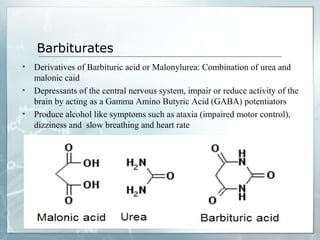
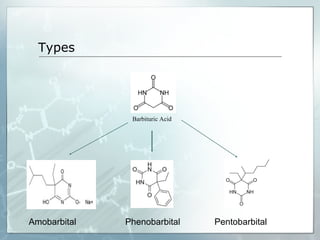
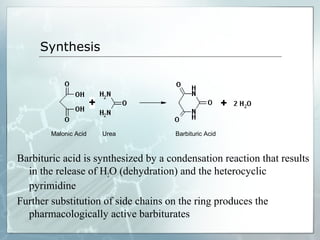
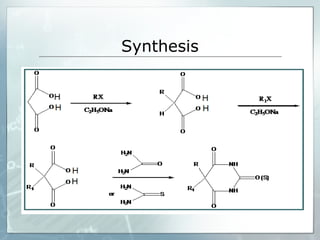
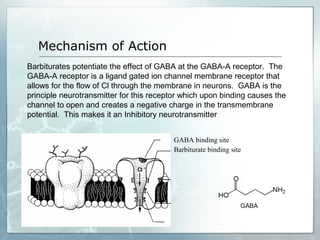
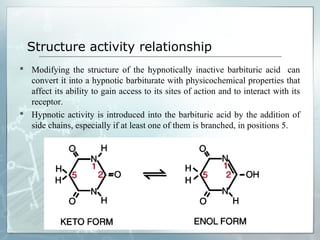
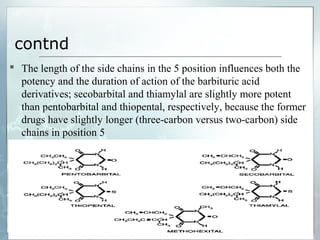
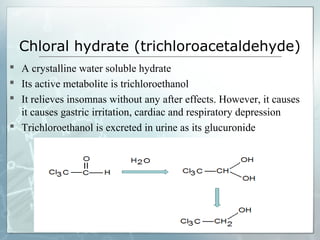
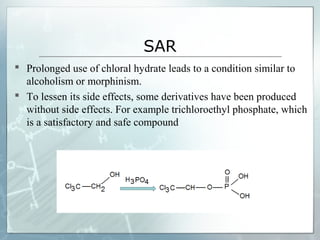
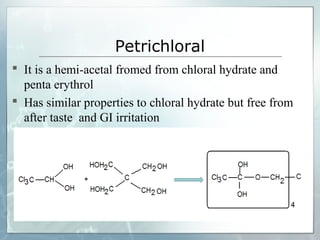
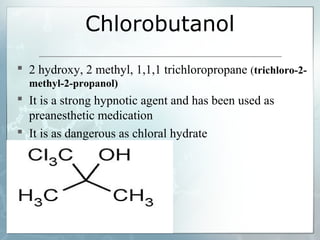
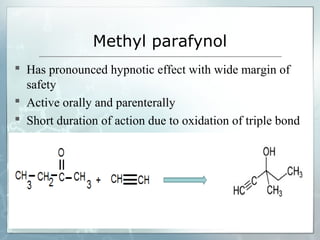
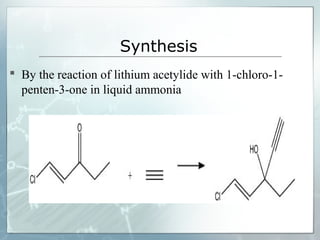
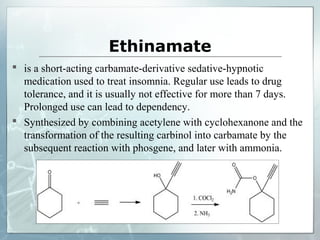
Sedatives and hypnotics work by calming agitation, inducing sleep, and reducing anxiety. Barbiturates are central nervous system depressants that produce their effects by potentiating the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Their mechanism of action, uses, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships are described. While formerly widely used, barbiturates have largely been replaced by benzodiazepines due to risks of addiction and tolerance. Other sedative-hypnotics discussed include paraldehyde, chloral hydrate, alcohols, ethchlorvynol, and glutarimide derivatives.