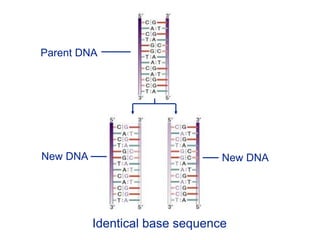
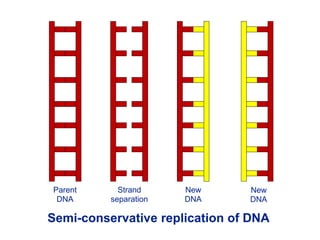
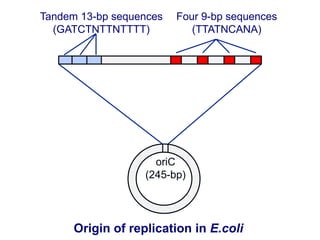
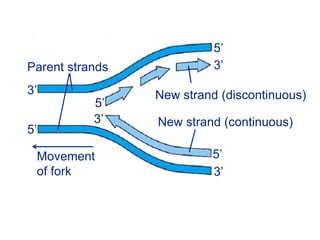
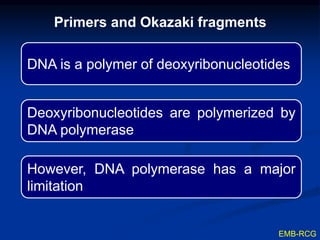
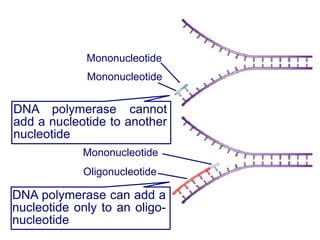
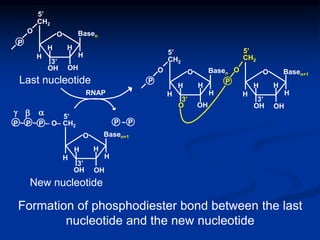
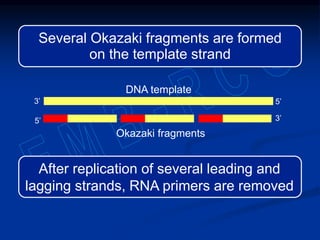
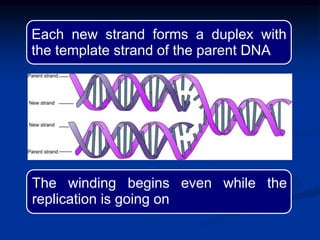
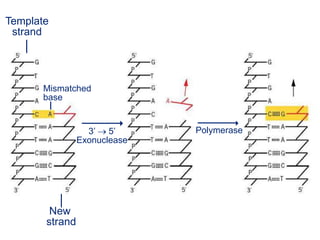
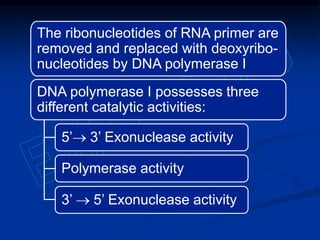
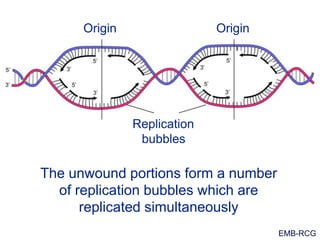
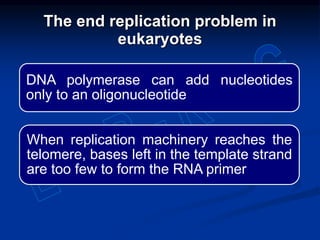
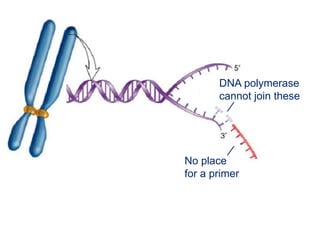
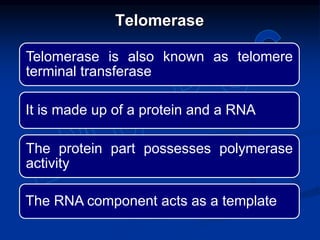
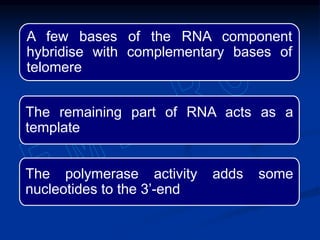
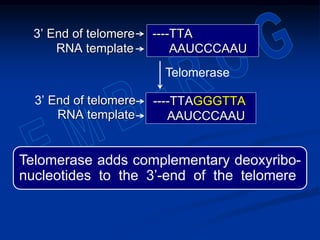
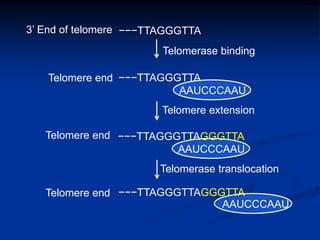
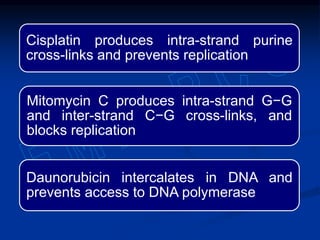
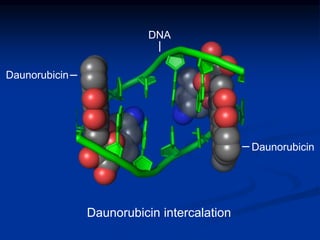
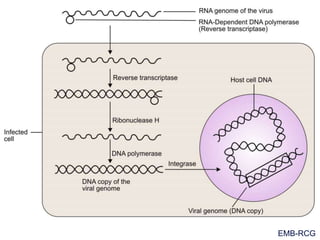
This document summarizes the process of DNA replication. It begins with parent DNA unwinding and separating into two strands. Each strand then serves as a template for new strand synthesis in a semi-conservative manner. In prokaryotes, replication occurs bidirectionally from a single origin of replication. Eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication to allow for simultaneous replication bubbles. The document discusses enzymes involved like DNA polymerases and primase, as well as mechanisms like Okazaki fragment formation and resolution. It concludes by describing the unique process of telomere replication through the reverse transcriptase telomerase to overcome the end-replication problem.