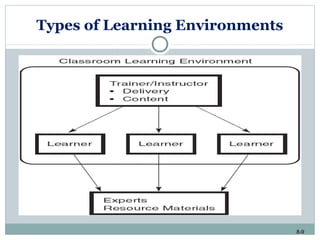
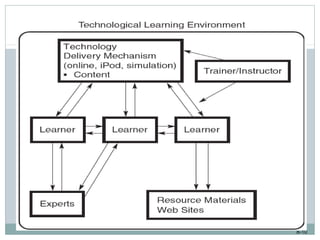
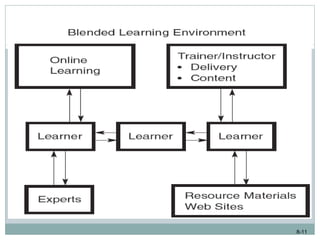
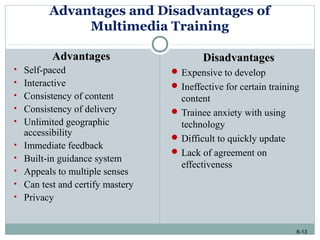
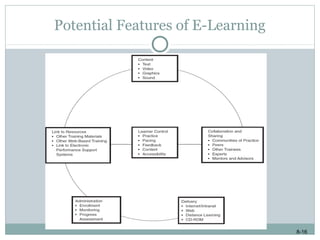
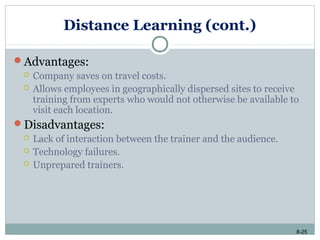
This document discusses e-learning and how new technologies are influencing training. It covers topics like different types of e-learning, distance learning, simulations, and learning management systems. The key benefits of technology in training are that it allows employees to learn anywhere and anytime, reduces costs, and increases the effectiveness of the learning environment. However, factors like high development costs and lack of technical skills can limit the use of e-learning. Overall, the document examines how new technologies are enhancing learning and training delivery methods.