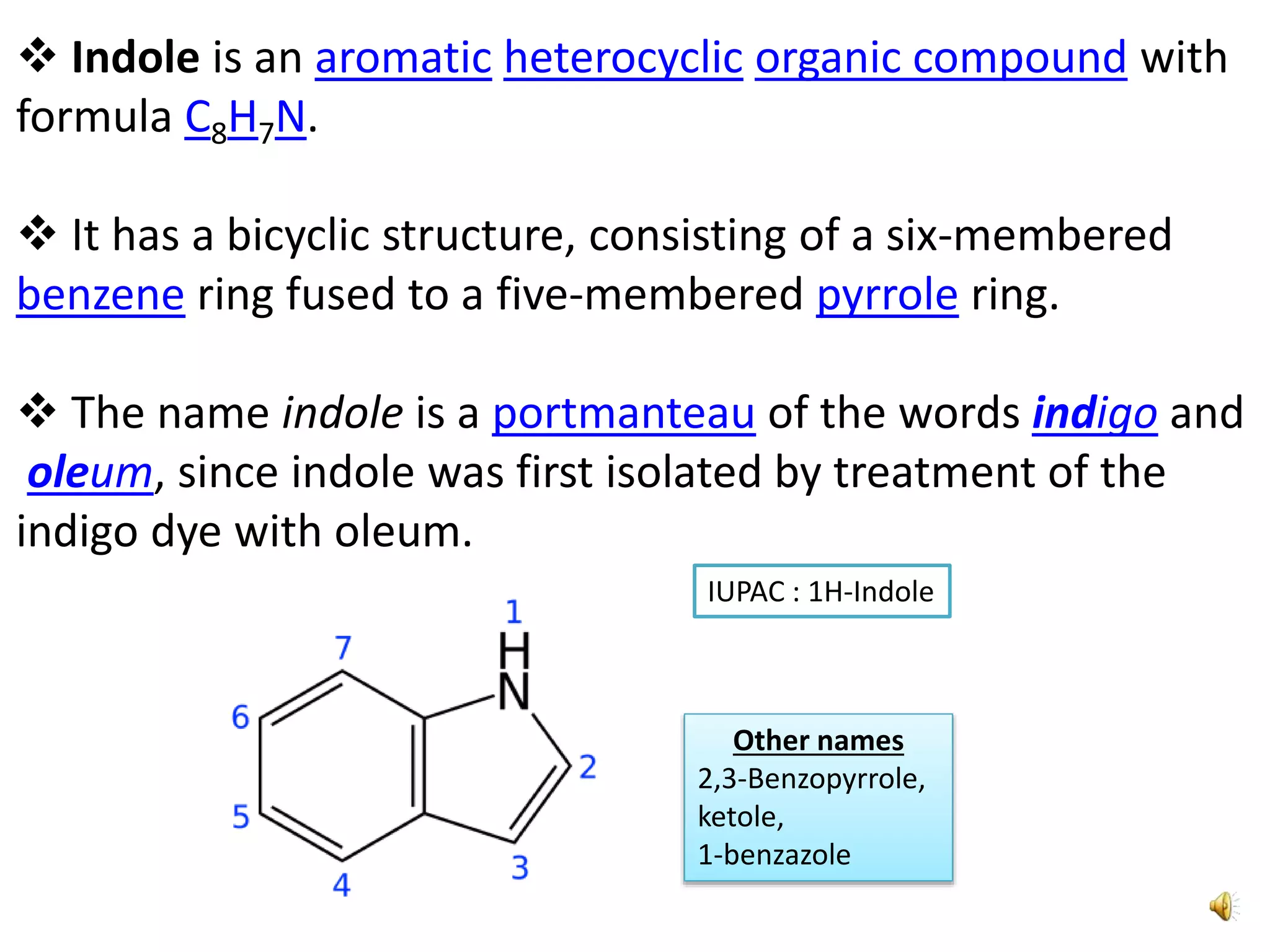
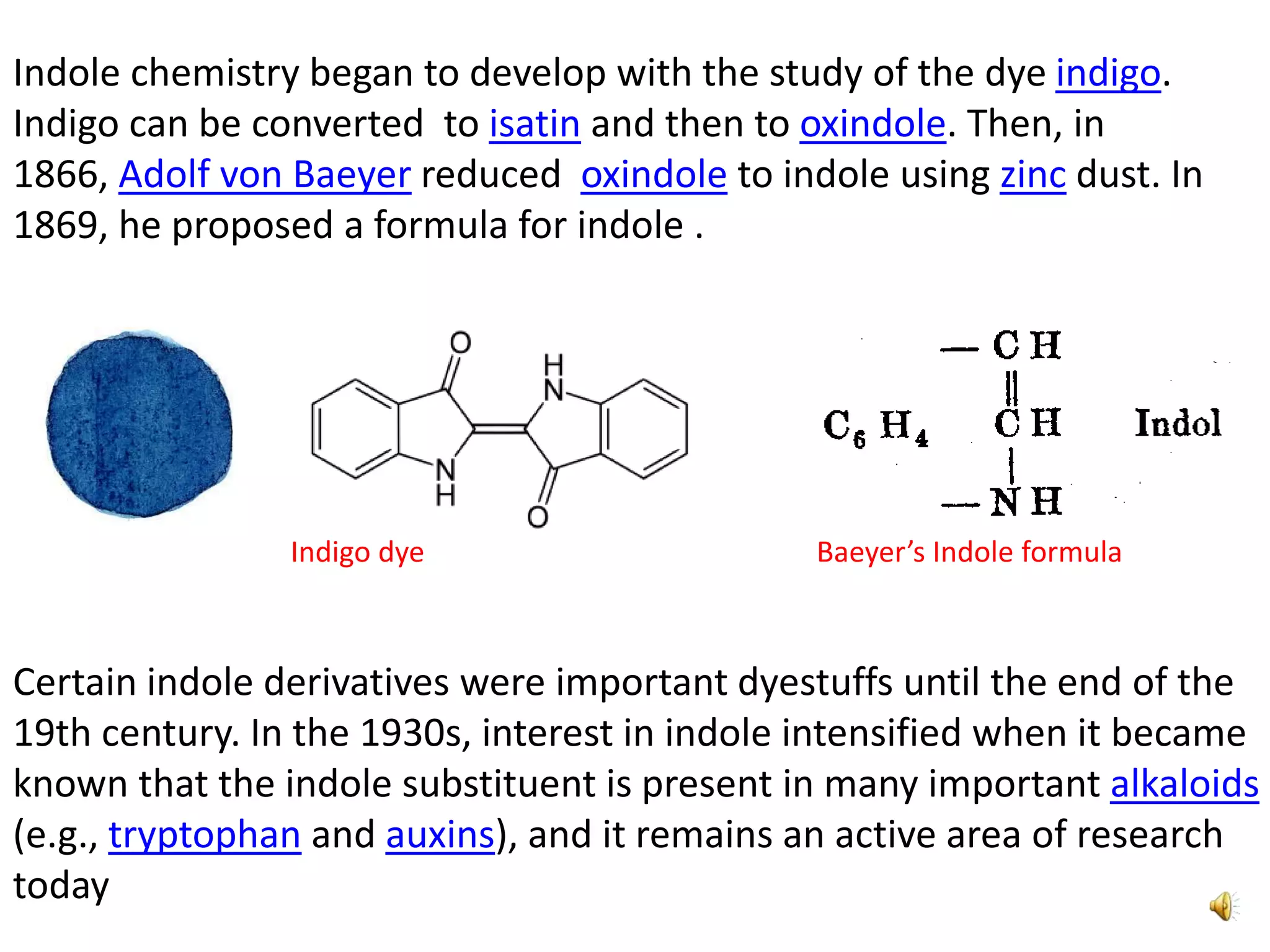
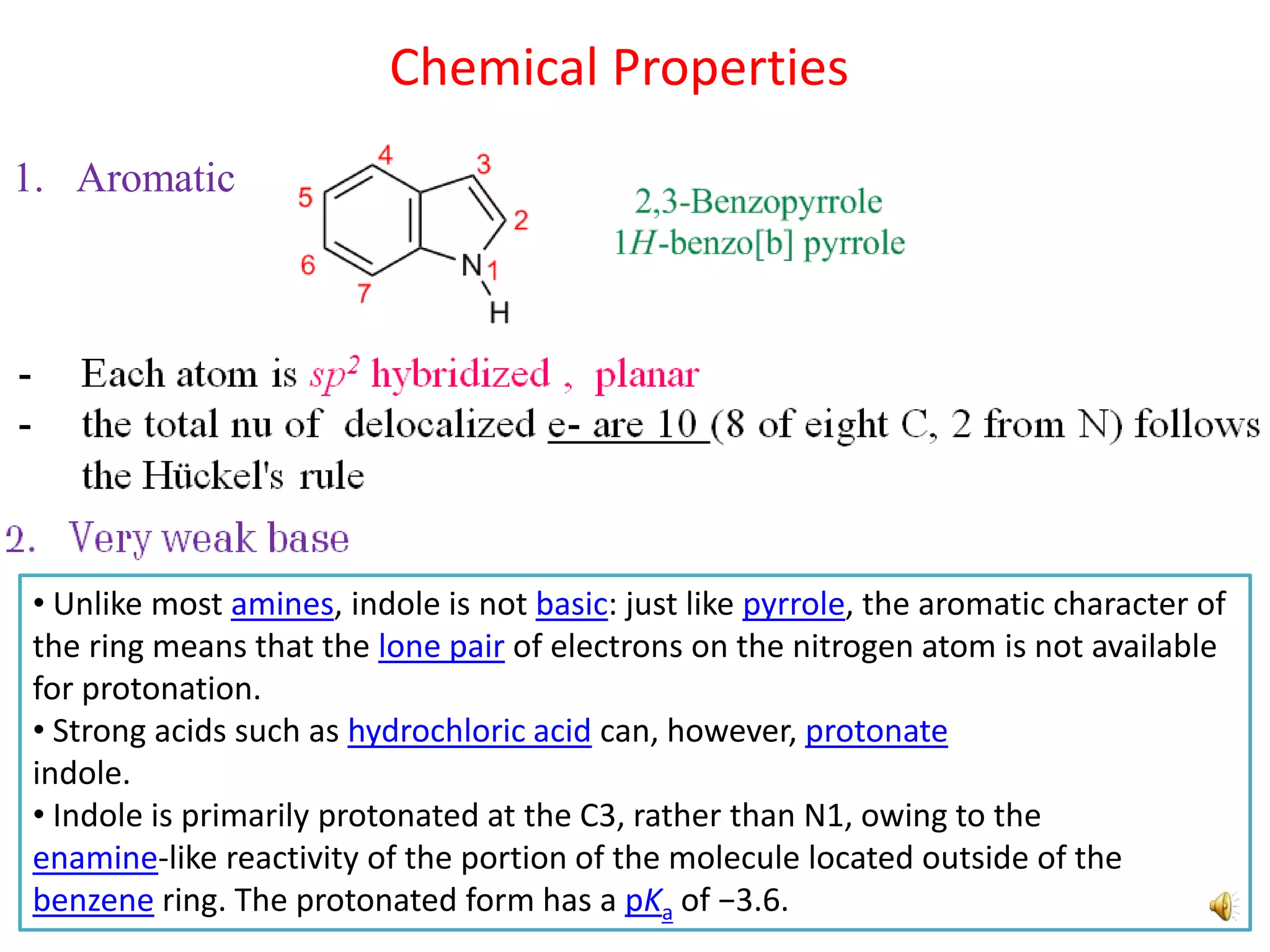
