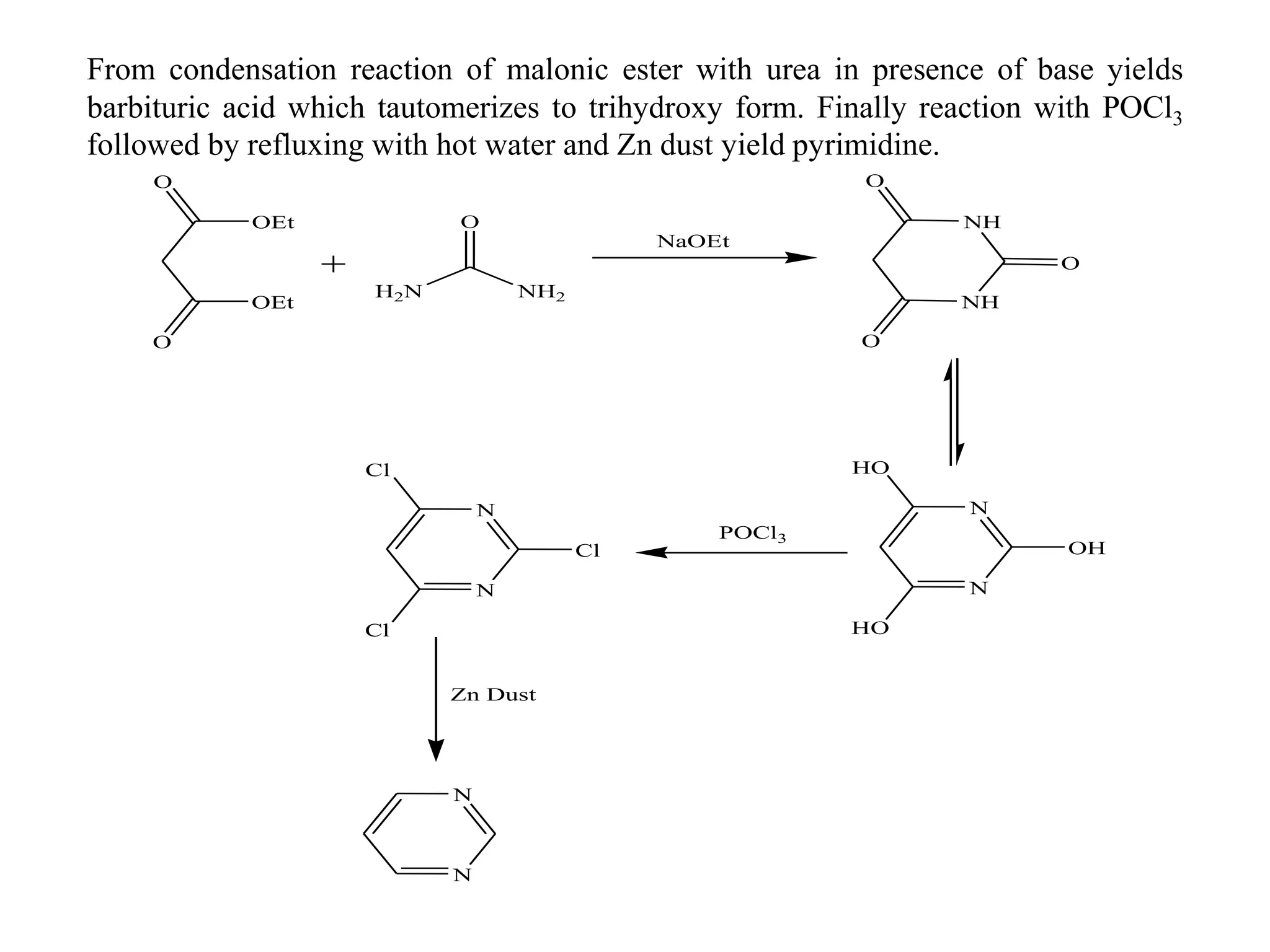
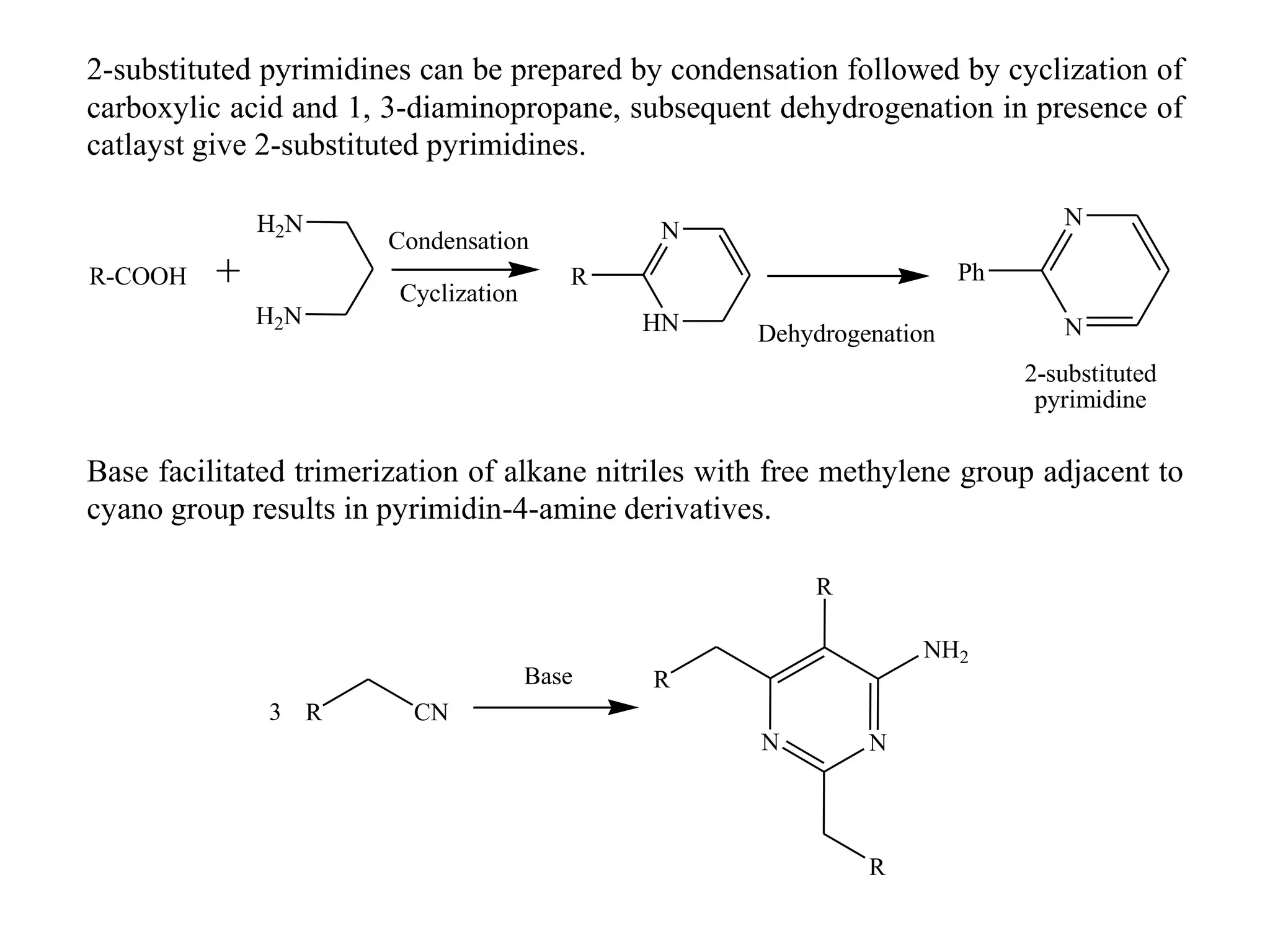
1) Diazines are six-membered heterocyclic compounds derived from benzene where two CH groups are replaced by nitrogen atoms. This can occur at the 1,2; 1,3; or 1,4 positions.
