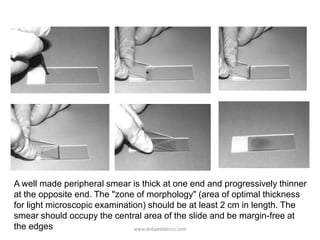
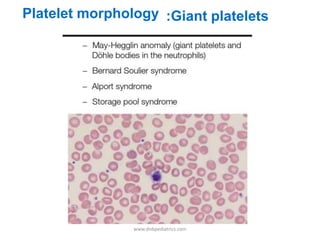
This document provides information about performing and interpreting a peripheral blood smear examination. It discusses how to make a well-prepared smear and the staining process. It then describes the systematic approach to examination, including assessing cellular distribution and quality. The document outlines how to perform white blood cell differential counts and estimates. Finally, it provides detailed descriptions and images of abnormalities seen in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that may indicate various hematological conditions.