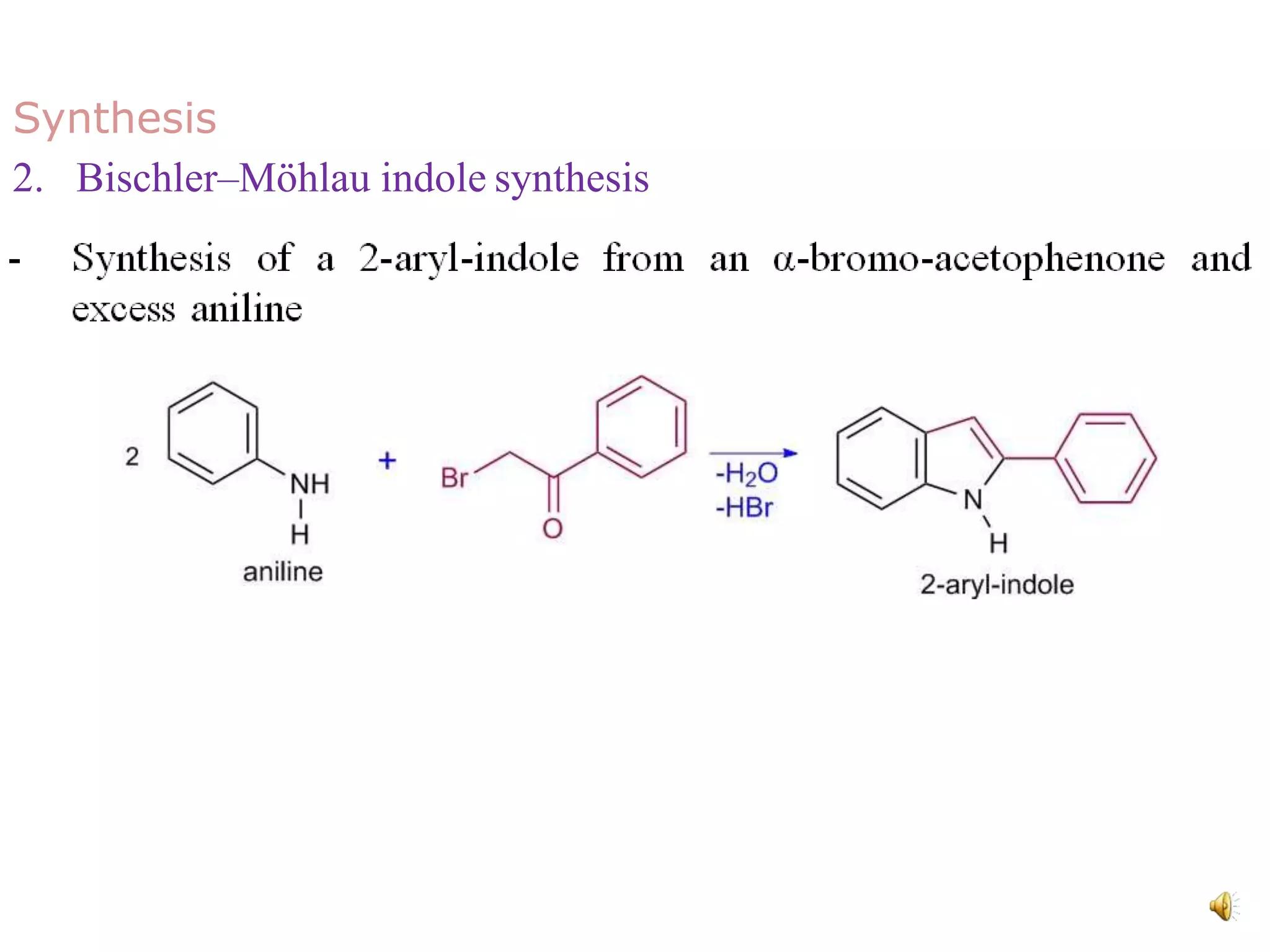
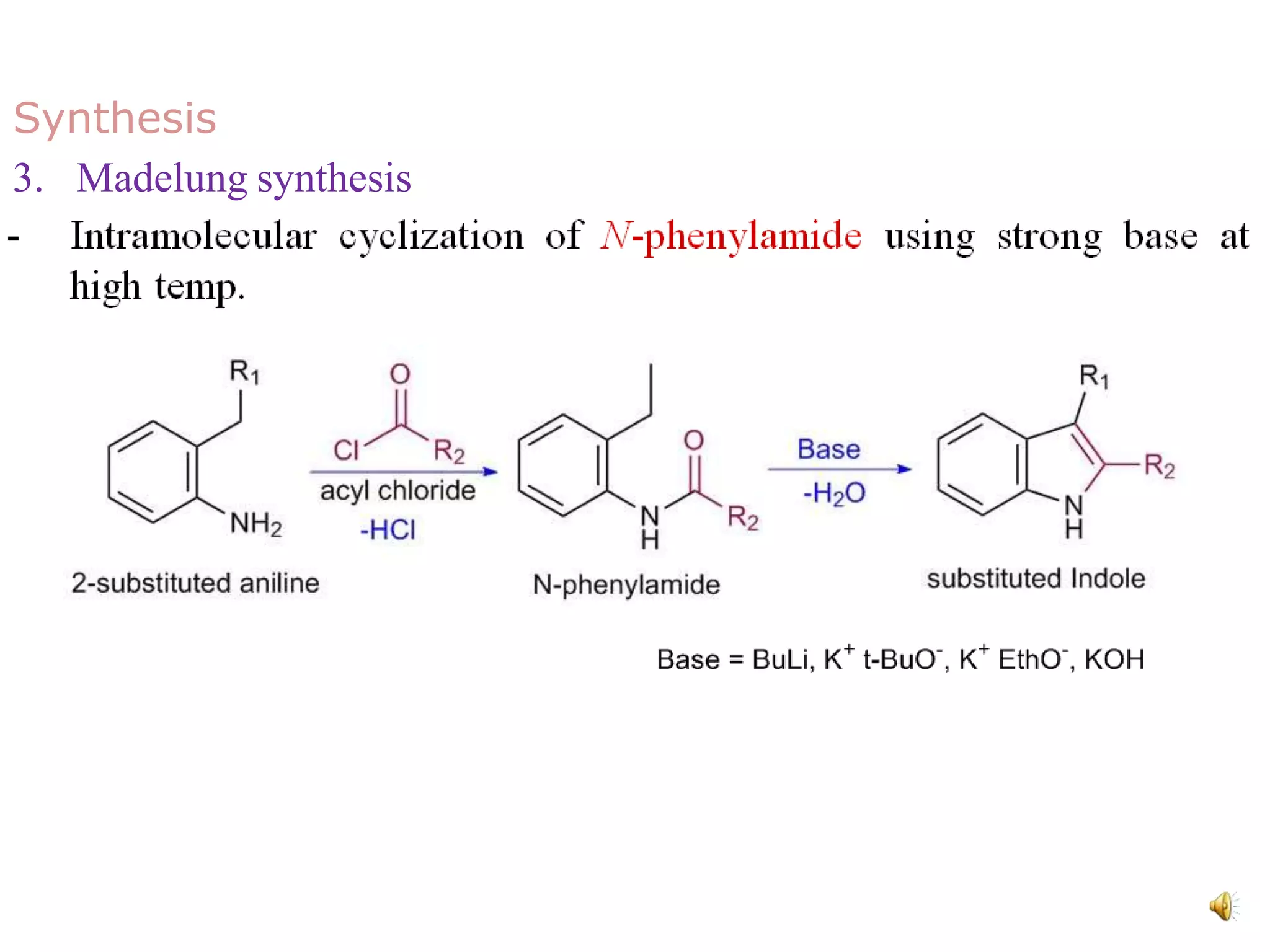
