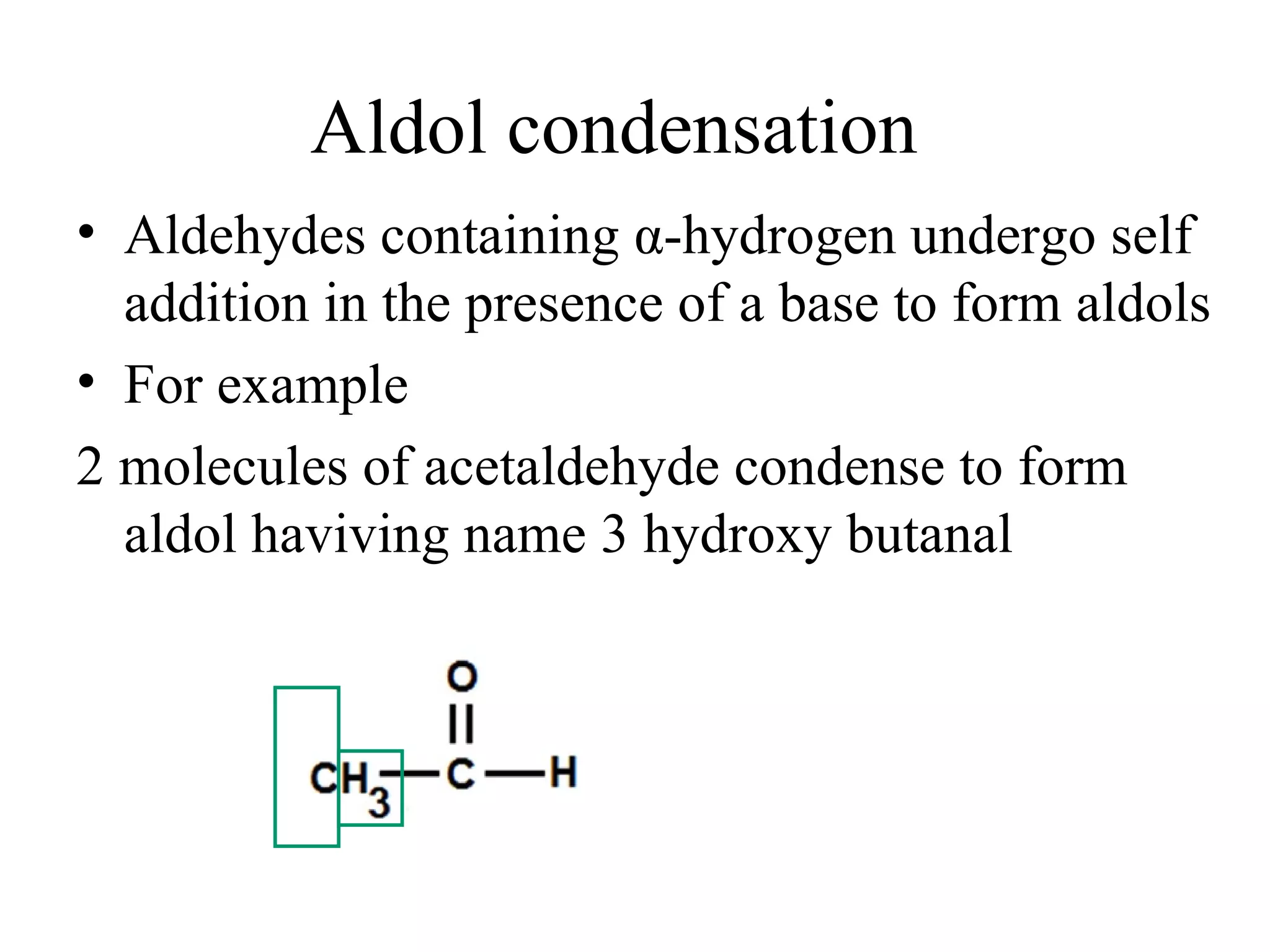
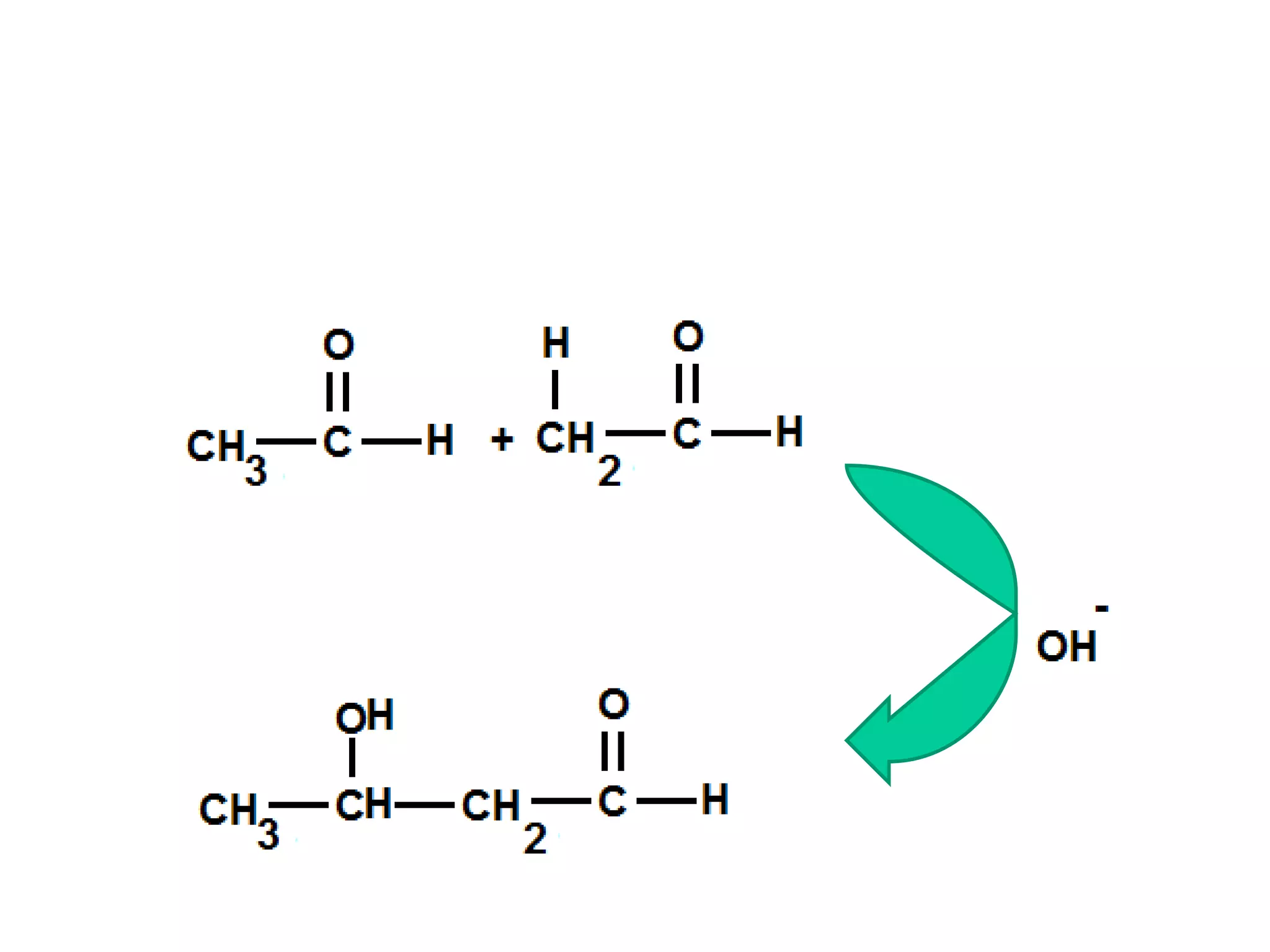
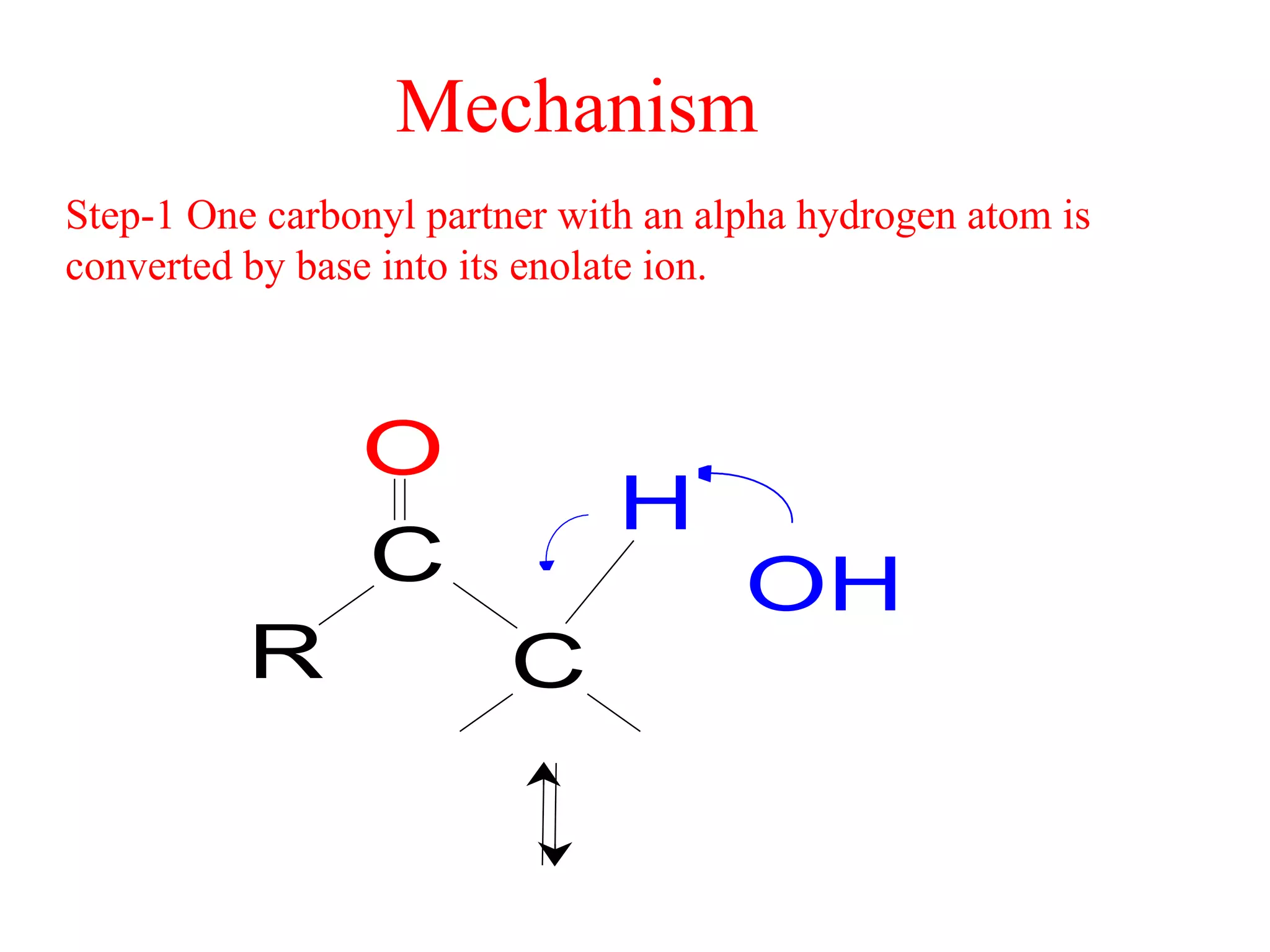
