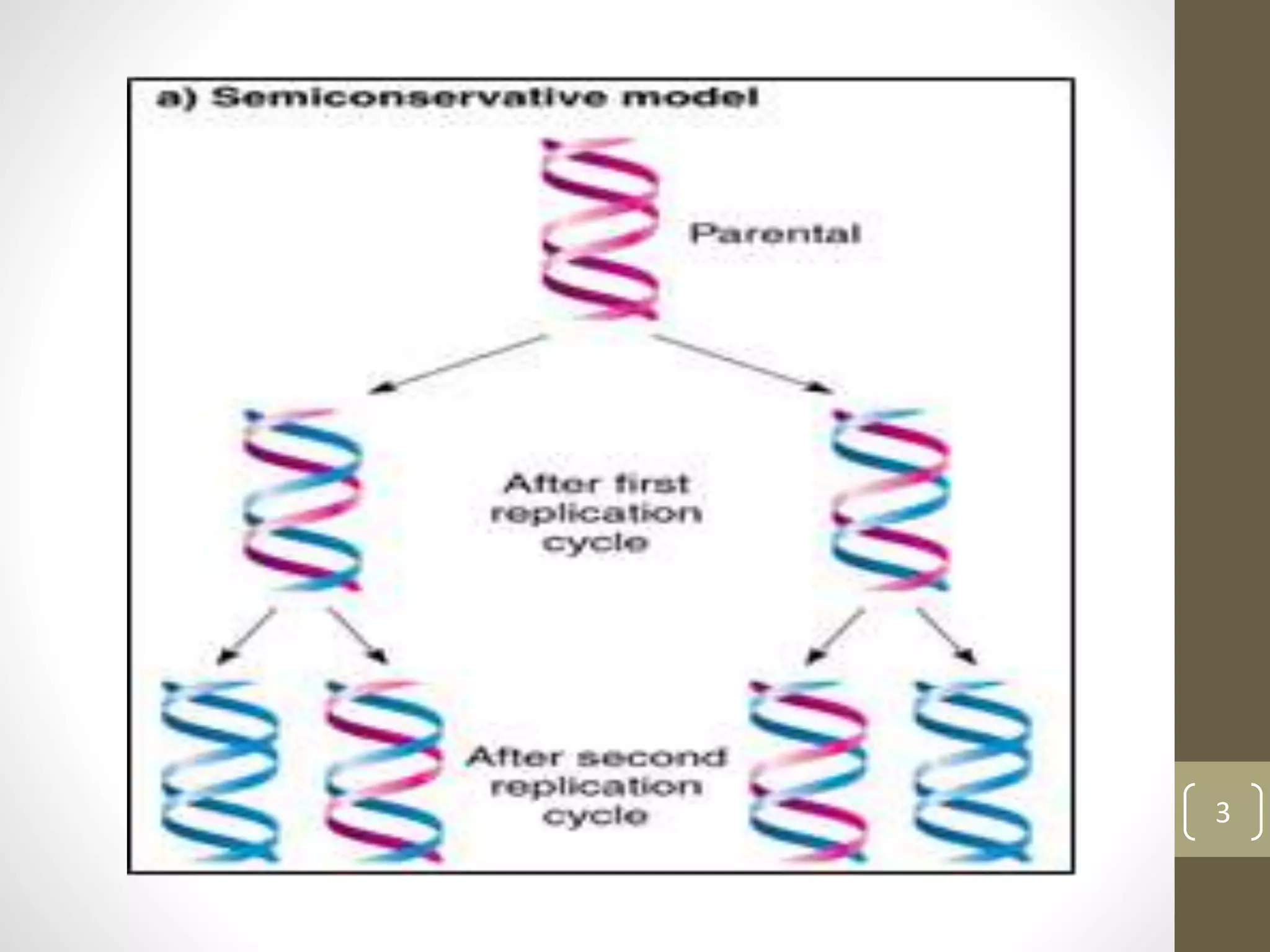
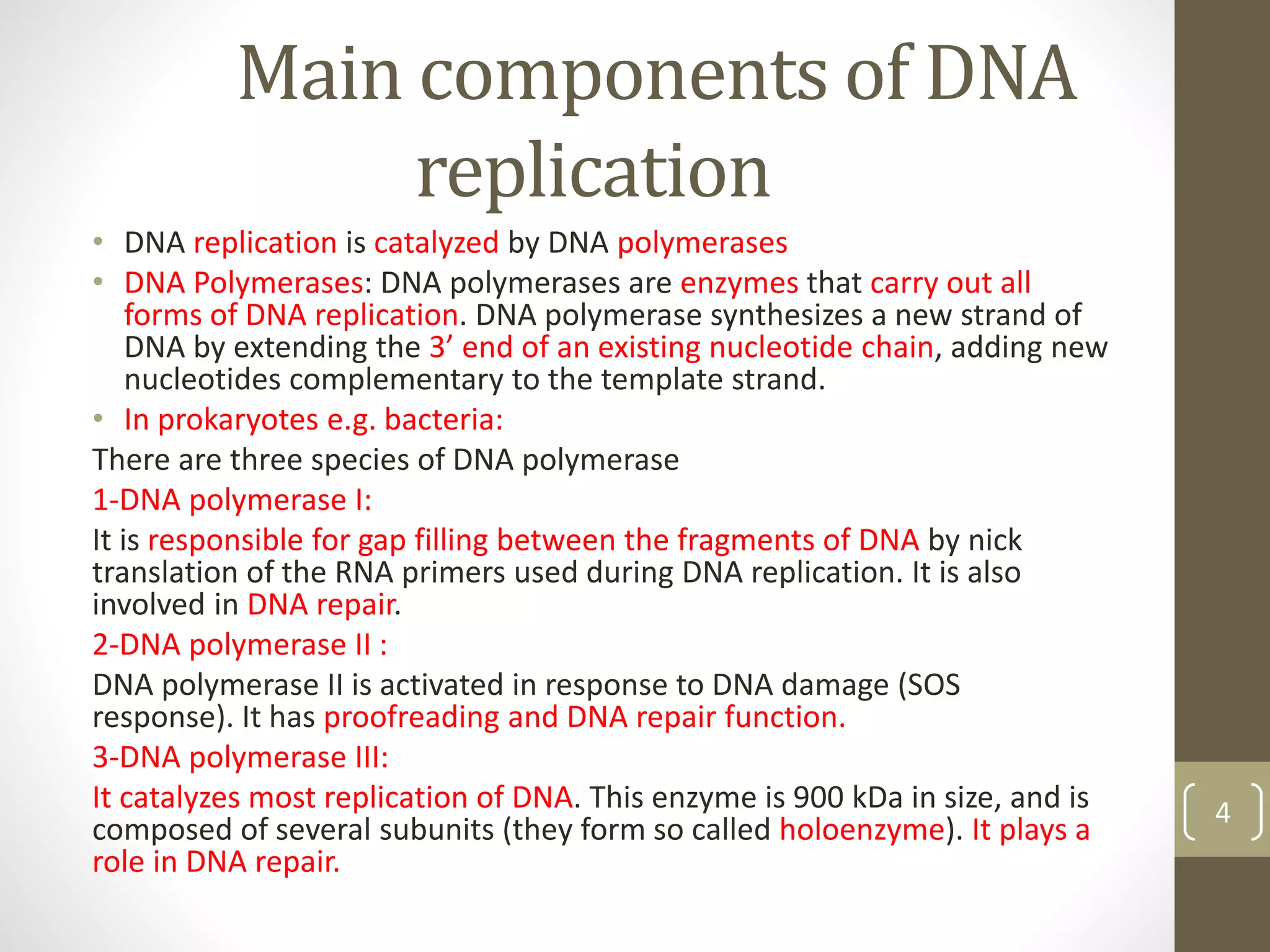
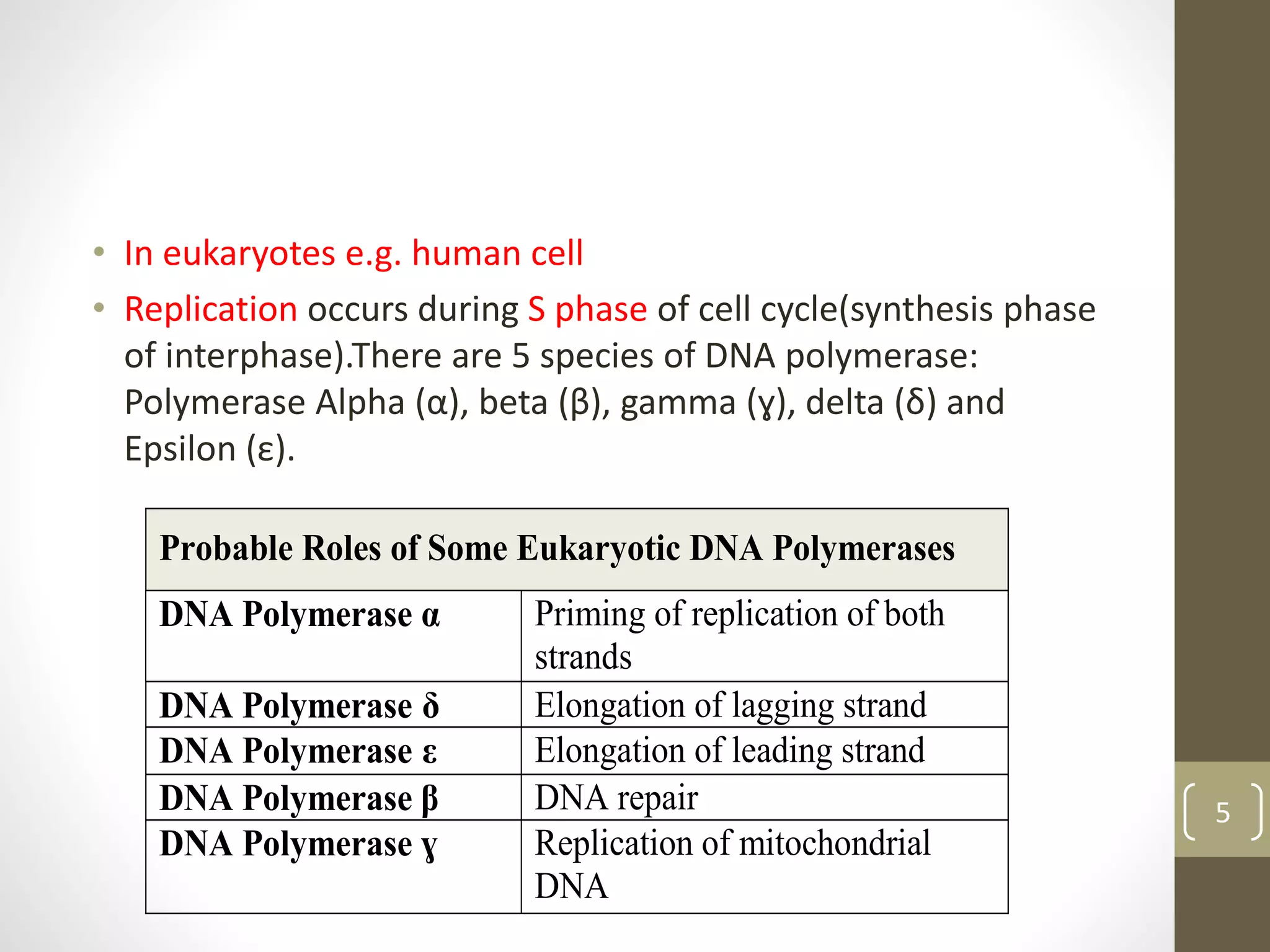