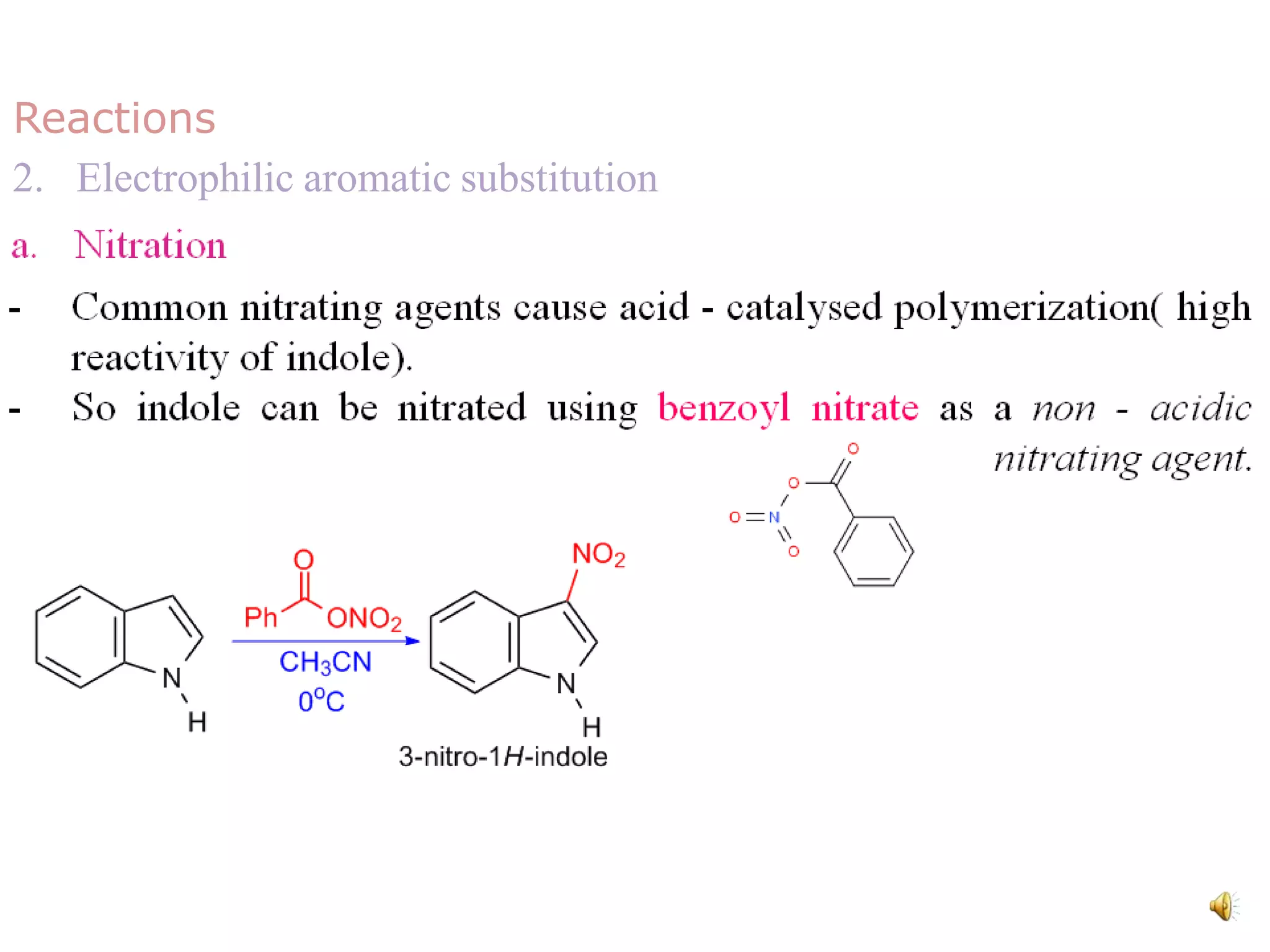
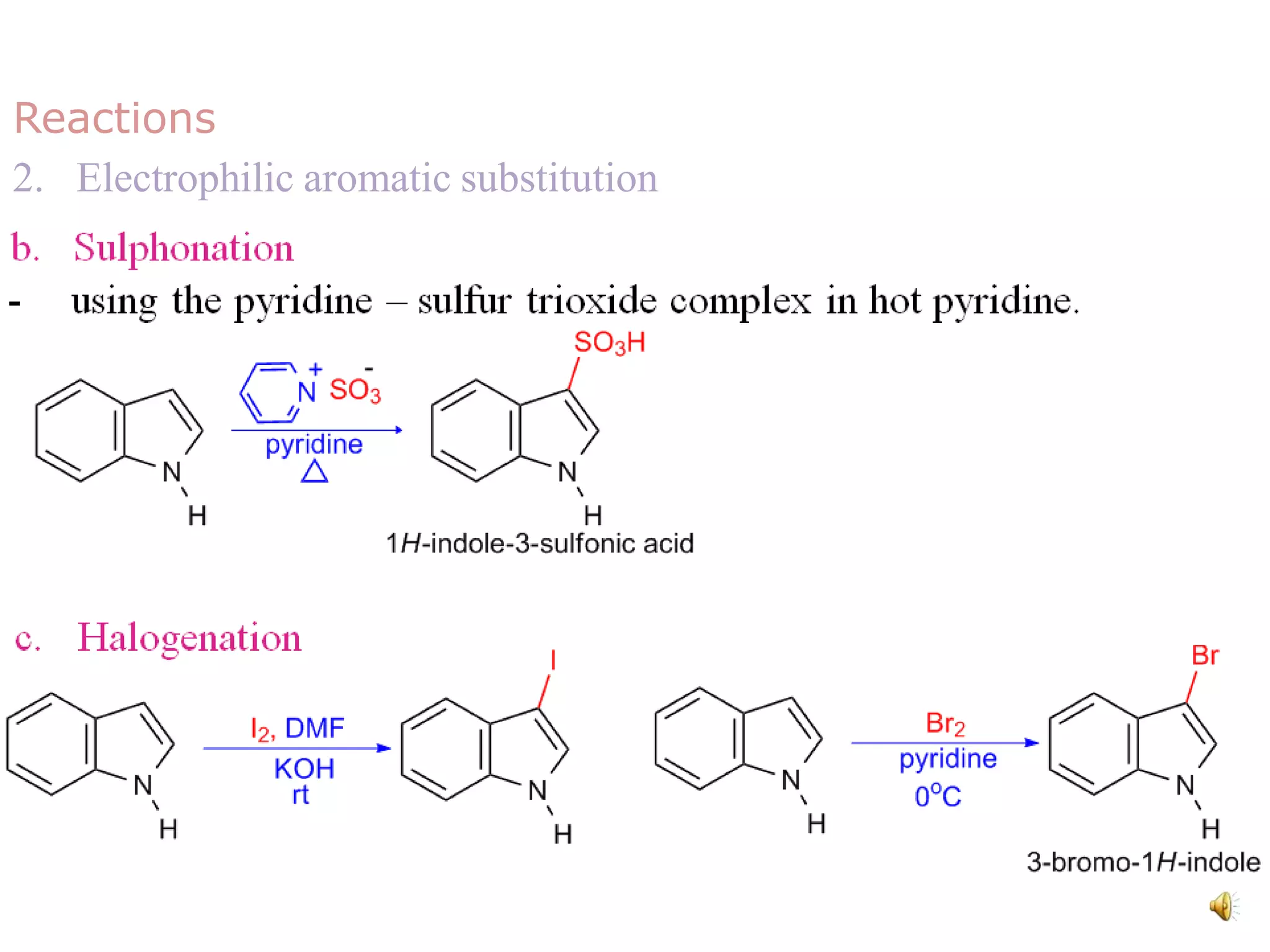
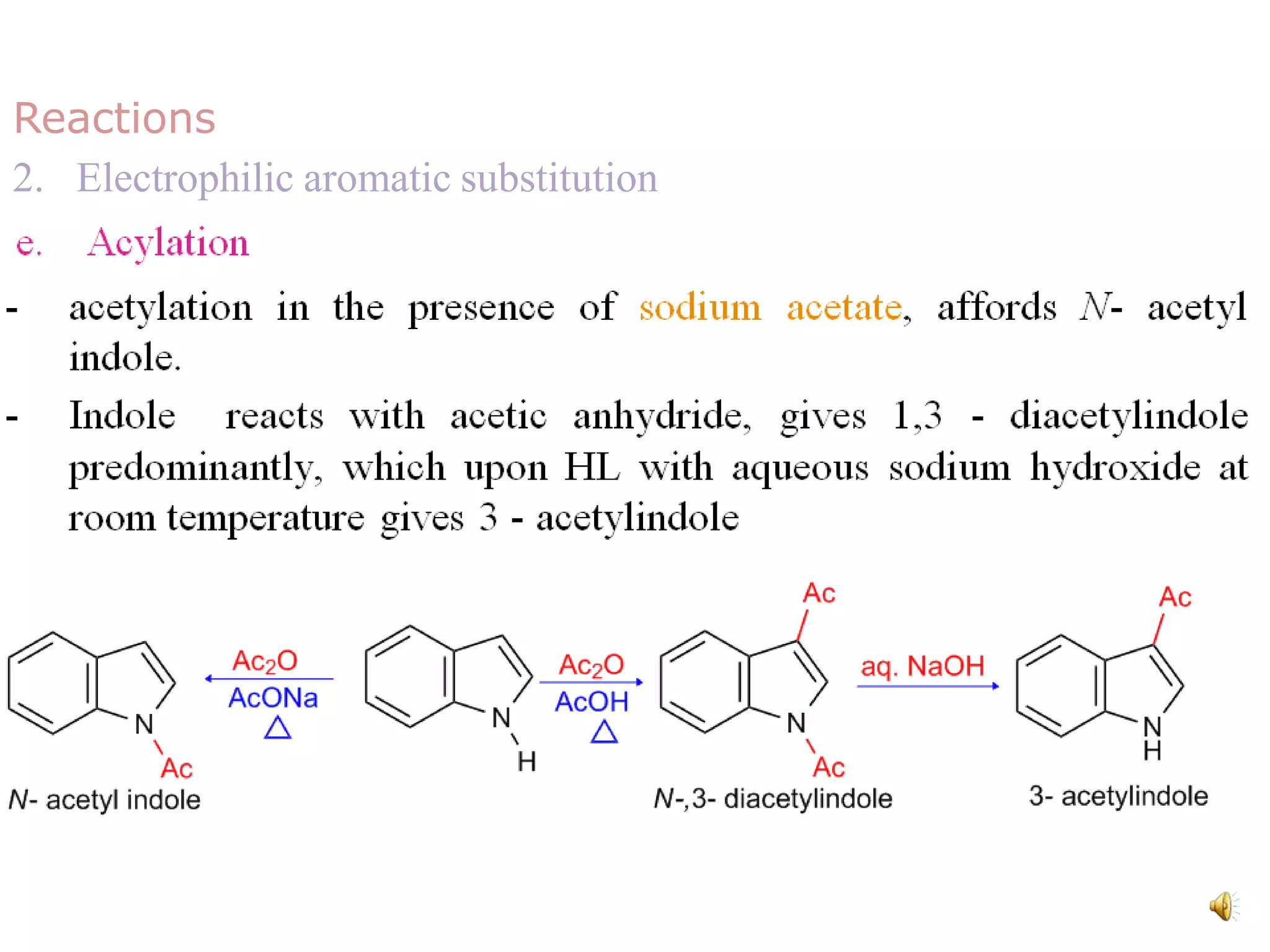
