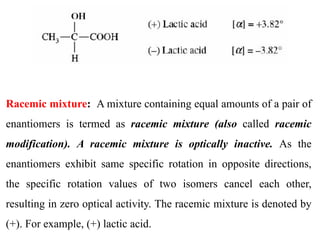
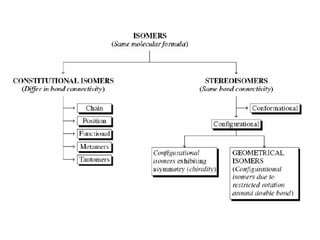
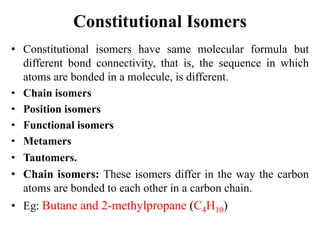
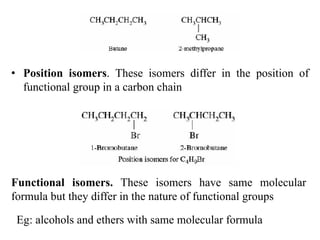
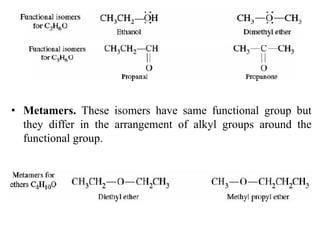
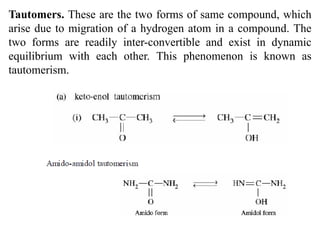
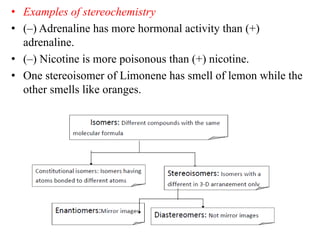
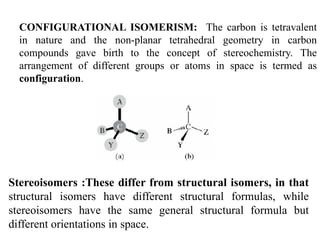
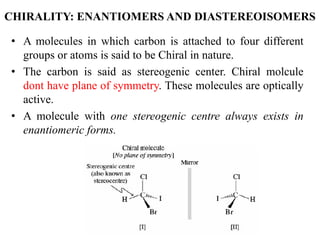
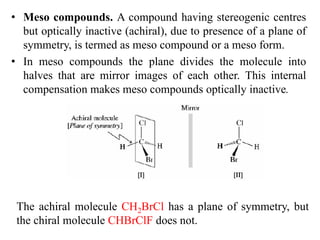
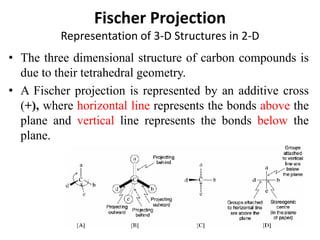
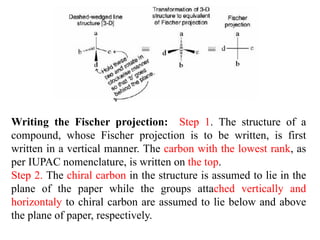
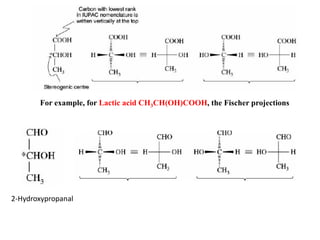
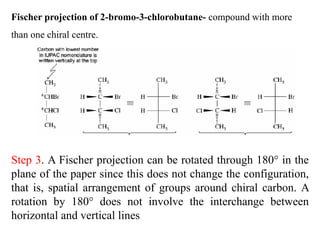
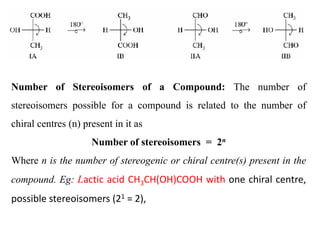
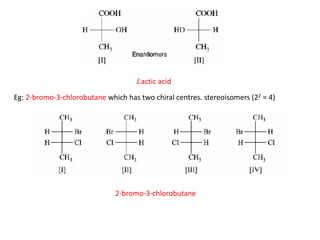
This document discusses stereochemistry and isomerism. It defines constitutional and stereoisomers, and describes different types of constitutional isomers like chain, position, functional, and tautomeric isomers. It also discusses configurational isomerism including optical isomers like enantiomers and diastereomers. Chirality and chiral centers are explained. Methods to represent 3D structures in 2D like Fischer projections are introduced. The document also covers topics like optical activity, polarimetry and racemic mixtures.

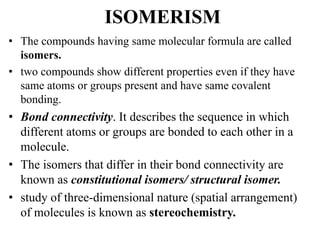





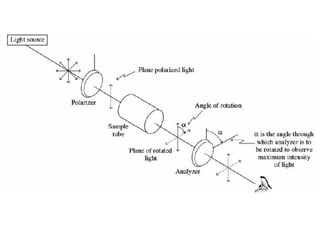
![• Specific rotation [α], is the rotation caused by a sample at a
concentration of 1.0 g/mL in a sample tube of length 1.0 dm
(10.0 cm). The value of specific rotation depends on the
concentration of sample, its structure, wavelength of light
source, temperature, length of the sample tube, and solvent.
• The temperature t (in oC) and wavelength λ of light source are
indicated as superscript and subscript respectively while writing
the specific rotation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isomerism-1-200409061411/85/Isomerism-PART-1-Optical-Isomerism-26-320.jpg)