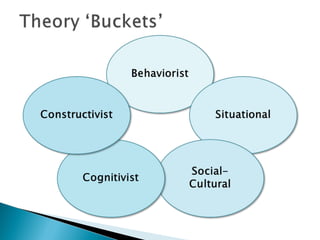
The document provides an overview of learning theories and strategies for applying them in eLearning design. It discusses several major learning theory "buckets": behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and social learning theory. For each bucket, it outlines key characteristics and examples of influential theorists. It then provides strategies for applying each theory through eLearning design elements like feedback mechanisms, contextualization, reflection opportunities, and simulating real-world experiences. The document concludes with scenarios asking how different learning theories could inform the design of eLearning in specific organizational contexts.