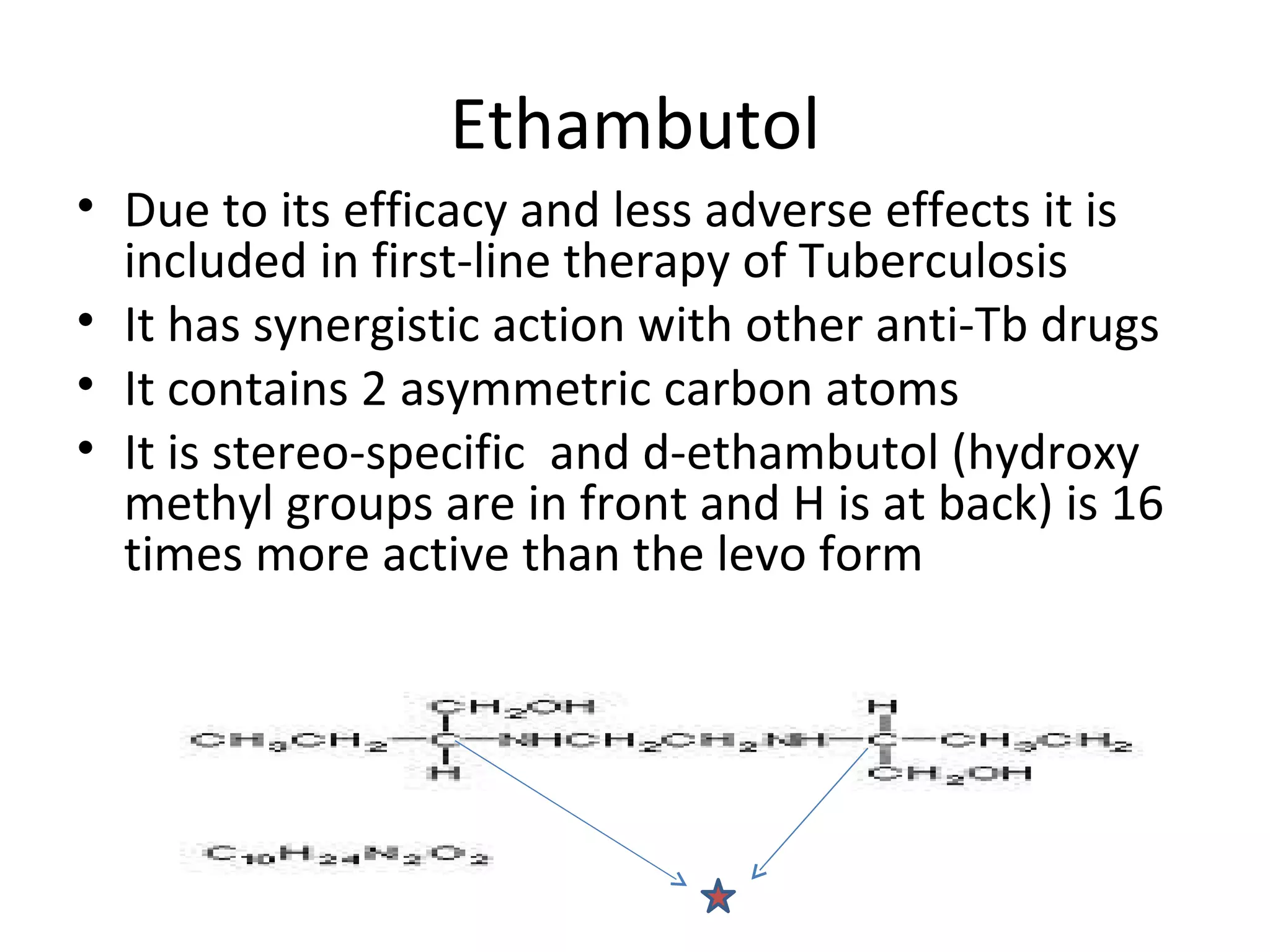
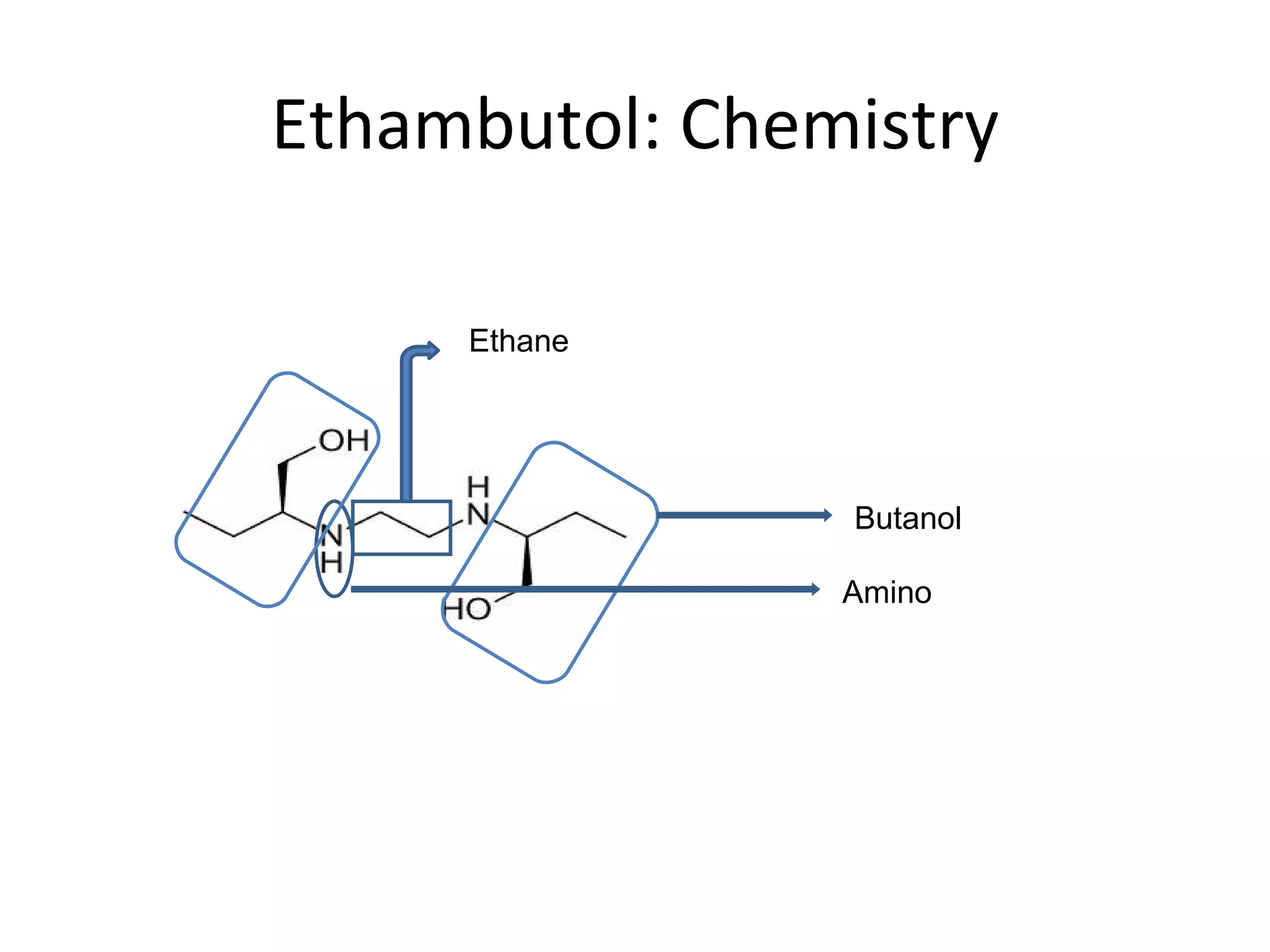
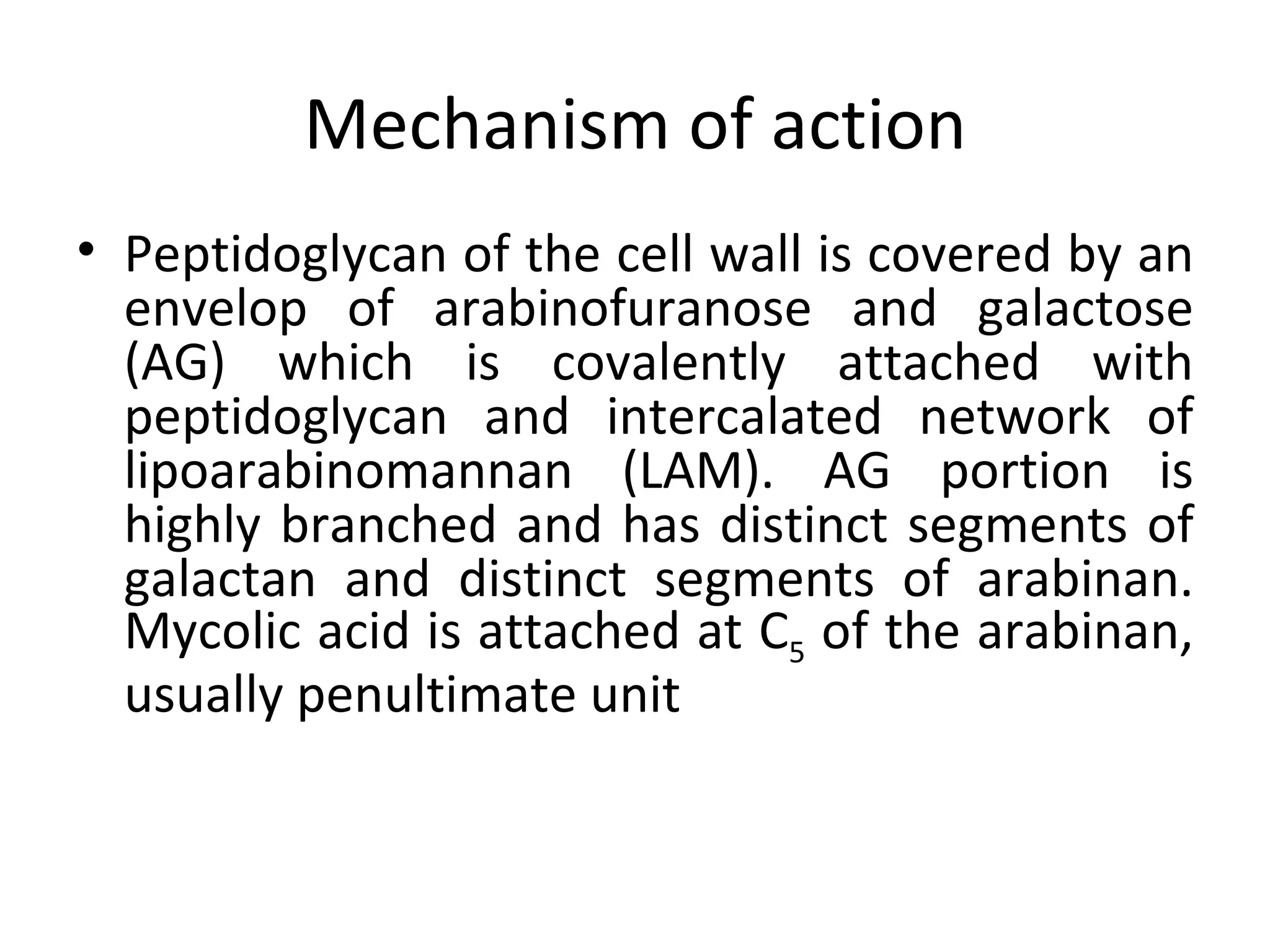