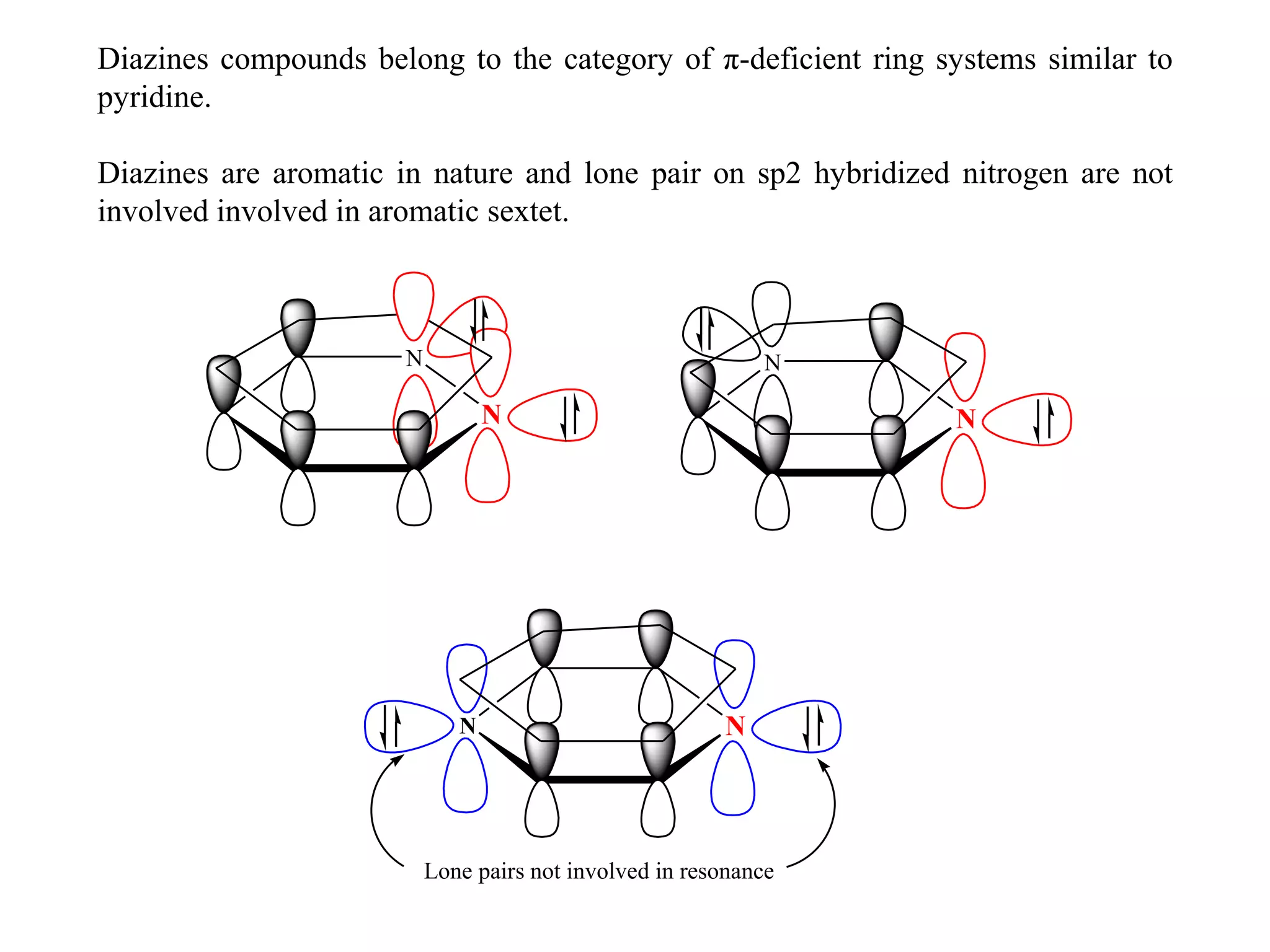
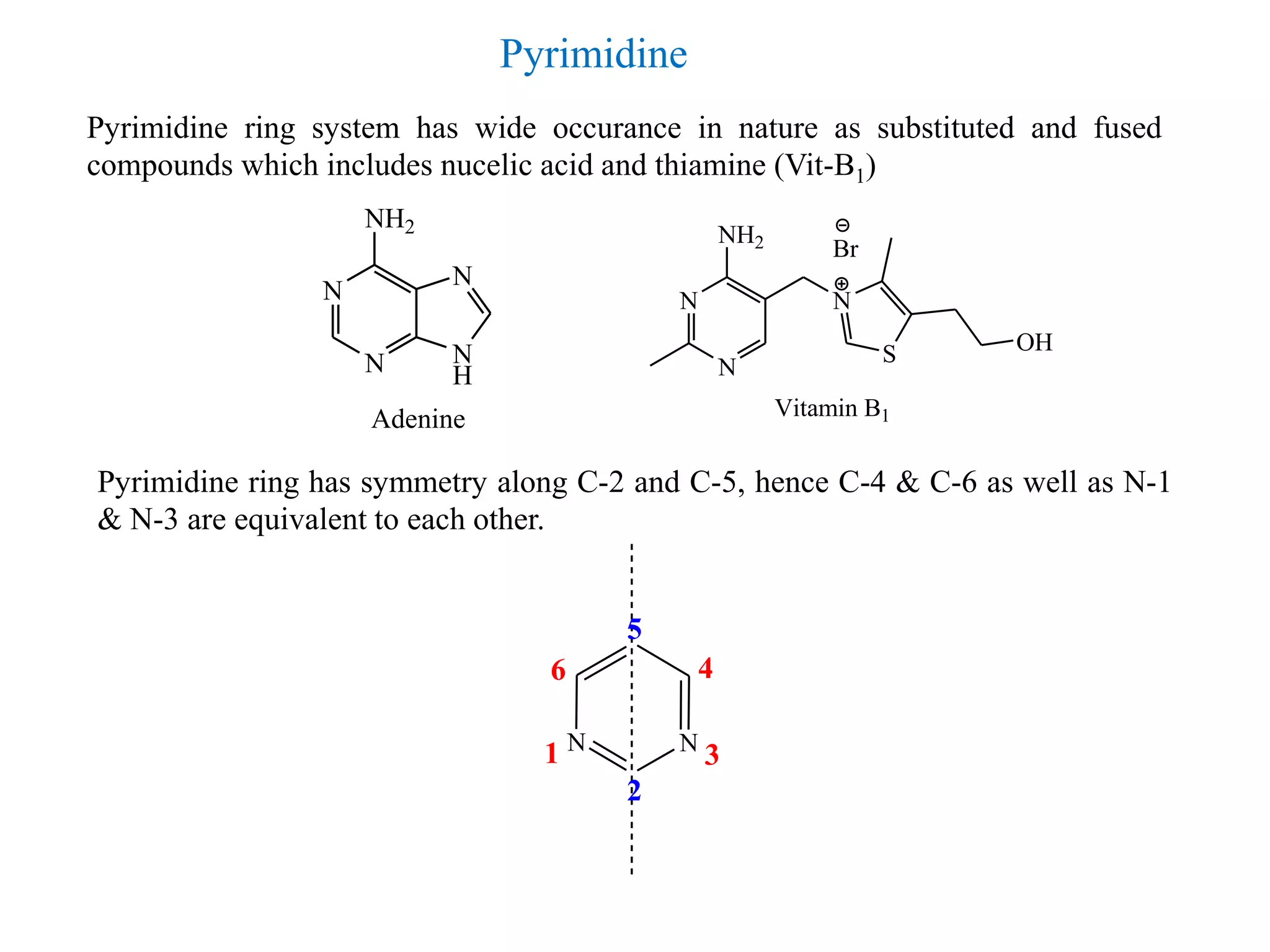