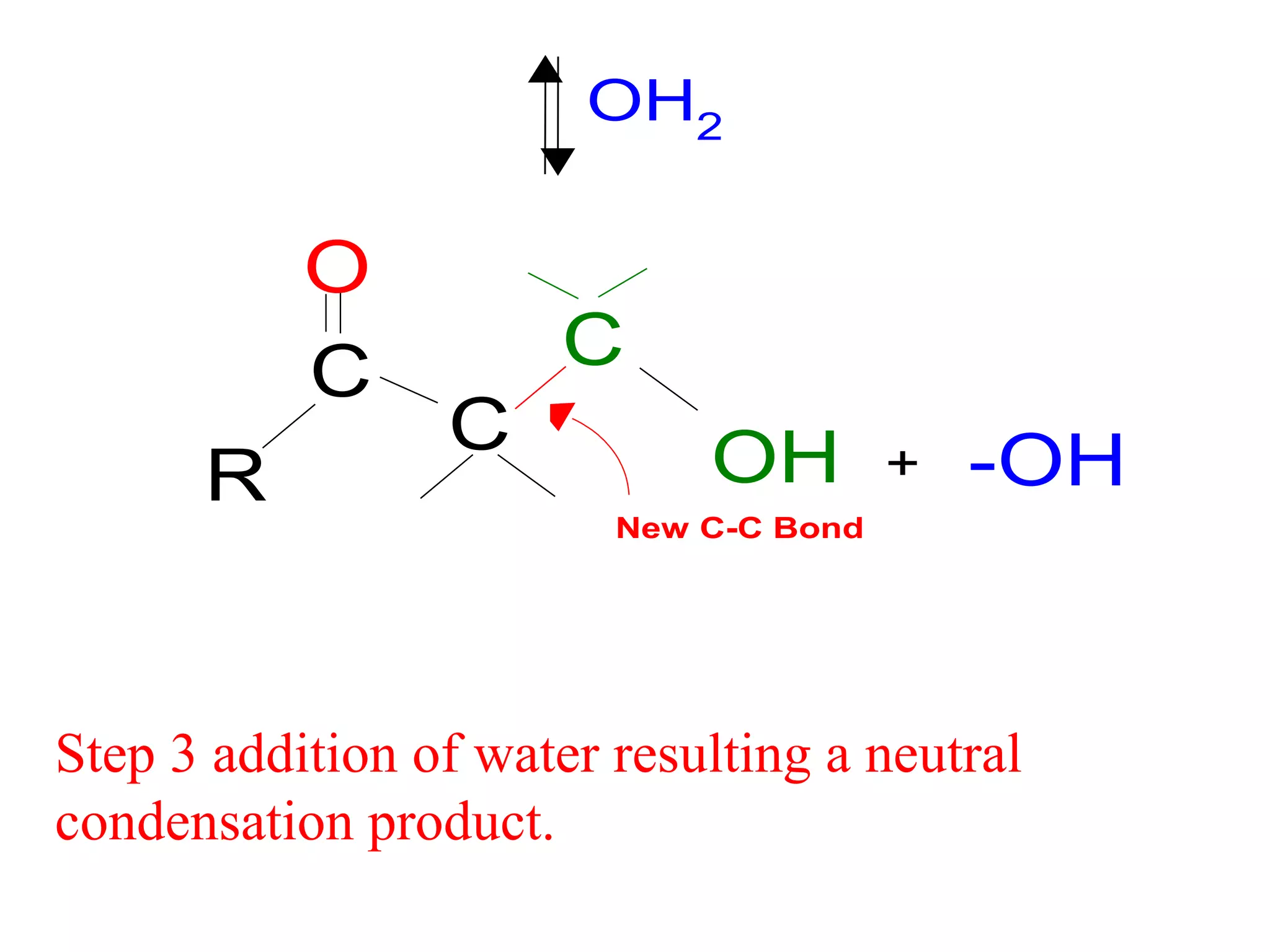
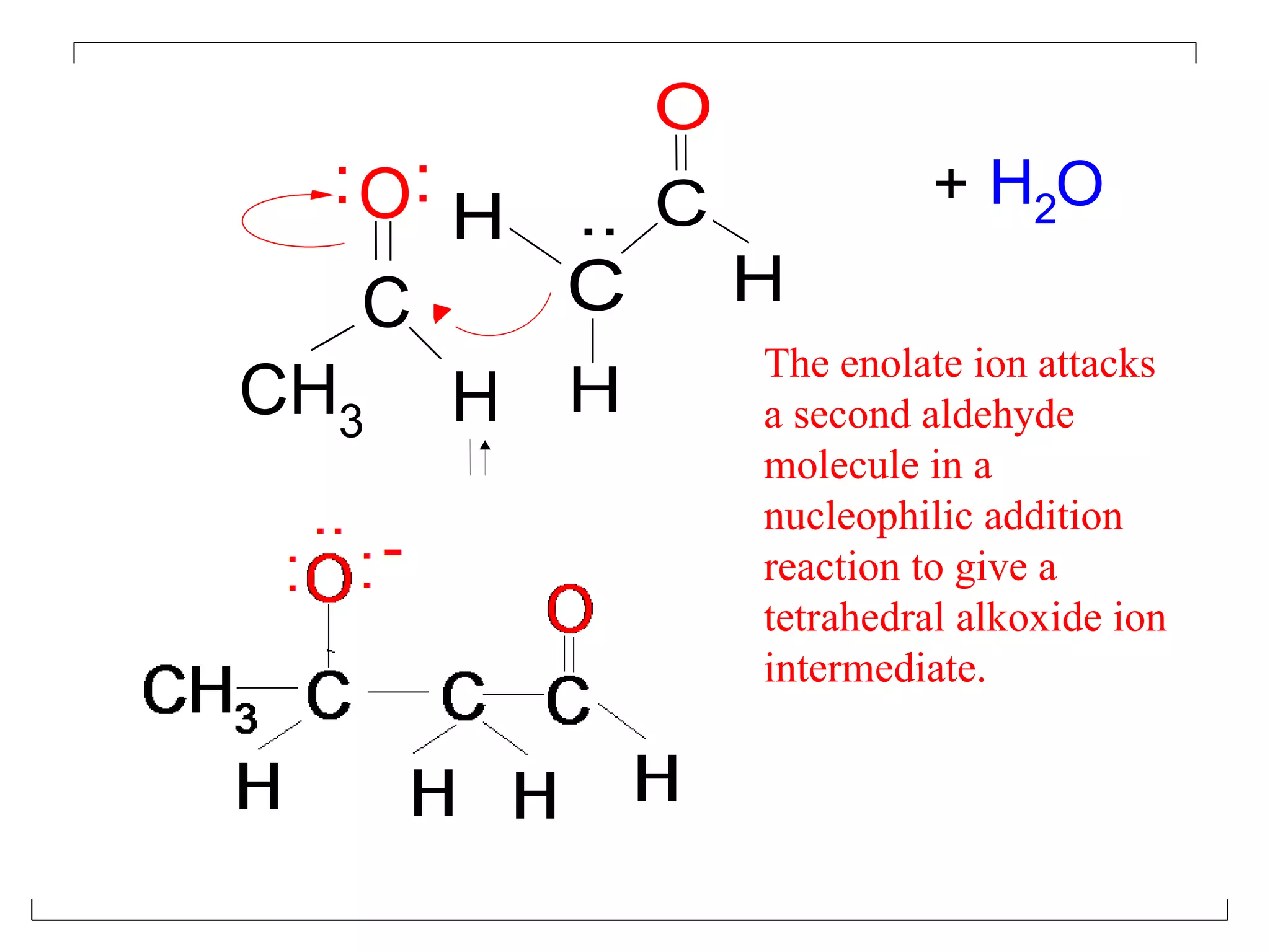
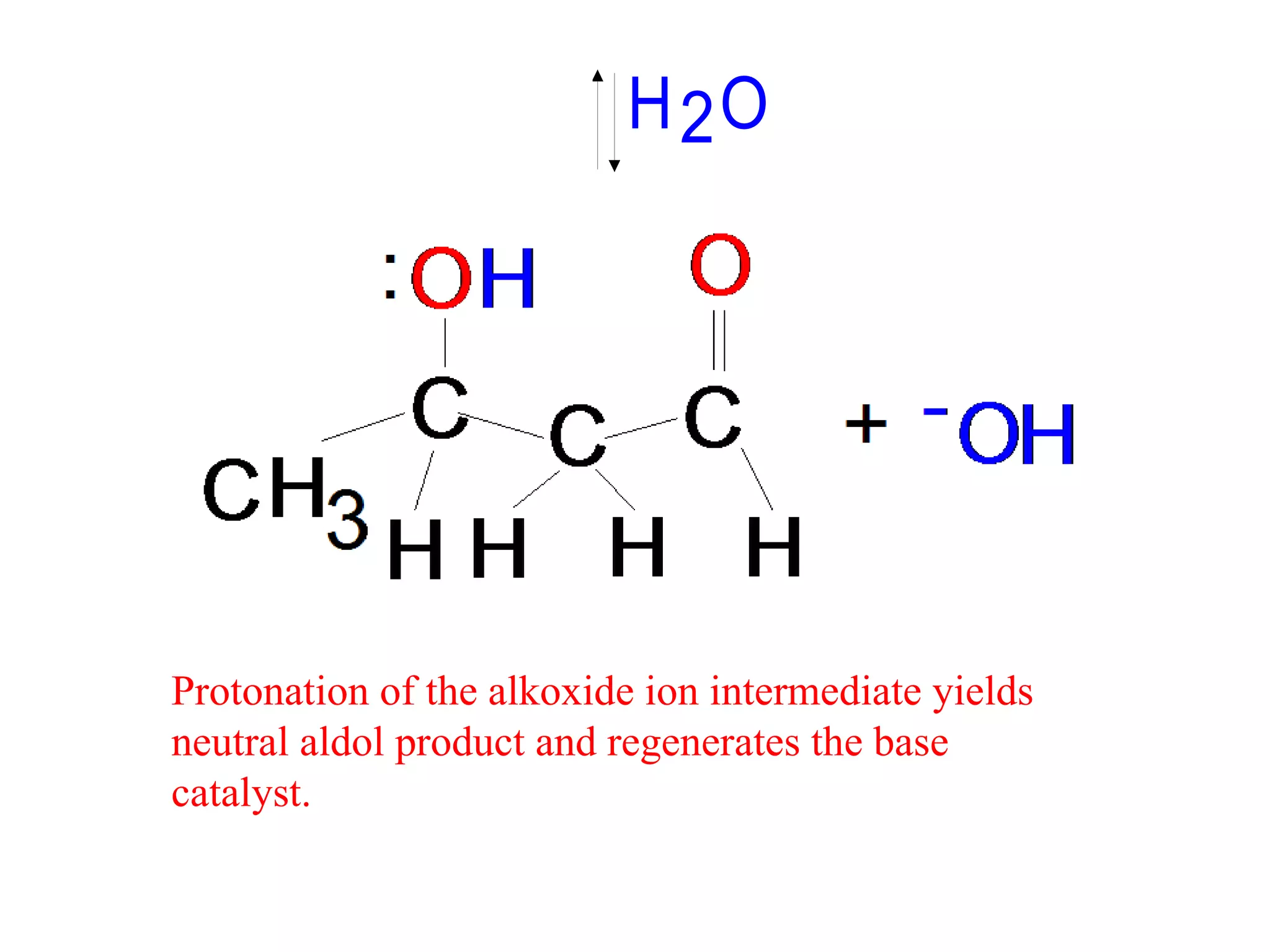
