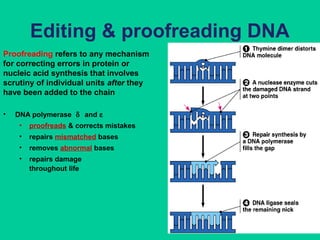
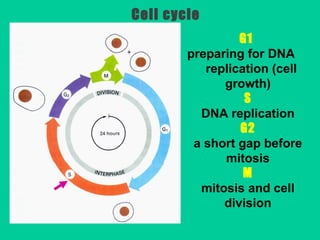
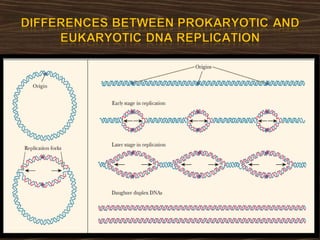
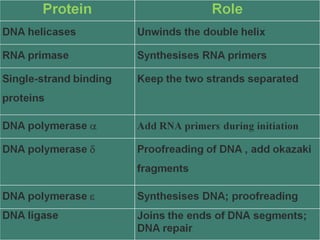
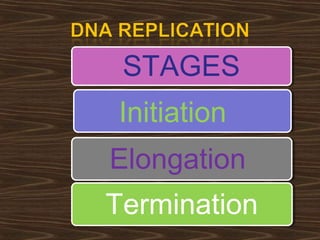
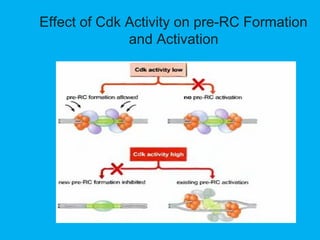
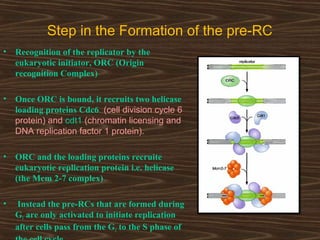
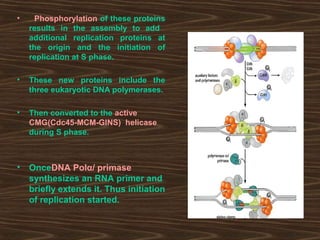
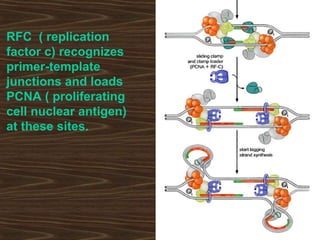
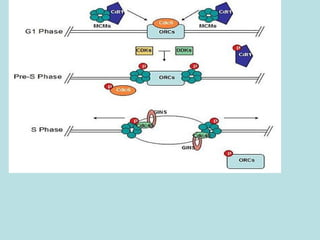
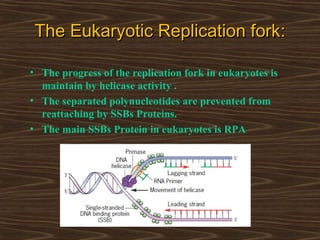
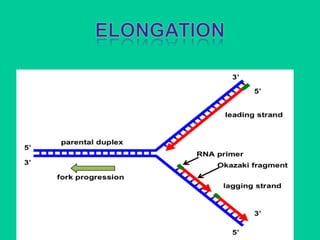
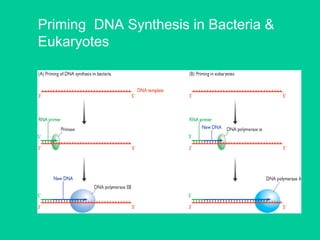
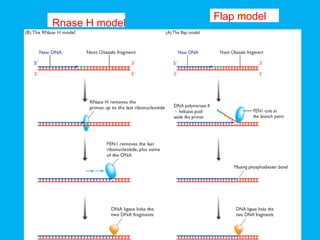
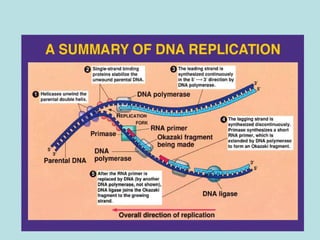
Eukaryotic DNA replication occurs in the cell nucleus and involves multiple protein complexes. It begins with the assembly of pre-replication complexes at origins of replication during G1 phase. During S phase, these complexes are activated by cyclin-dependent kinases and Dbf4-dependent kinases to initiate bidirectional replication forks. Leading strand synthesis is continuous while lagging strand occurs discontinuously in short Okazaki fragments. Replication terminates once the replication forks from opposing origins meet.



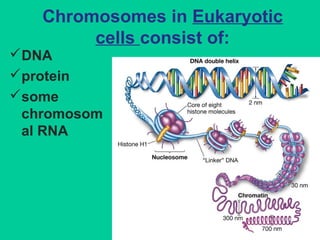


















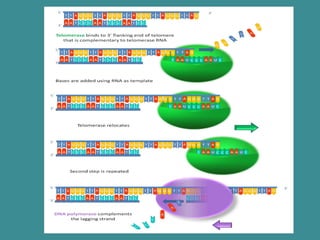




![Telomeric replication
• Telomeres are special nucleoprotein structures composed of double-
stranded (TTAGGG)n DNA repetitive sequence ranging from 3 to 15 kb∼
and a number of telomere associated proteins.
• The ds telomeric DNA terminates at a 3′ single-stranded G-rich
overhang of about 12–500 bases. This protruding 3′ end can invade
the duplex DNA and form a lariat-like structure called ‘t-
loop’.Establishing a protective cap that shields chromosome ends
from being recognized as damaged DNA and prevents nucleolytic
degradation and inappropriate fusions of telomeres.
• The t-loop is stabilized by a complex of ds and ss stranded telomere
binding proteins known as the ‘shelterin’ proteins [TRF1, TRF2]. The
primary role of shelterin is to mark telomeres as the natural
chromosome ends and suppress the DNA damage response pathways
at telomeres](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/015-150927161718-lva1-app6891/85/presentation-on-eukaryotic-dna-replication-47-320.jpg)