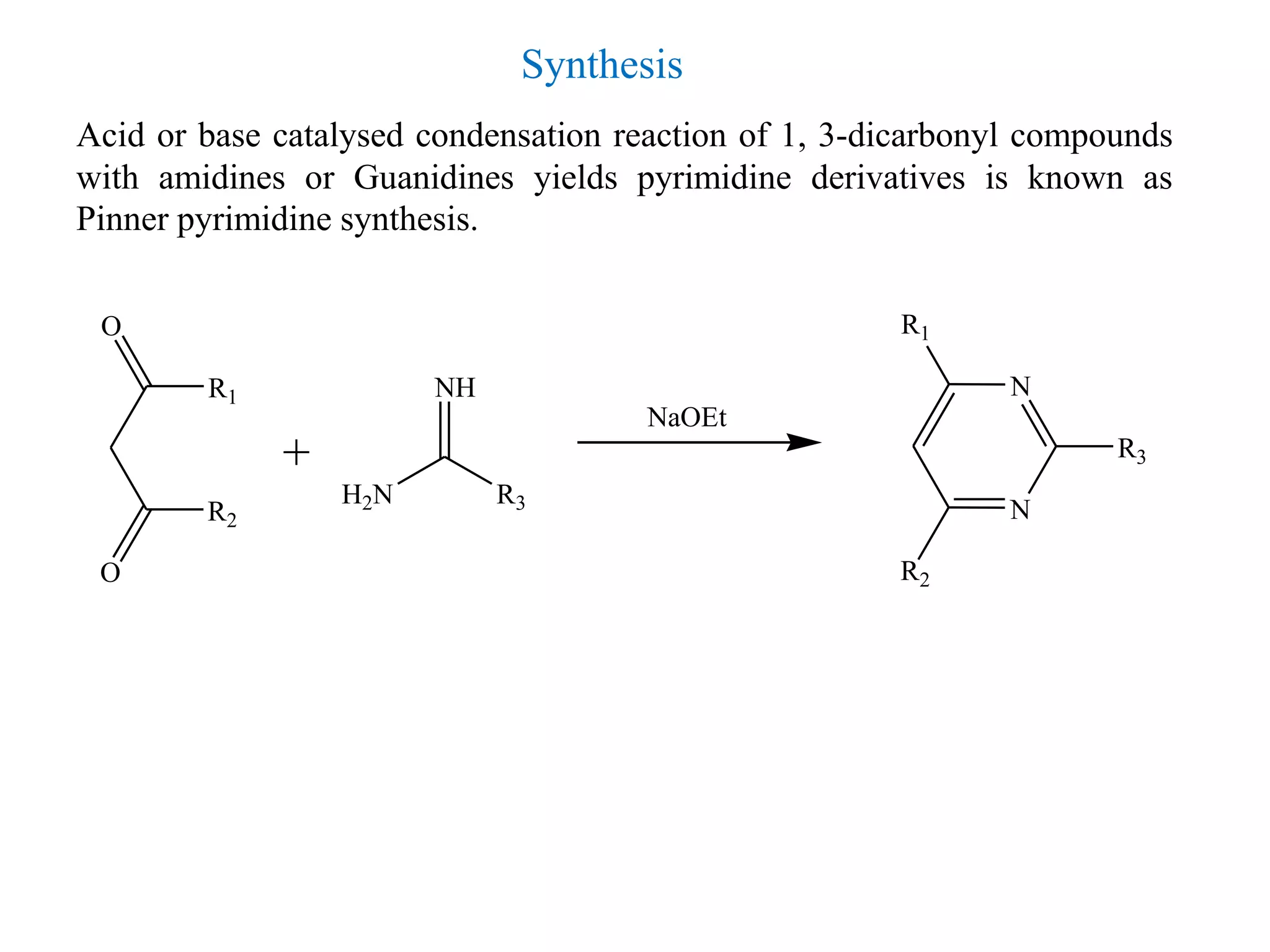
2) Pyrimidine is a diazine where the nitrogen atoms are at the 1,3 positions. It is aromatic in nature and plays an important role in nucleic acids and vitamin B1.