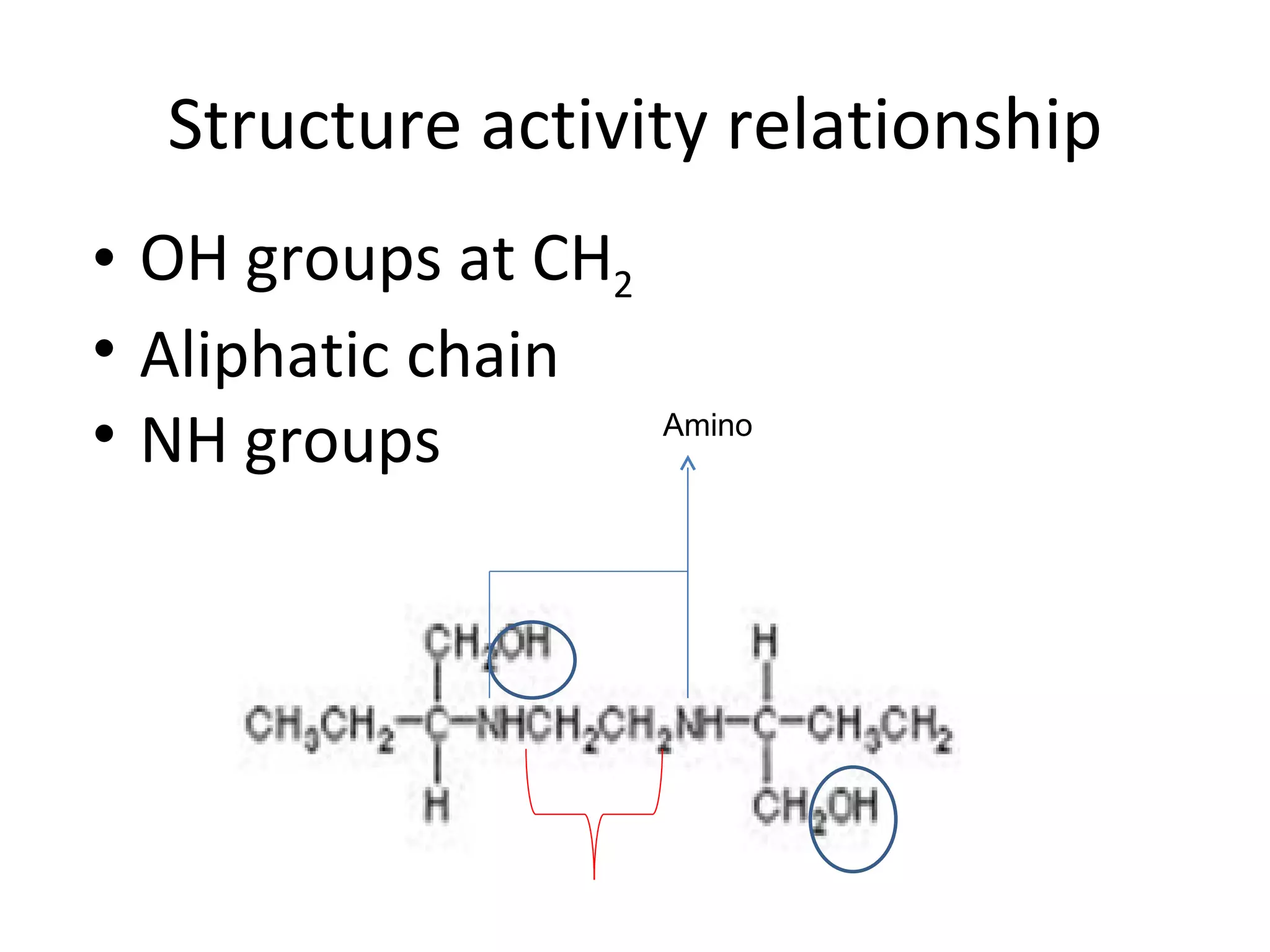
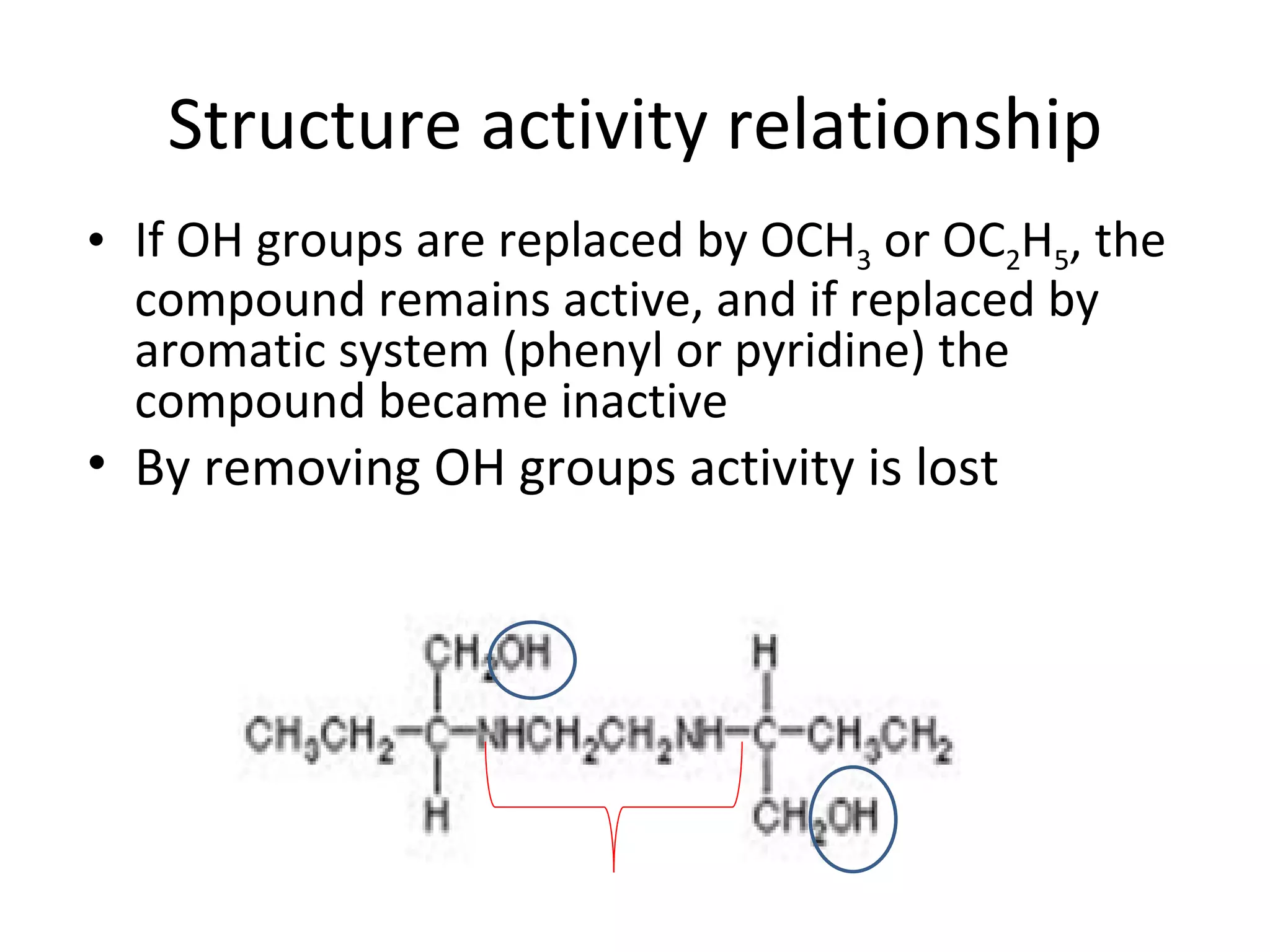
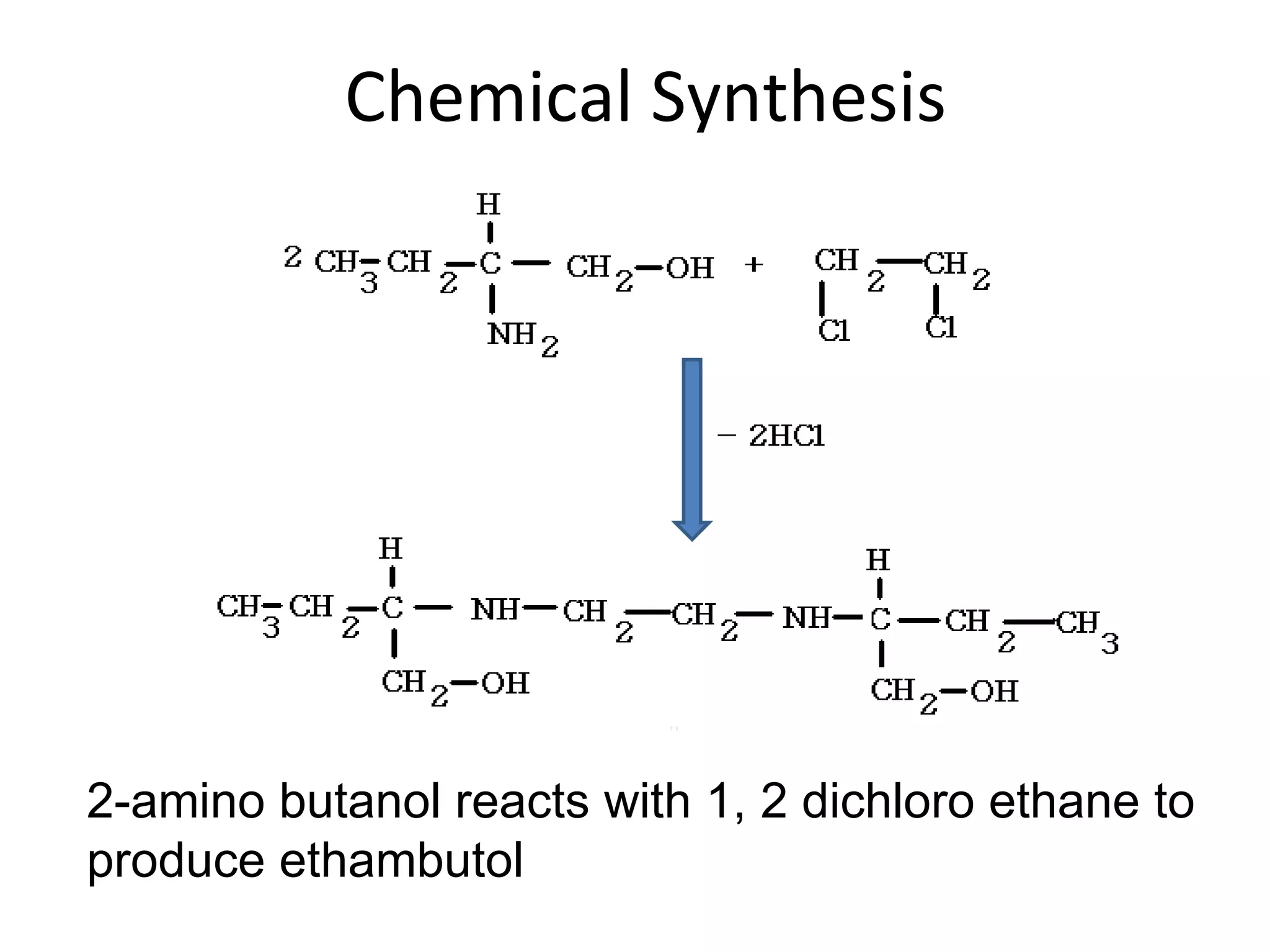