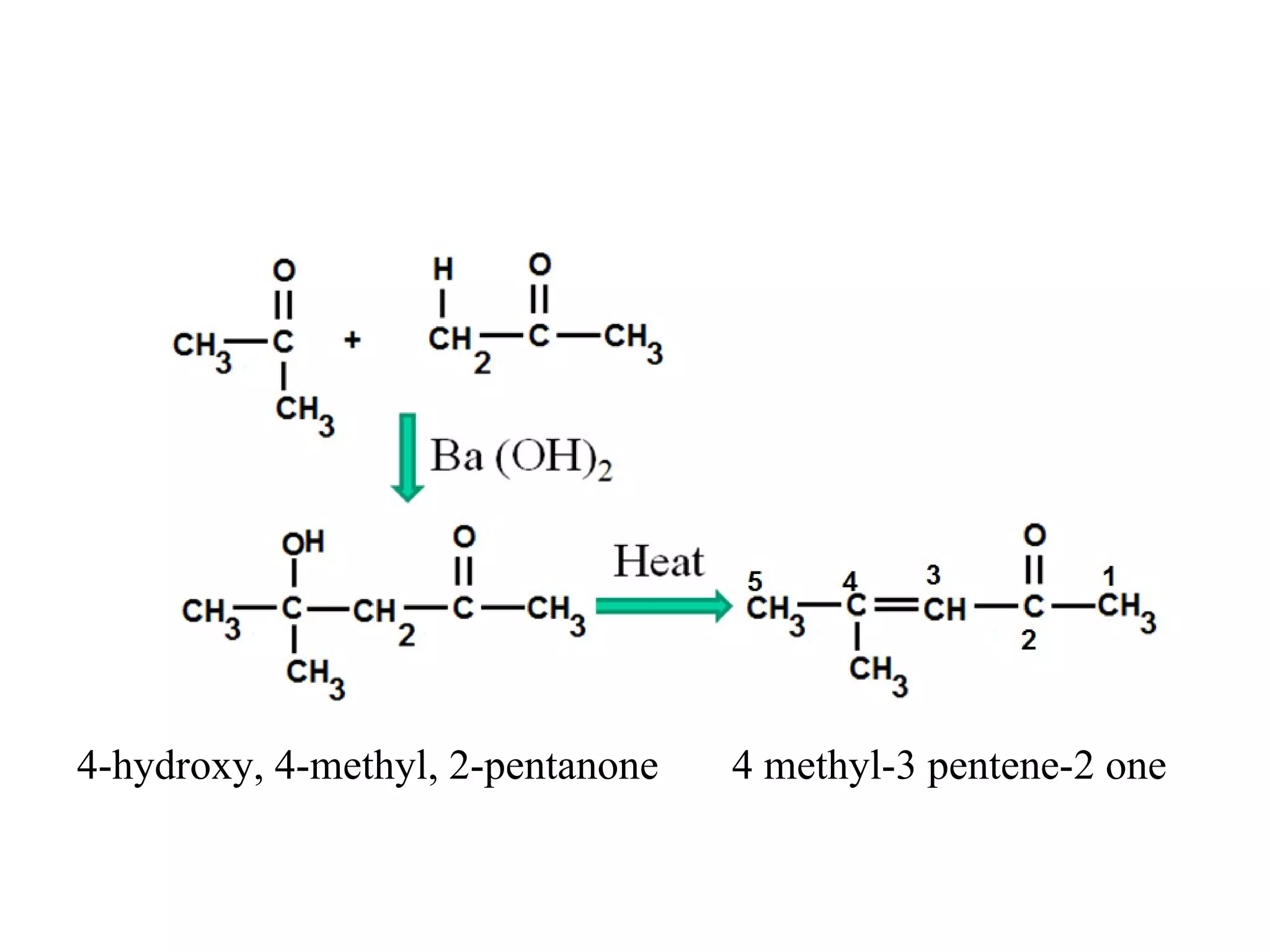
The aldol condensation is a reaction where carbonyl compounds undergo condensation in the presence of a base to form β-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones. It can occur between two aldehydes, two ketones, or a mixed aldehyde and ketone. The reaction involves the base-catalyzed formation of an enolate ion from the α-hydrogen of one carbonyl compound, which then undergoes nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl carbon of the second reactant. Removal of a water molecule produces the β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone product.