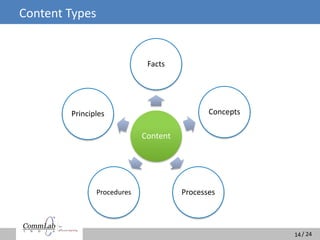
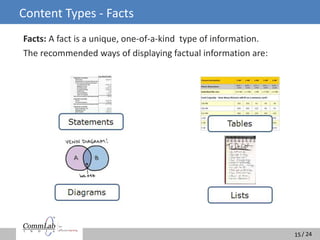
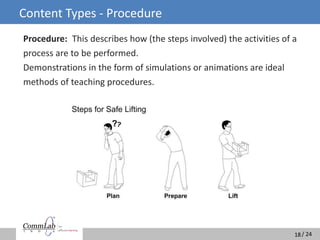
The document discusses the misconceptions surrounding e-learning and emphasizes the importance of designing courses that accommodate adult learning principles, various learning styles, and offer interactivity. It highlights the disconnect between learners' expectations for engaging content and the heavy textual, audio-dominated material often provided. The ideal e-learning solution involves a blend of visual, auditory, and interactive elements to enhance the learning experience and improve retention.