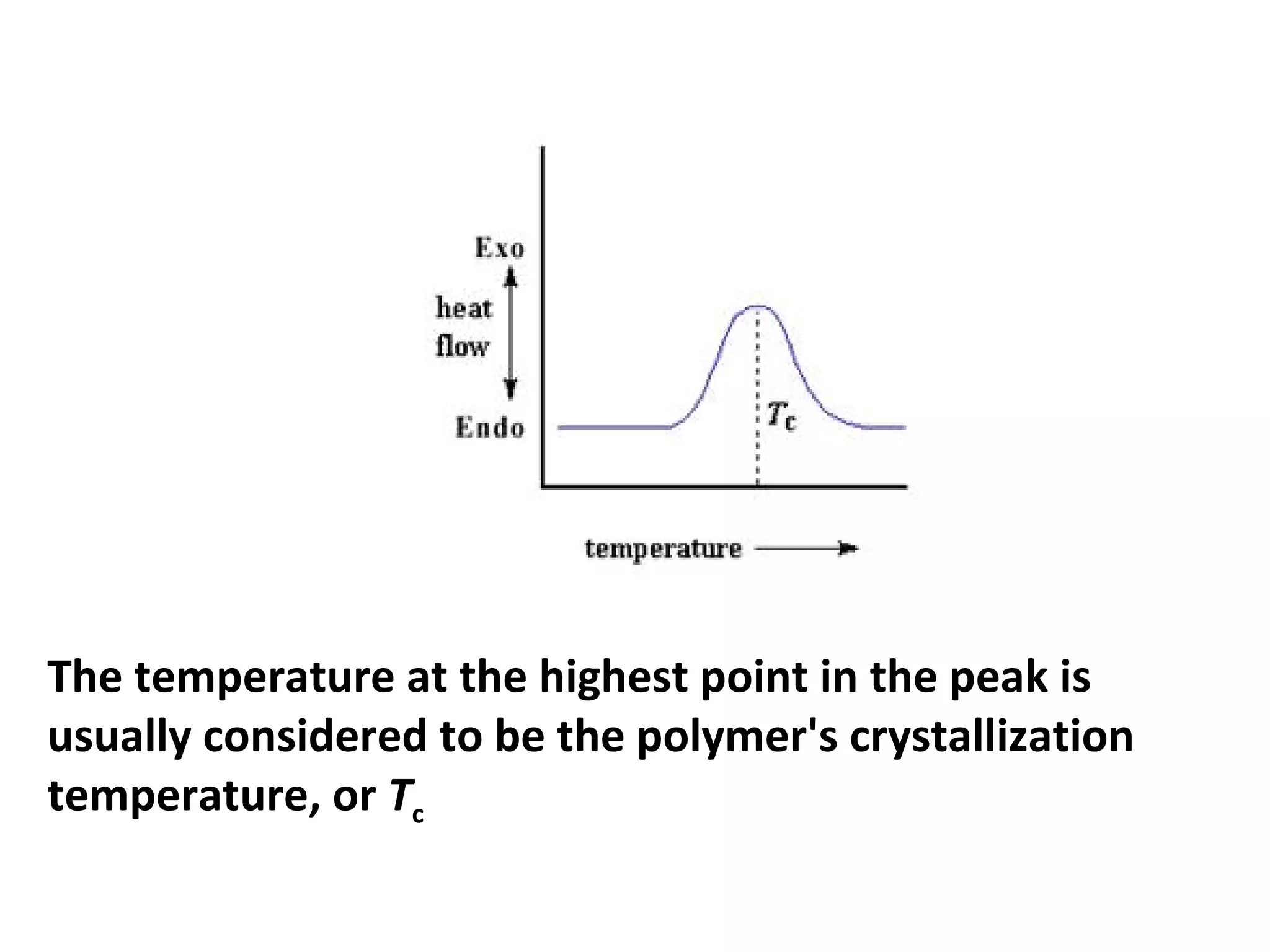
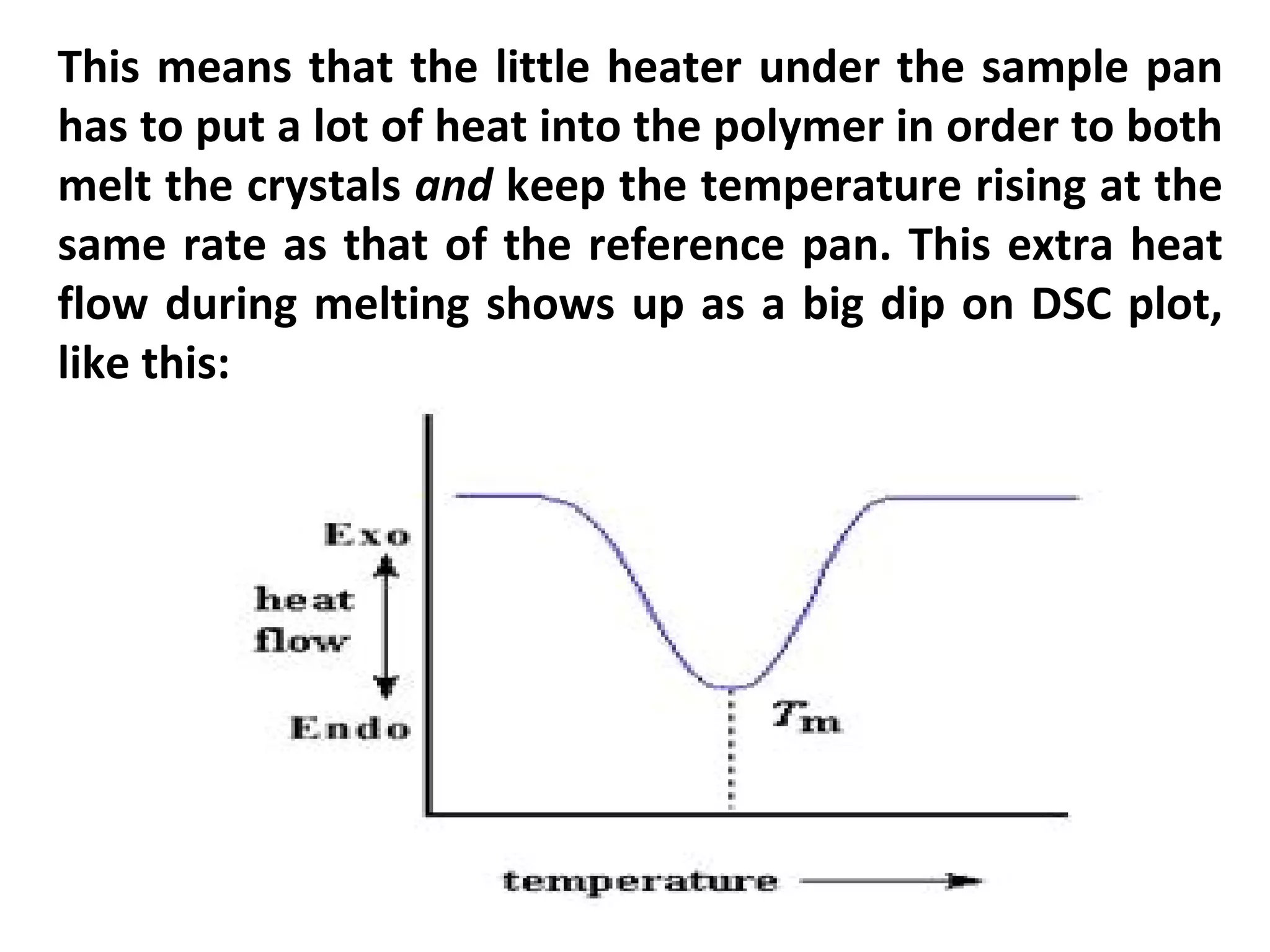
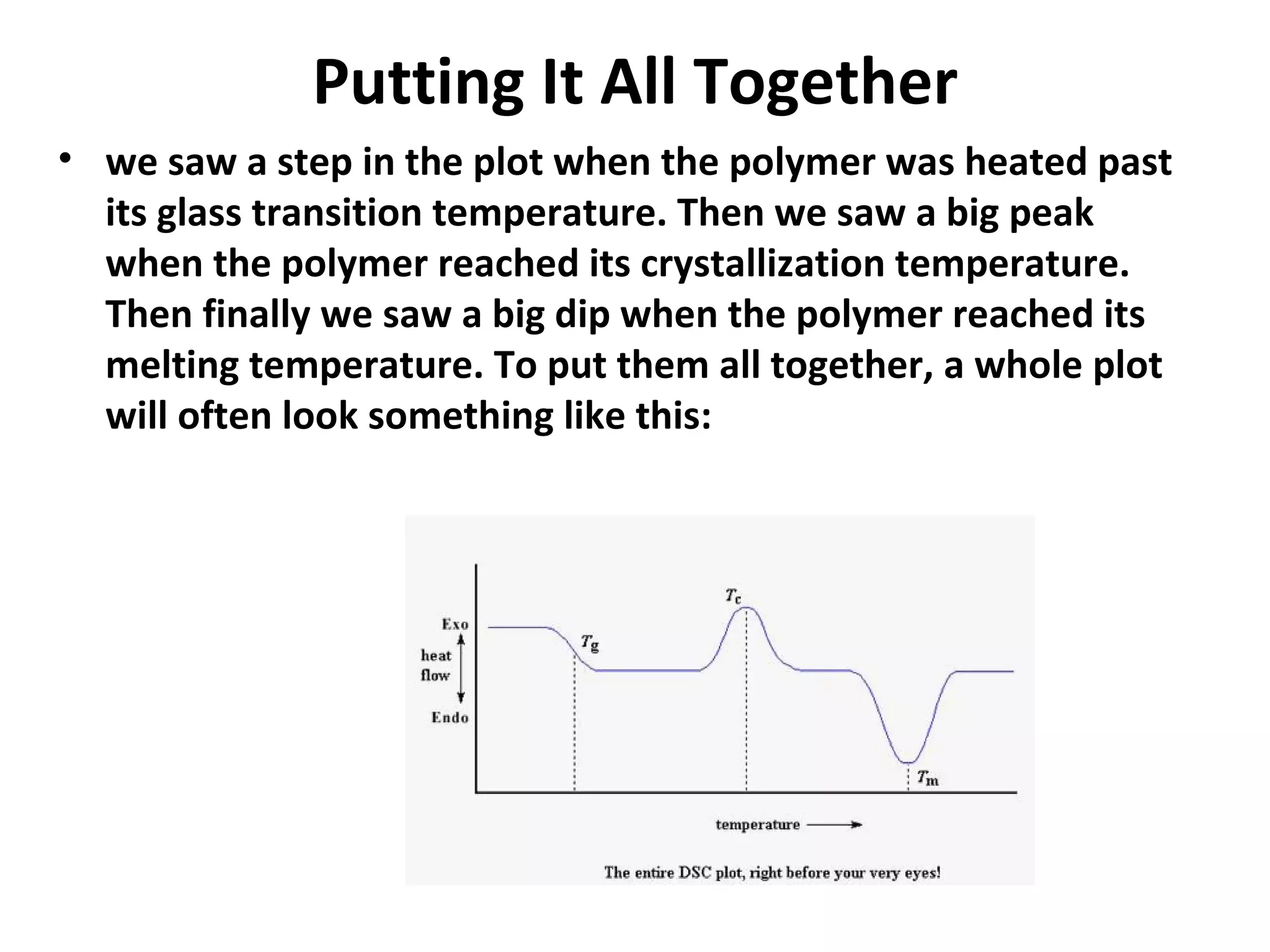
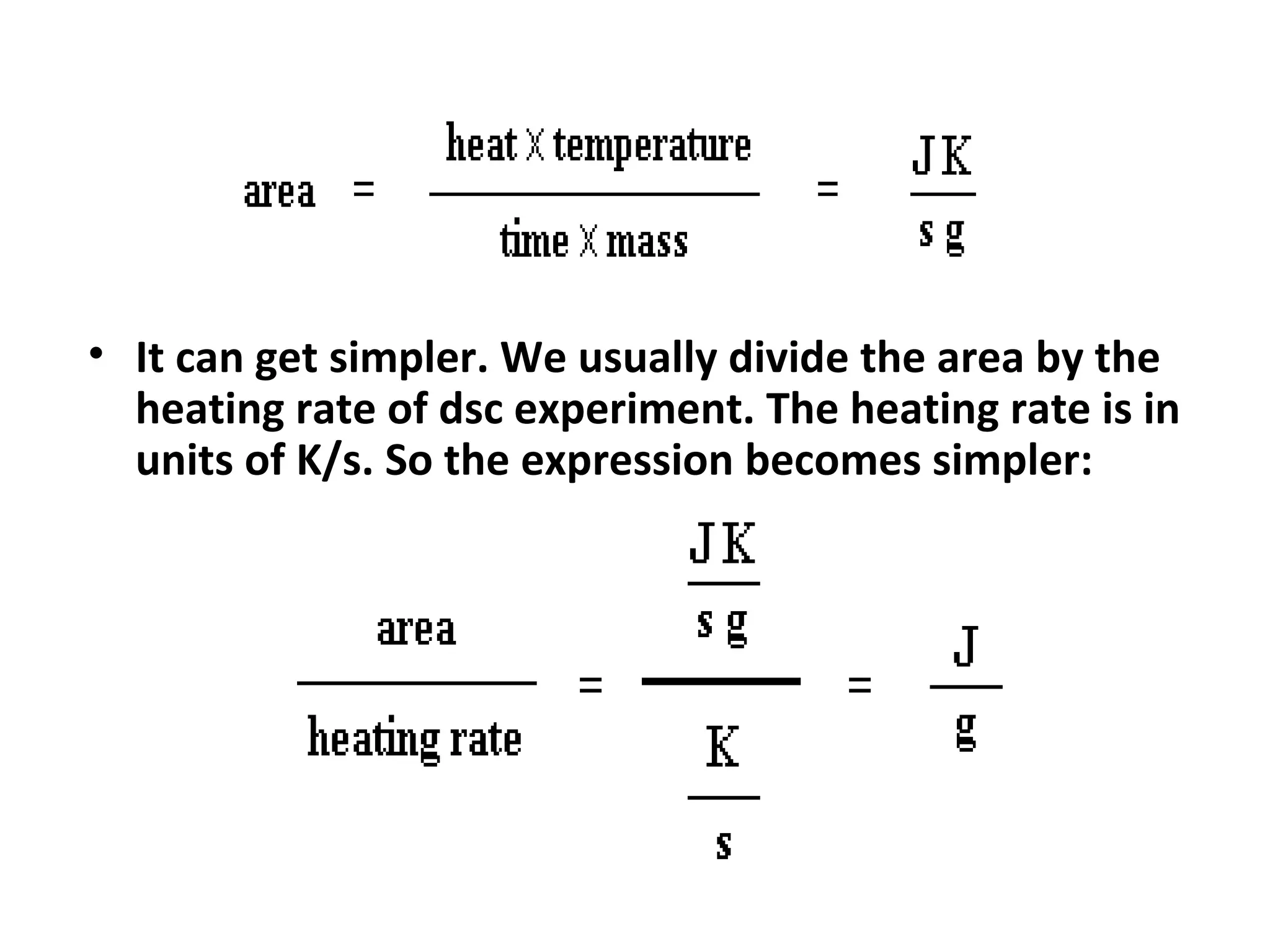