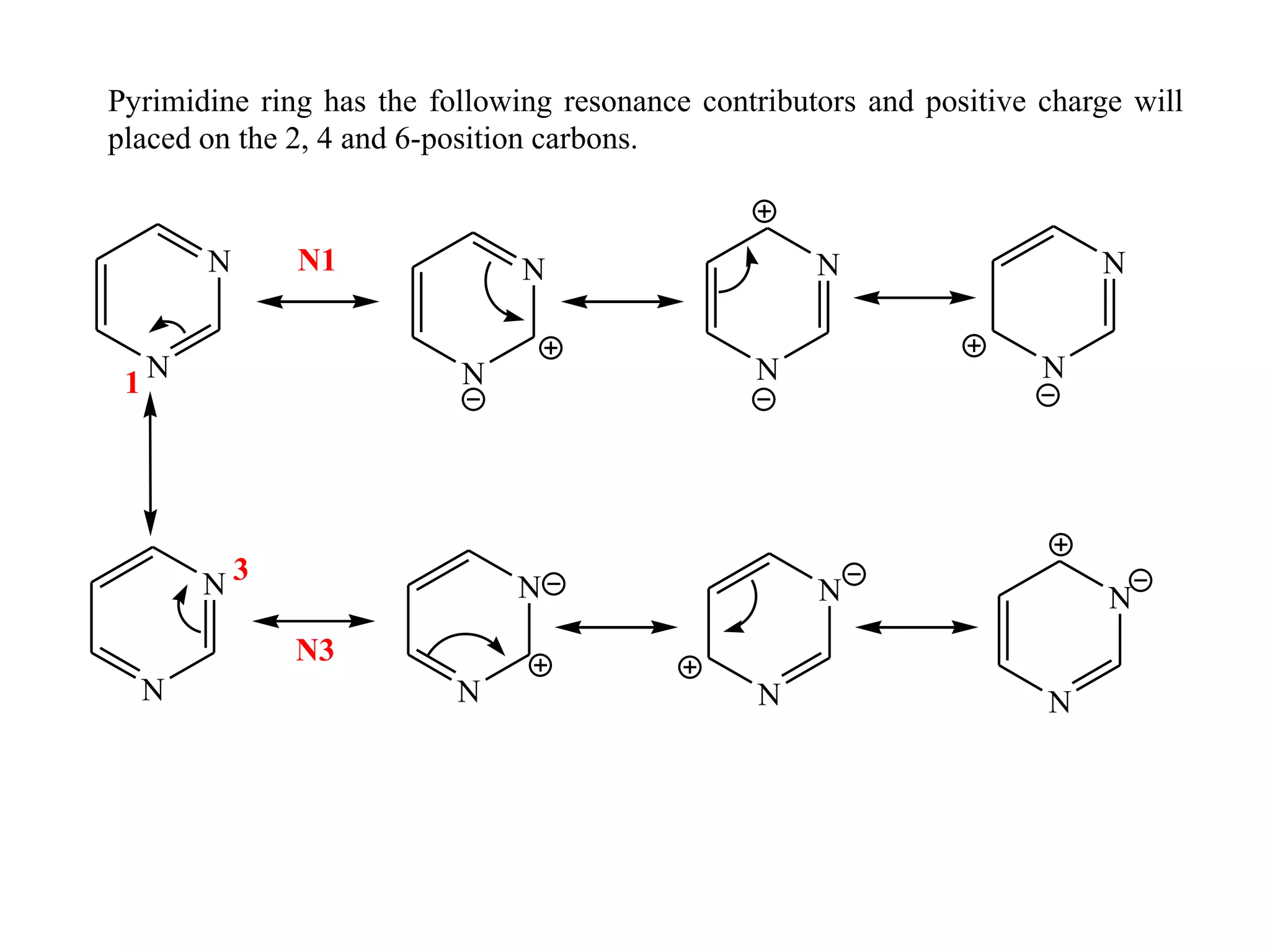
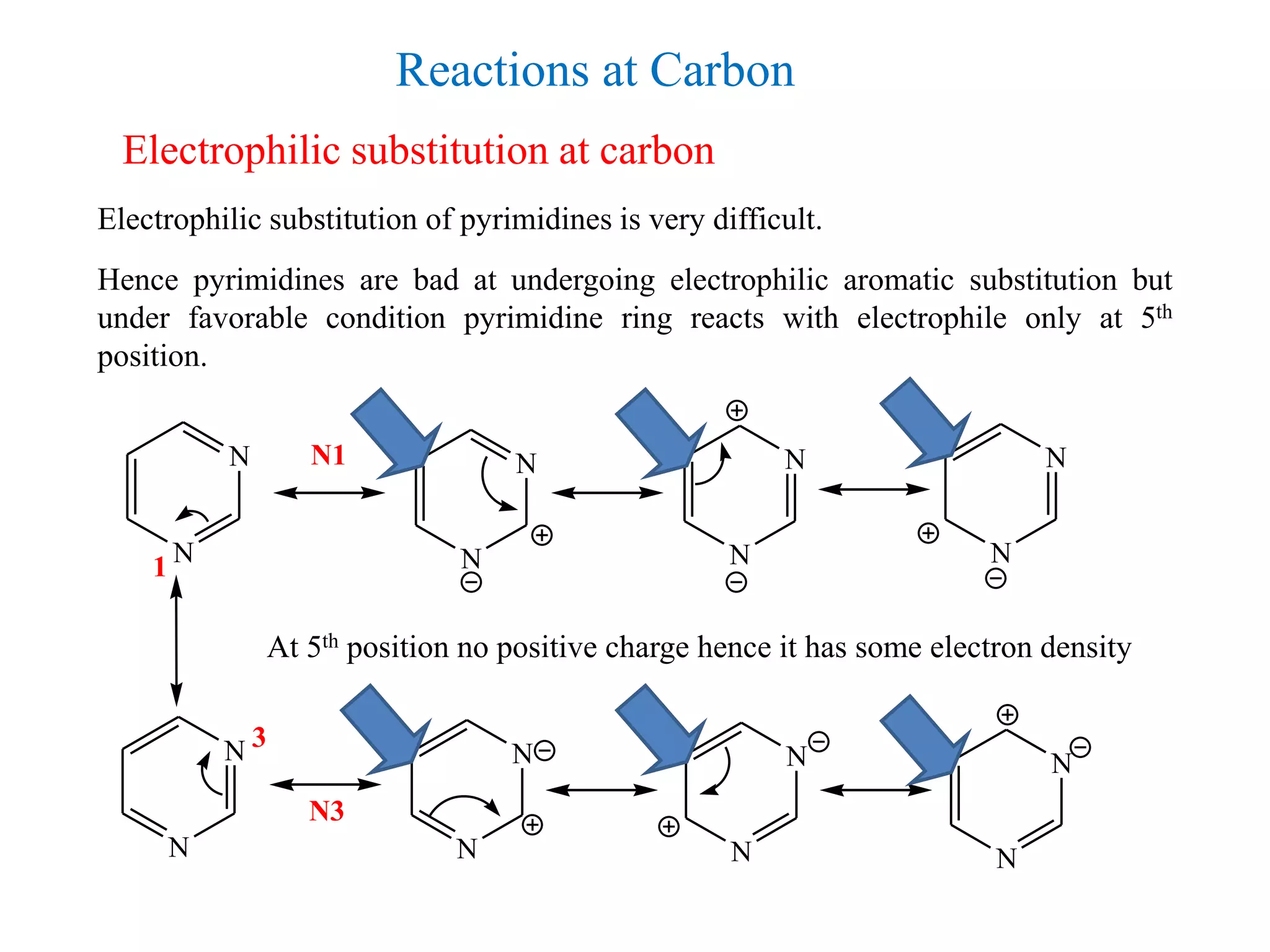
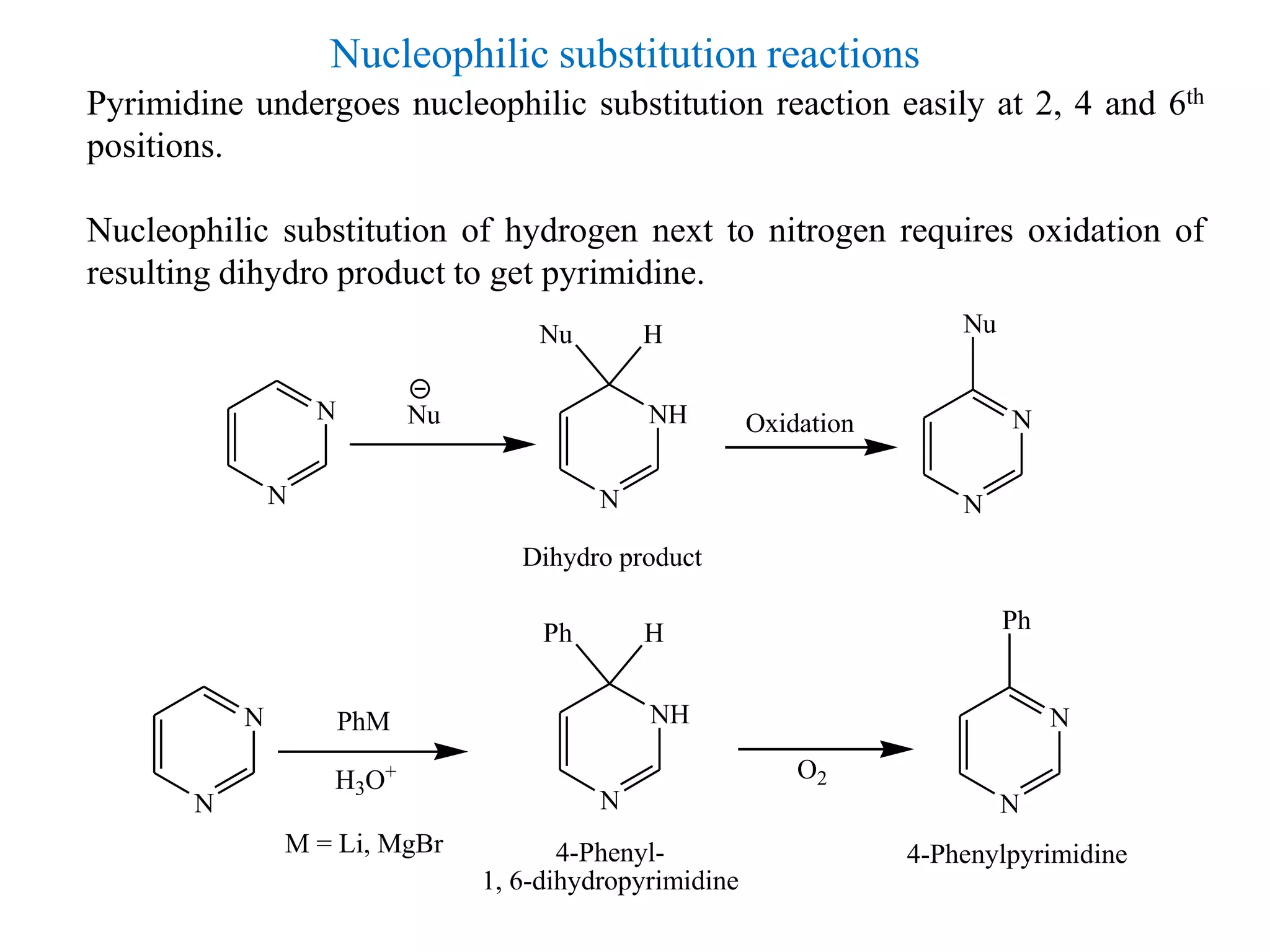
3) Pyrimidines undergo electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions. Electrophilic substitution preferentially occurs at the 5th position while nucleophilic substitution occurs at the 2, 4, and 6th positions.