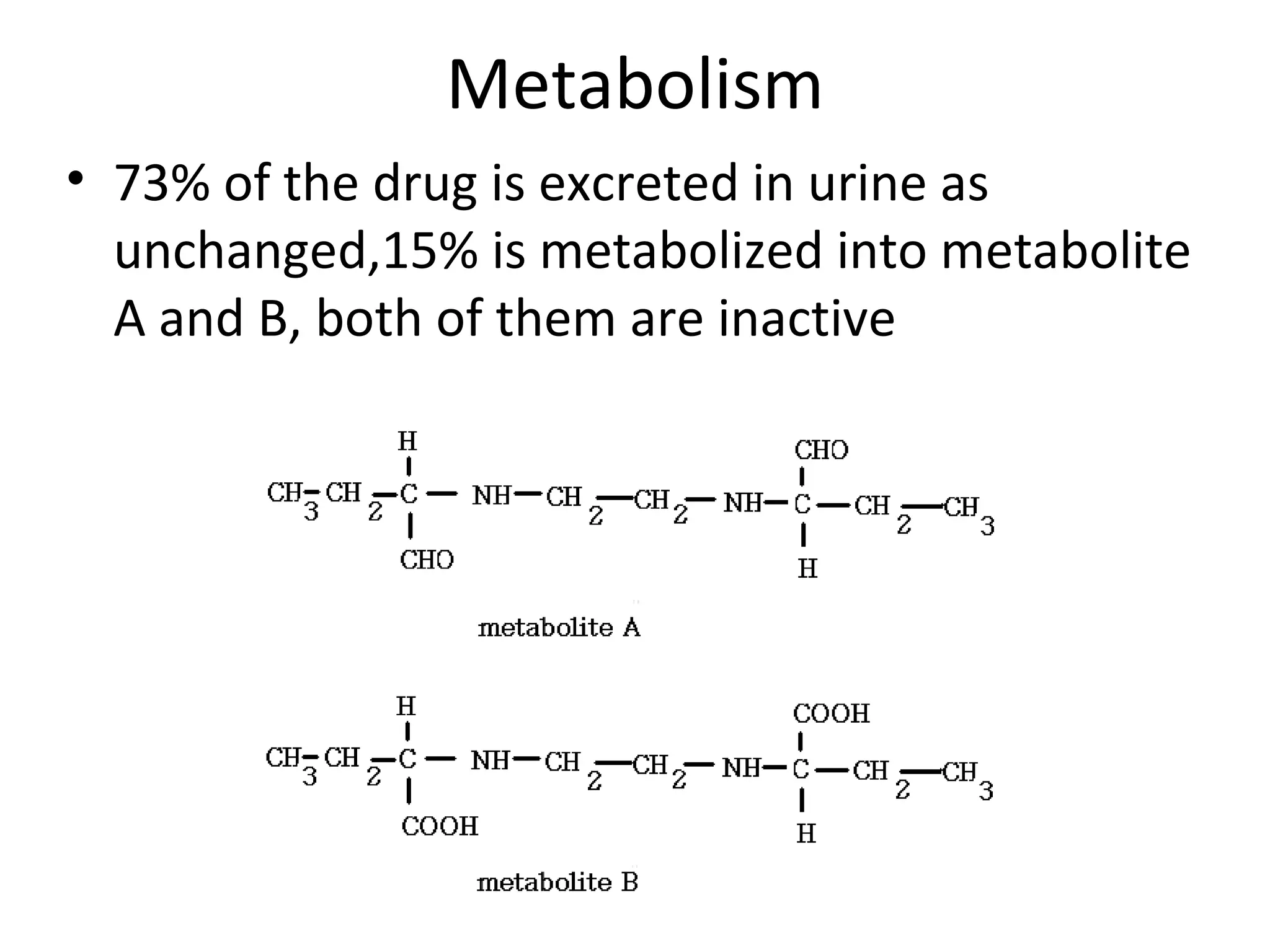
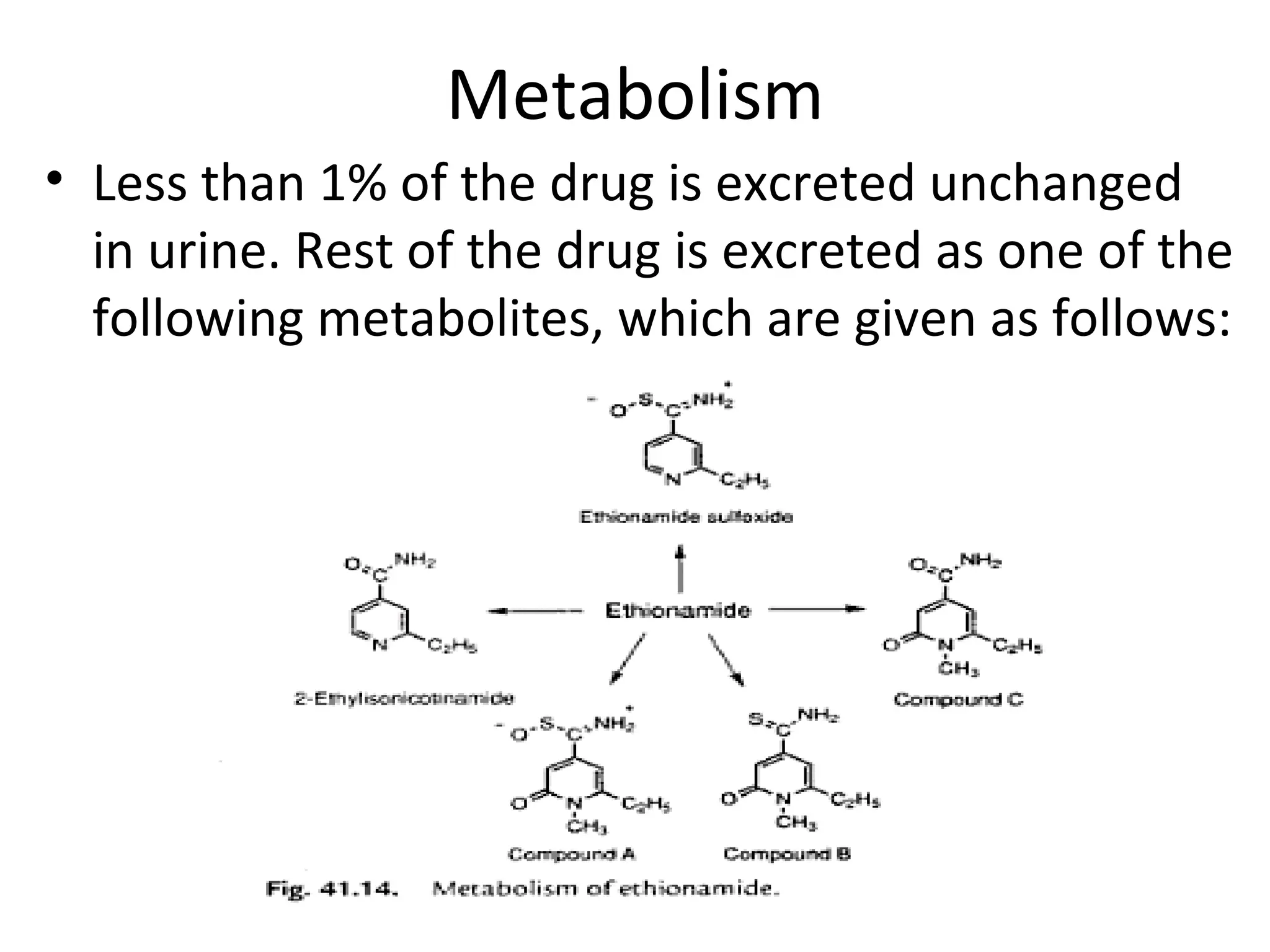
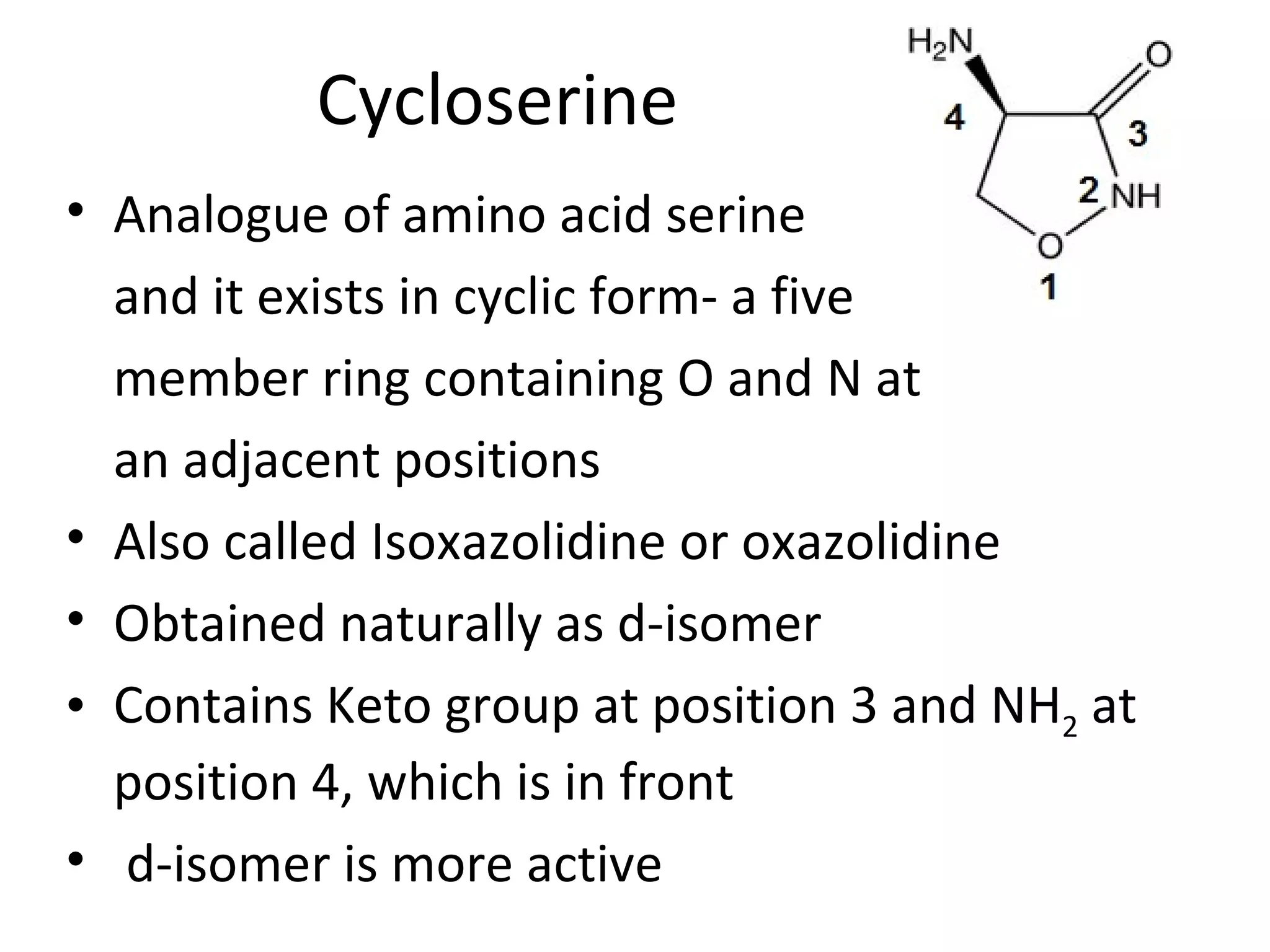
