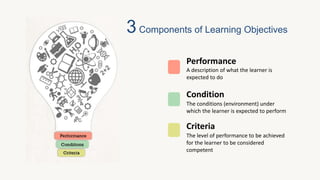
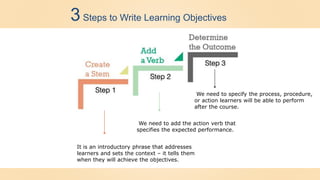
The document discusses learning objectives for training programs. It defines a learning objective, outlines the key components of objectives, and describes Bloom's Taxonomy - a framework for classifying objectives according to cognitive complexity. The document also explains why objectives are important for guiding training development and evaluation, and provides a 3-step process for writing objectives: including a stem, verb, and expected outcome.