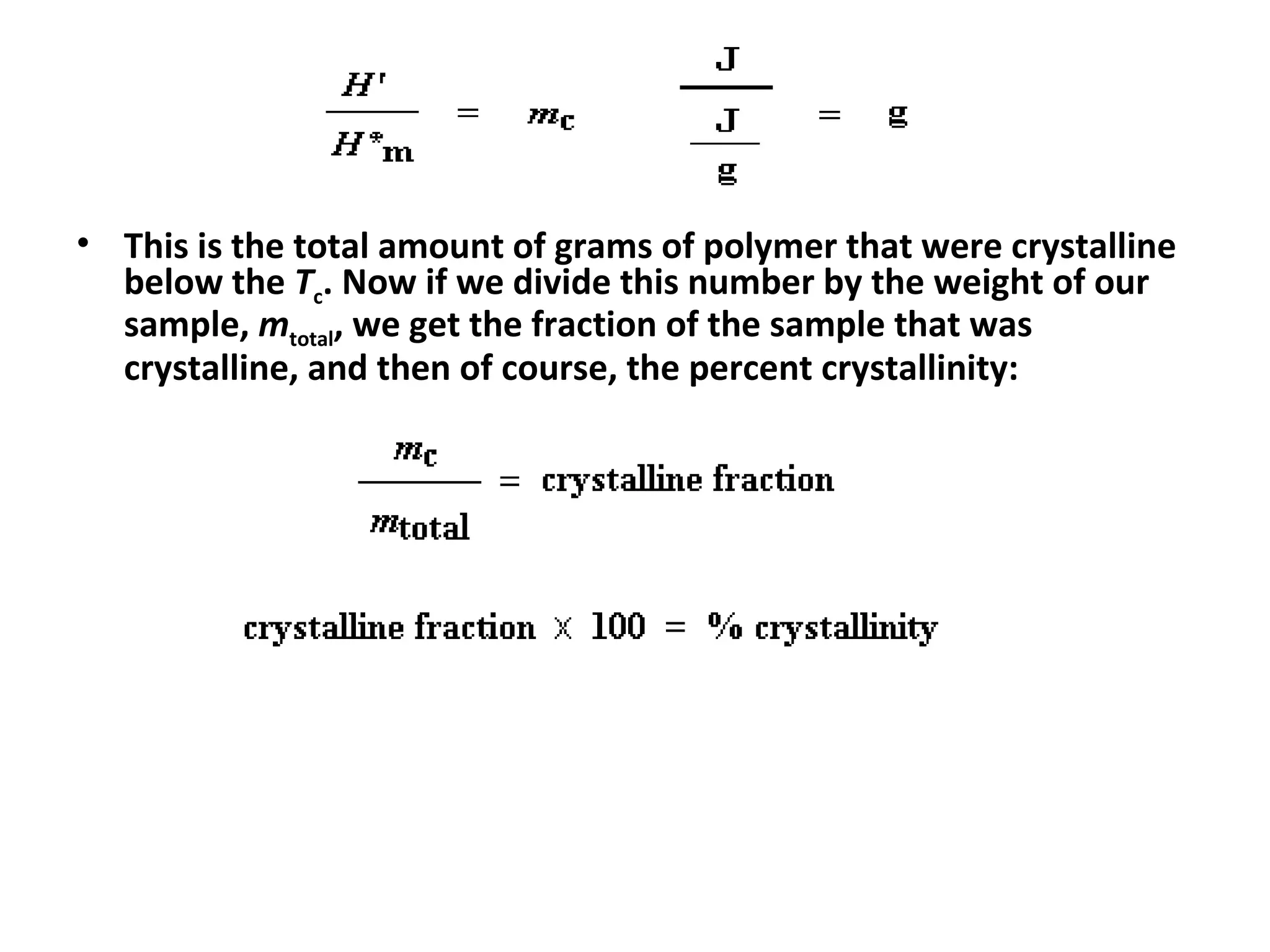
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a technique used to study thermal transitions in polymers and other materials. It works by heating a sample and reference simultaneously while measuring the difference in energy required to keep them at the same temperature. This allows thermal transitions like glass transitions, crystallization, and melting to be identified by features in the resulting DSC curve. The technique provides both qualitative and quantitative information about these transitions.