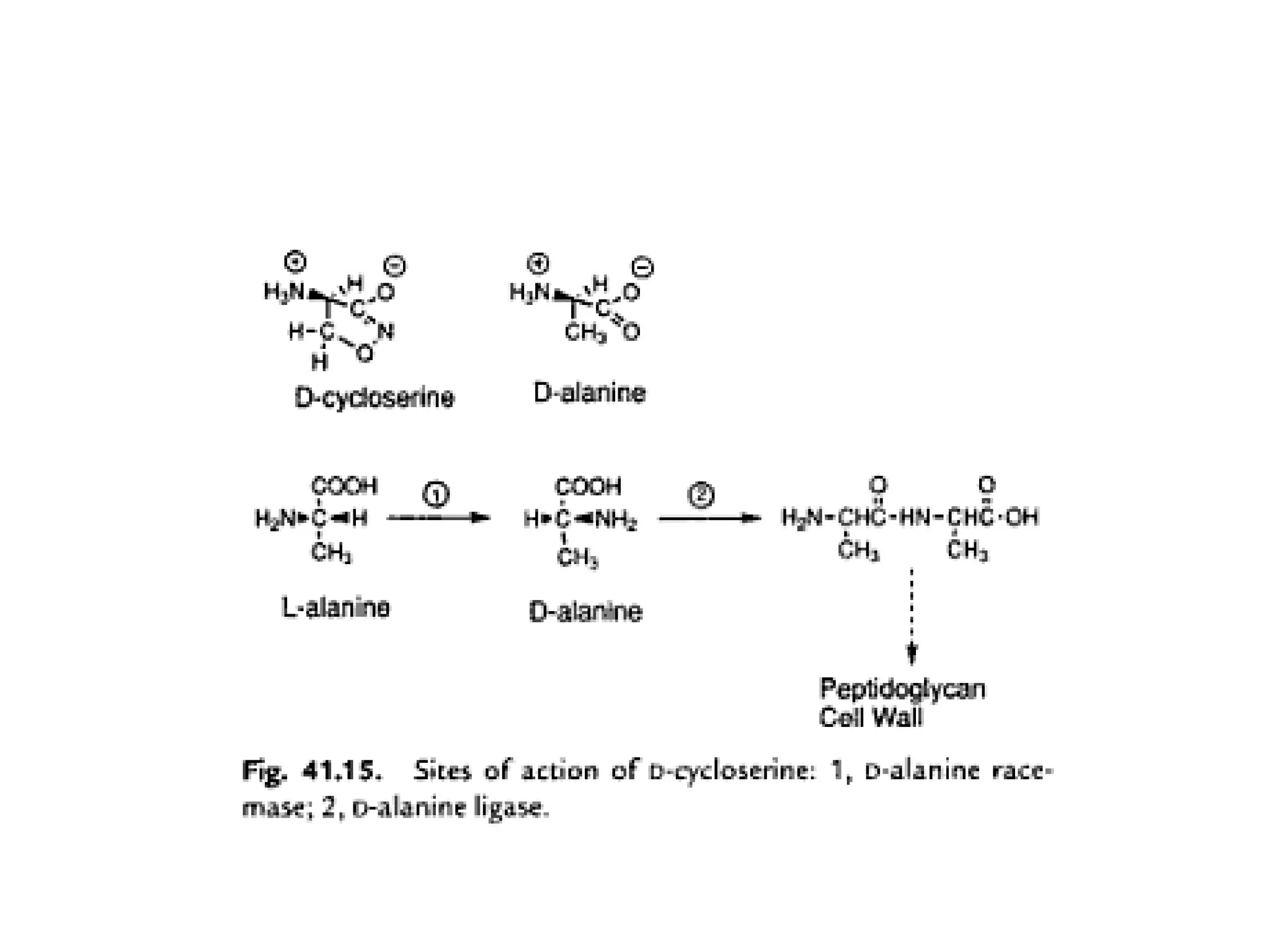
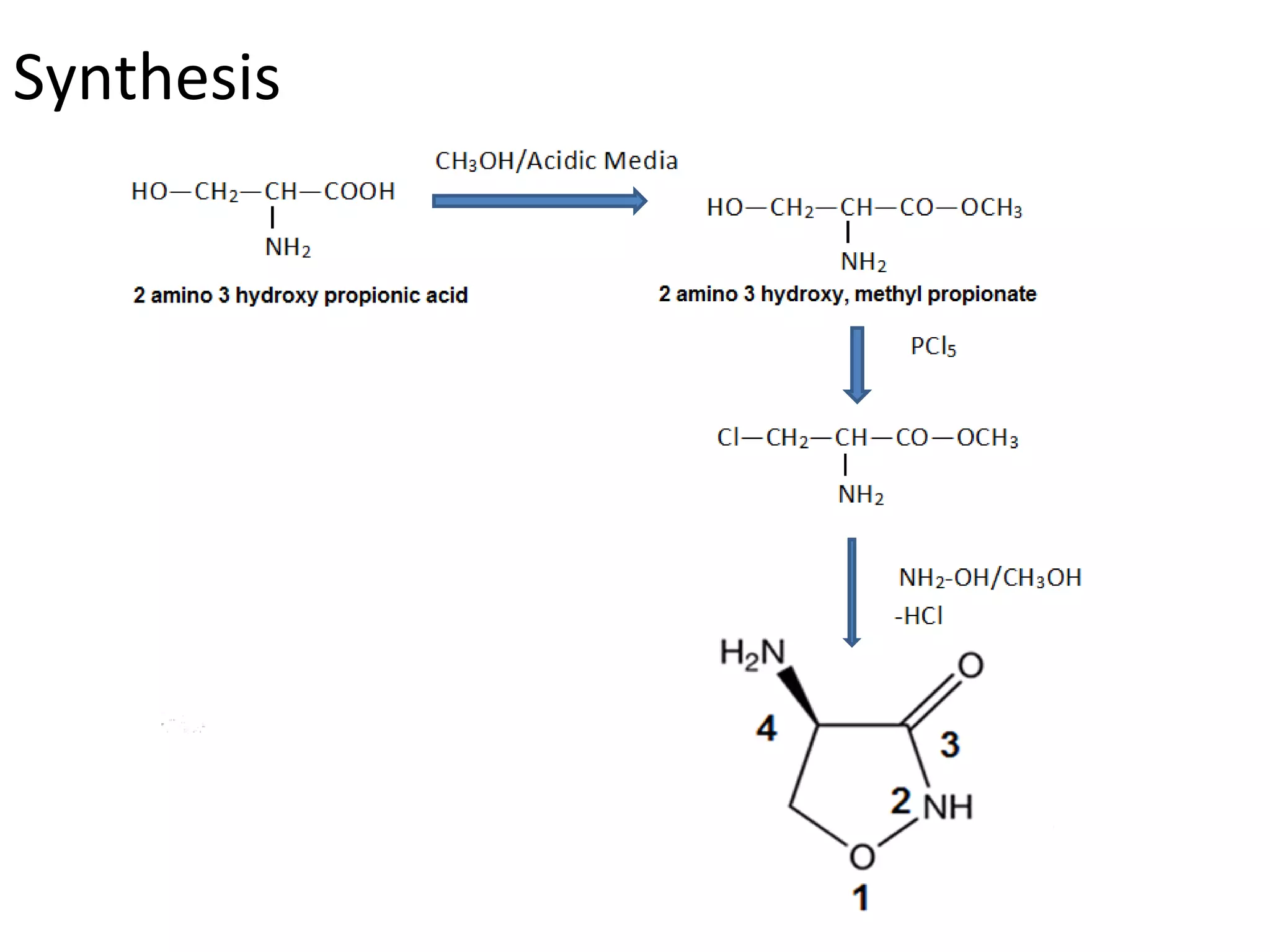
Ethambutol is included in first-line tuberculosis therapy due to its efficacy and fewer adverse effects. It has synergistic effects with other anti-tuberculosis drugs and contains two asymmetric carbon atoms, with the D-form being 16 times more active. Ethambutol inhibits the formation of mycolic acid in the cell wall, particularly through inhibiting arabinosyl transferase and preventing polymerization of D-arabinofuranose. Common adverse effects include optic neuritis and color blindness.