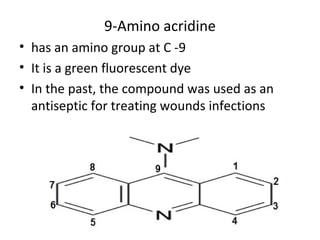
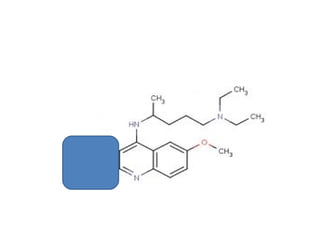
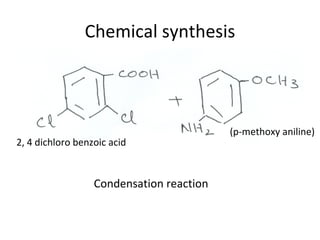
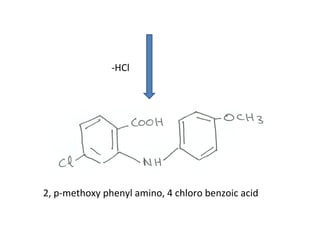
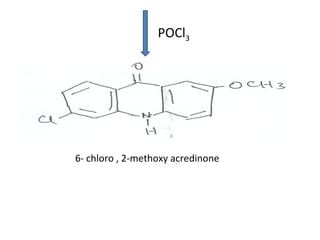
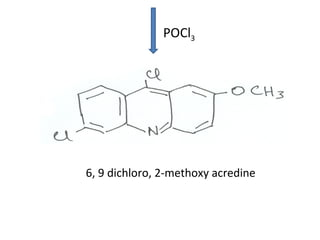
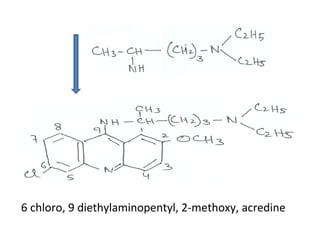
1) 9-aminoacridines are antimalarial drugs derived from acridine, which is formed by fusing an additional benzene ring to pyridine in quinoline.
2) Introducing certain functional groups or side chains at different positions on the acridine nucleus can enhance or reduce antimalarial activity. For example, adding a side chain at the 9 position makes it antimalarial.
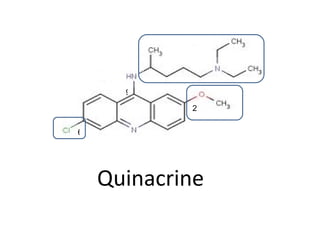
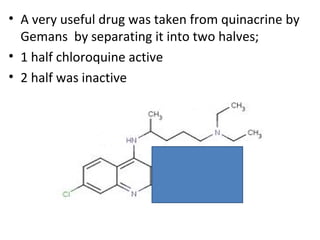
3) Examples of antimalarial 9-aminoacridines include quinacrine, which was one of the first synthetic antimalarials, and chloroquine, which was developed from quinacrine.