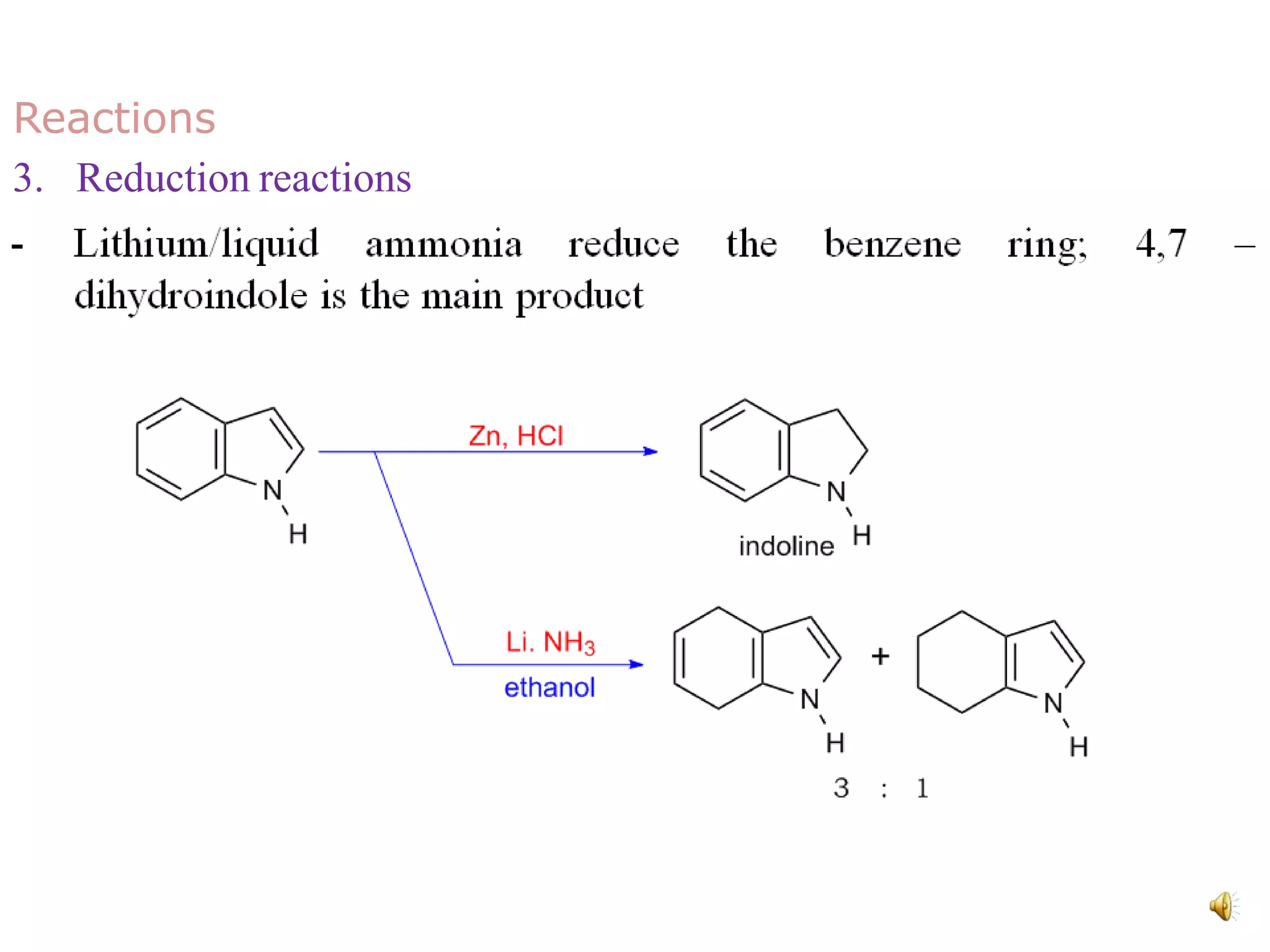
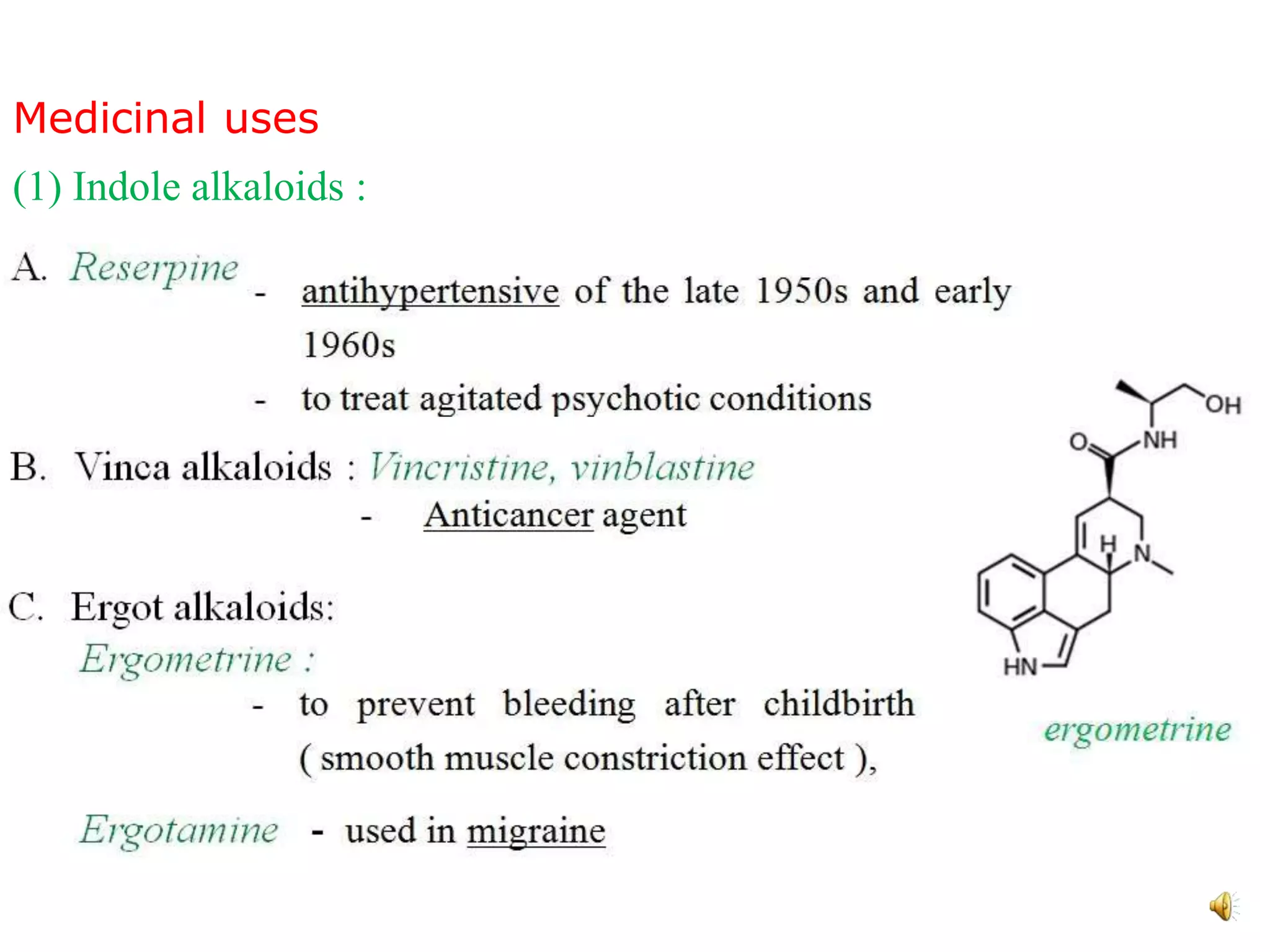
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound, notable for its structure combining a benzene ring and a pyrrole ring, with a formula of C8H7N. Its significance rose from its role as a precursor to important substances like serotonin and tryptophan, with its chemistry evolving from the study of indigo dye. Indole has unique physical and chemical properties, including an intense odor at high concentrations and various medicinal applications through its alkaloid derivatives.