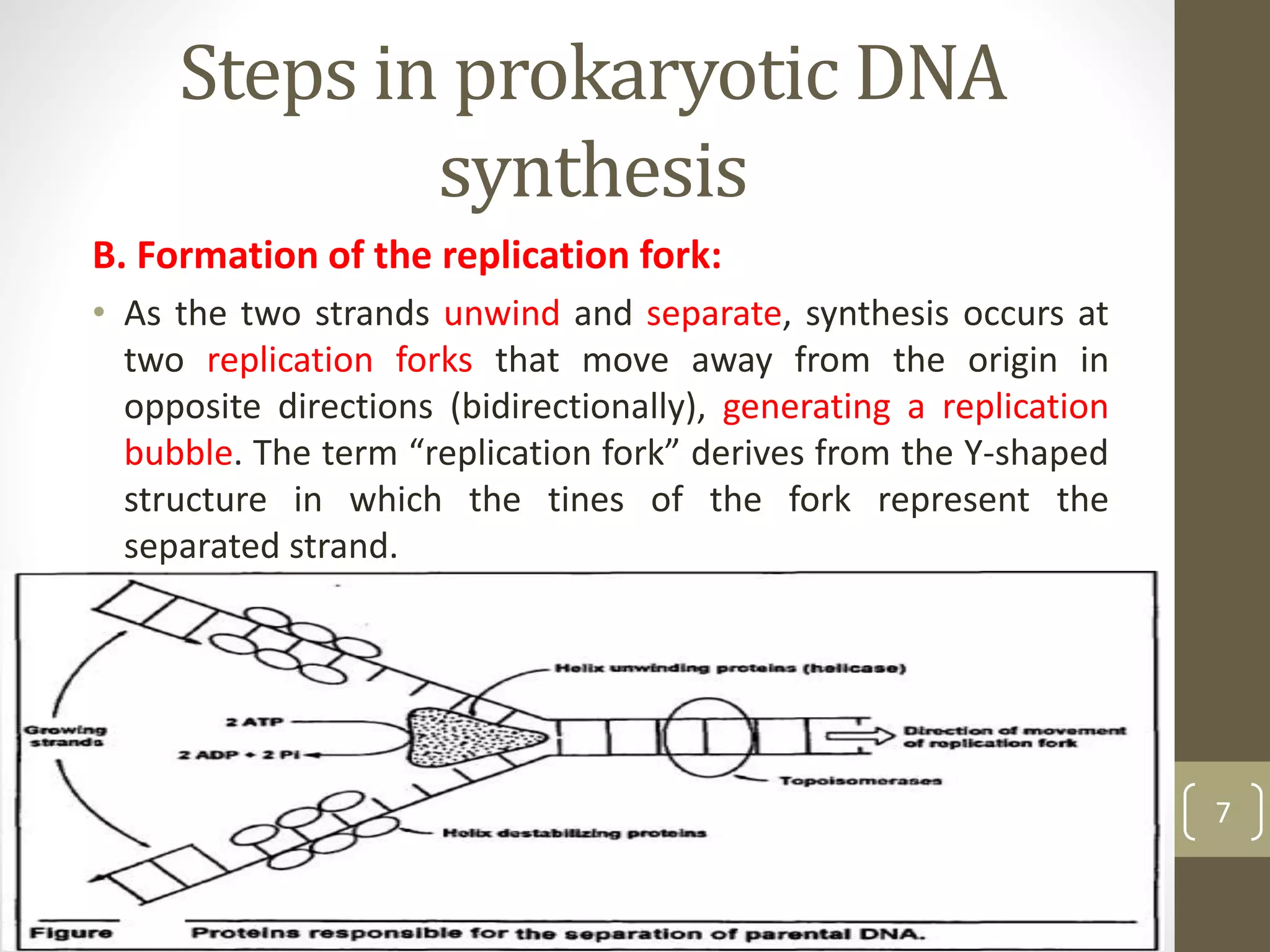
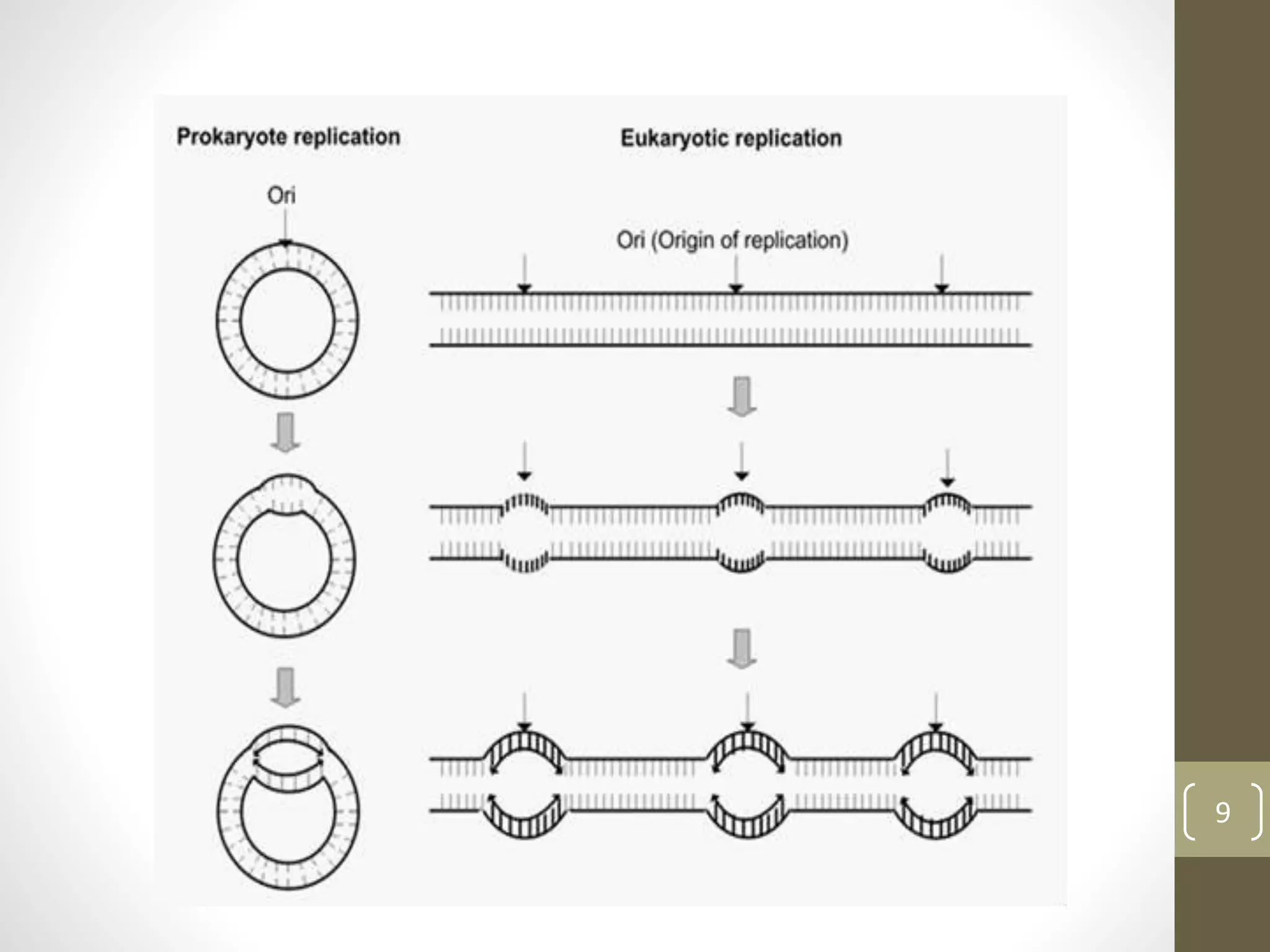
