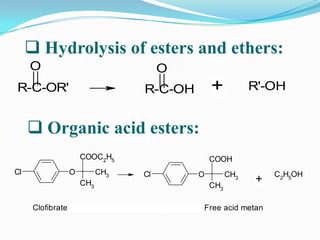
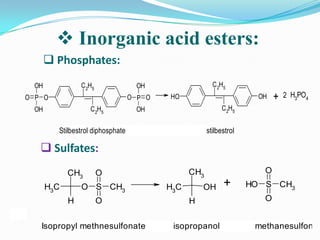
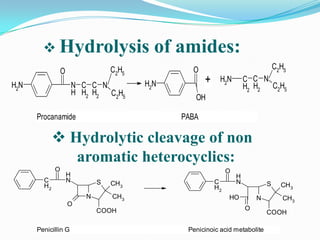
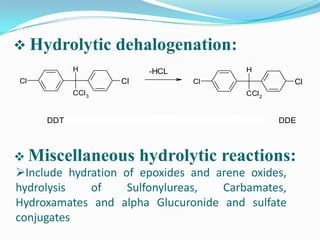
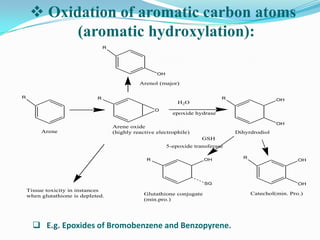
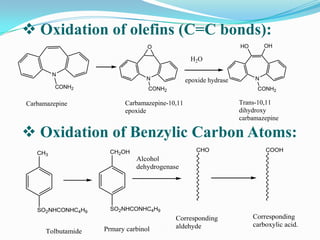
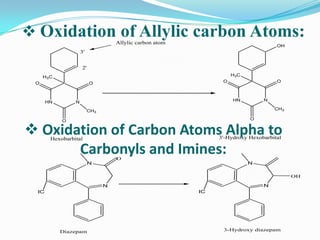
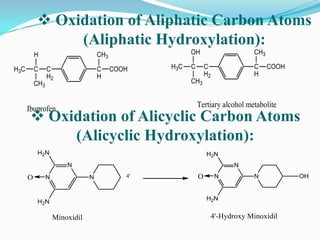
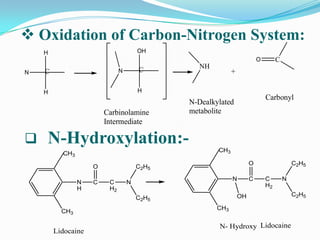
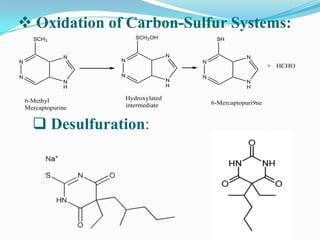
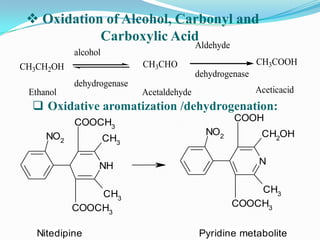
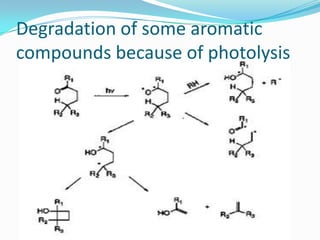
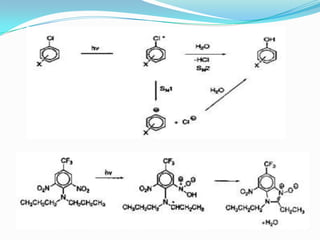
The document discusses the stability of pharmaceutical formulations. It defines stability as a formulation remaining within its physical, chemical, microbiological, therapeutic and toxicological specifications. Stability is important to ensure drug products maintain quality and intended effects until expiration. Chemical and physical degradation pathways include hydrolysis, oxidation, photodegradation, and interactions with excipients or other drugs. Factors like temperature, pH, moisture, and light can affect the rate of degradation. The document focuses on hydrolysis and oxidation as two major degradation pathways and provides examples of each.