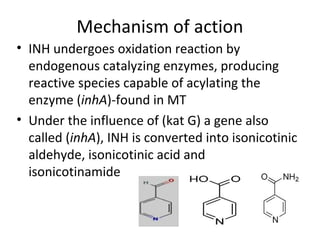
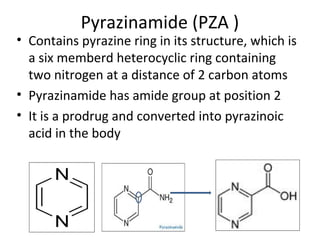
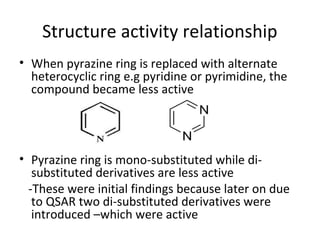
This document provides an overview of tuberculosis (TB) and summarizes key information about two important anti-TB drugs: isoniazid (INH) and pyrazinamide (PZA). It describes the characteristic cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes TB. It then discusses the development of INH and PZA as synthetic anti-TB drugs, their chemical structures, mechanisms of action, metabolism, and structure-activity relationships. INH and PZA are often used together in combination drug therapies to treat TB due to their ability to target actively dividing and dormant forms of the bacteria.