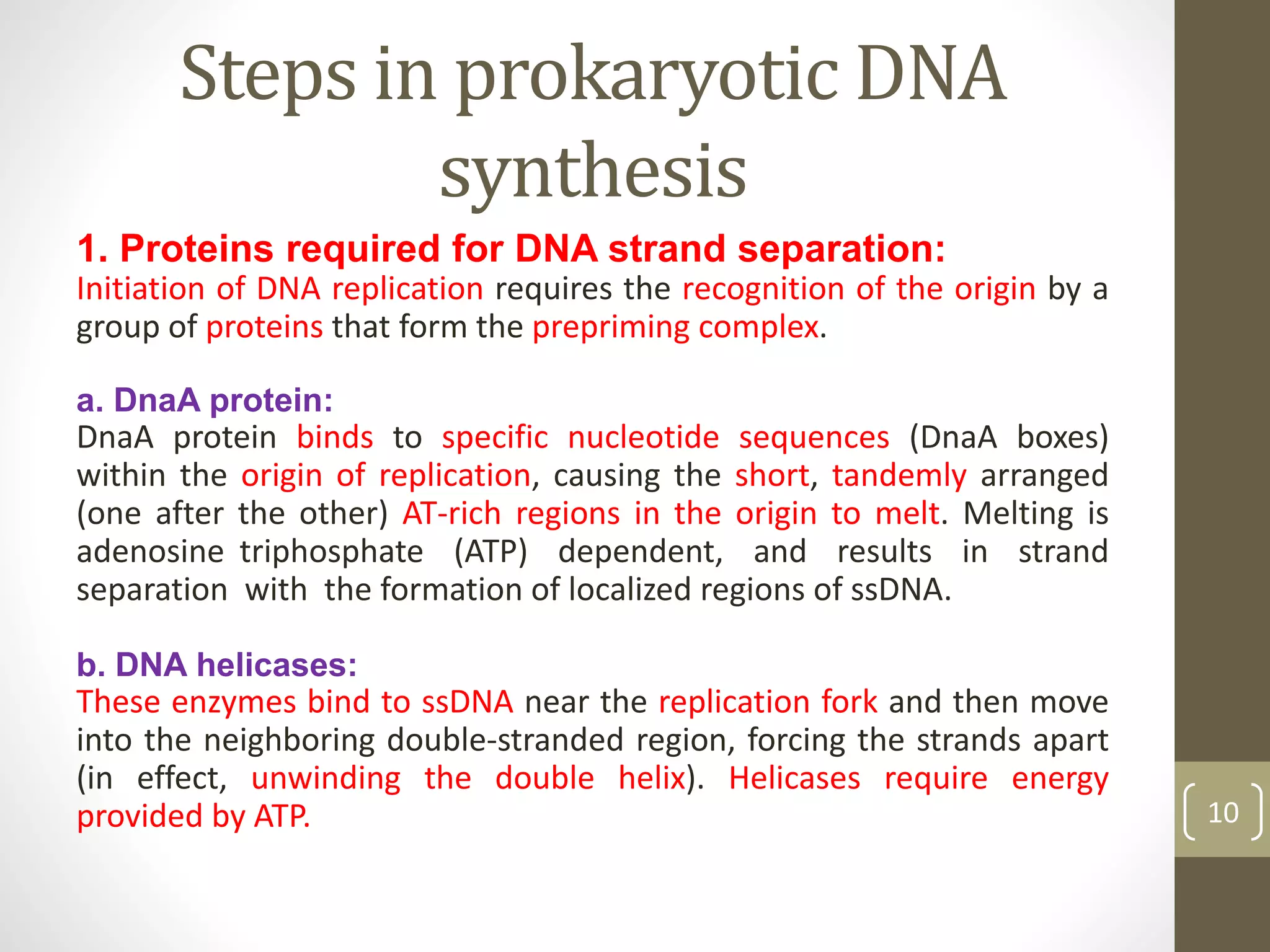
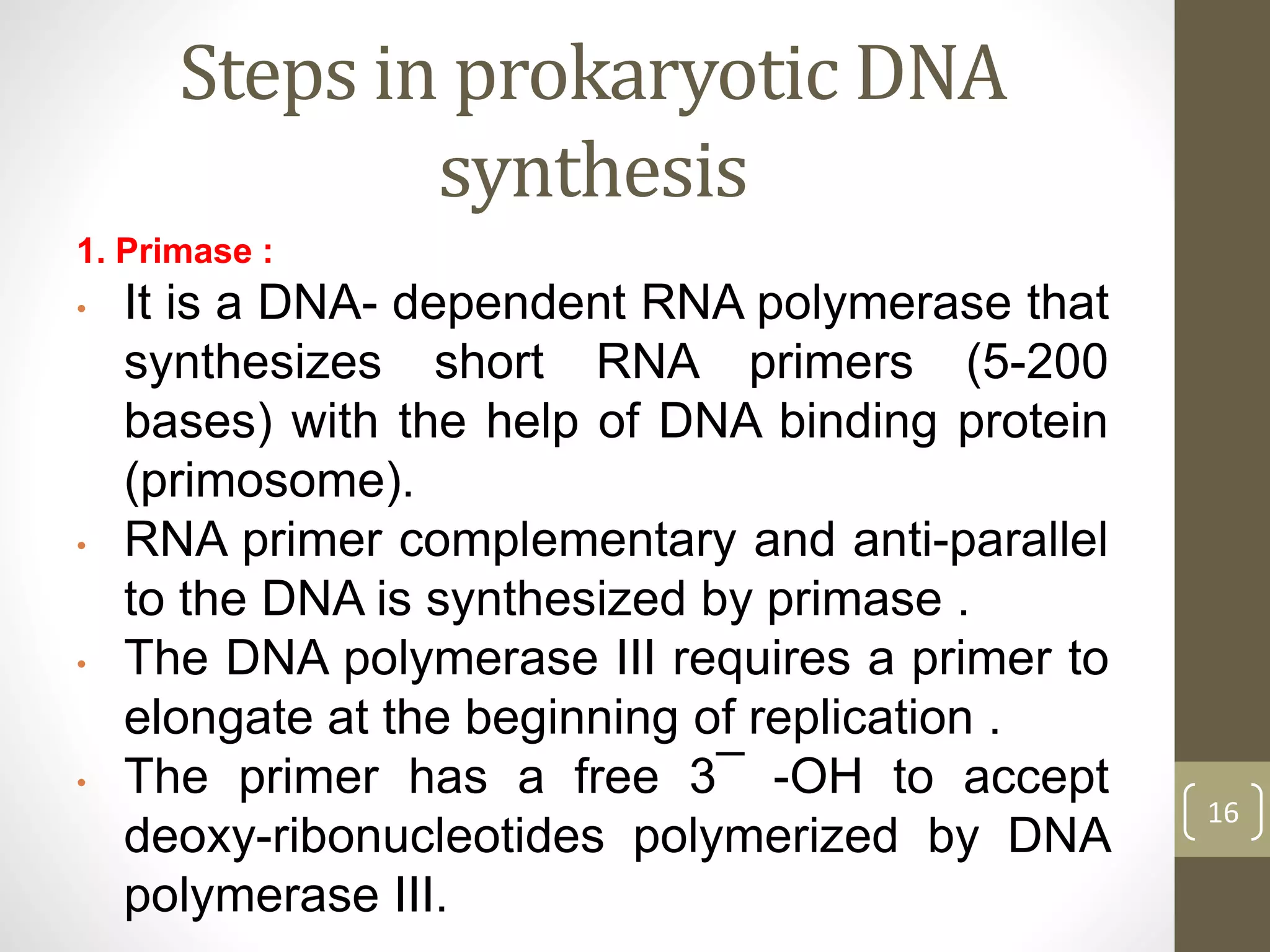
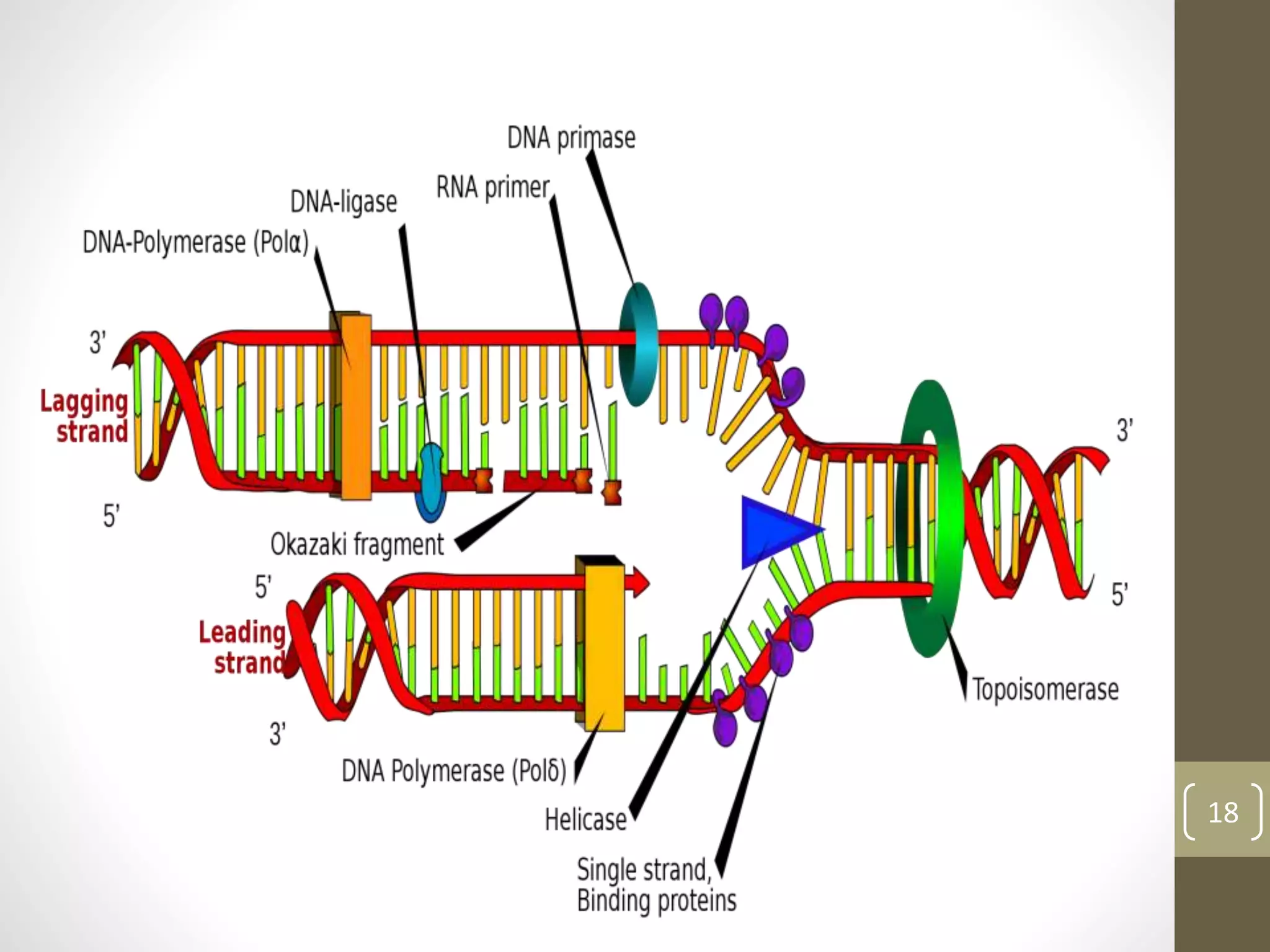
DNA replication involves separating the two strands of the DNA double helix to serve as templates for producing two new DNA molecules. Each new molecule contains one old strand and one newly synthesized strand. This process of semiconservative replication ensures that each cell receives a complete copy of the genome upon division. DNA polymerases are the key enzymes that catalyze DNA replication by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing DNA strand in a 5' to 3' direction. Replication occurs bidirectionally from an origin of replication.