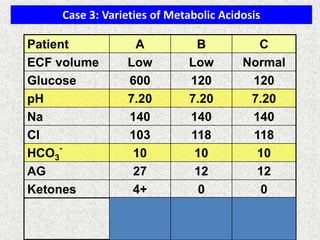
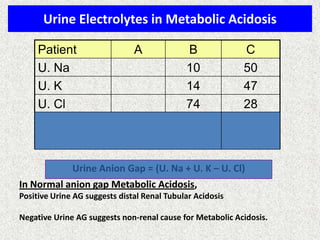
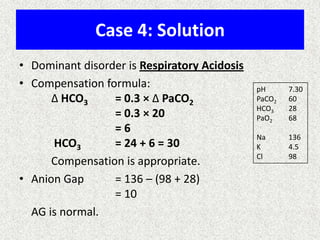
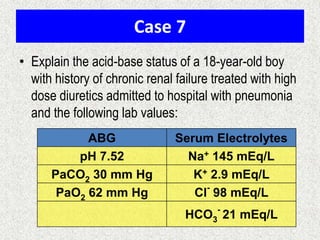
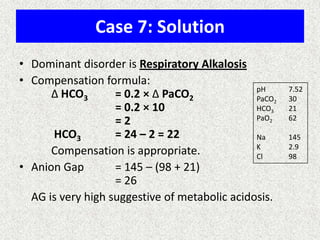
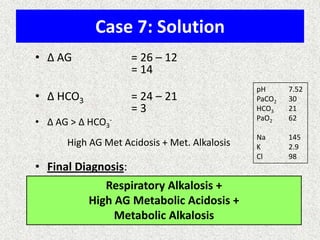
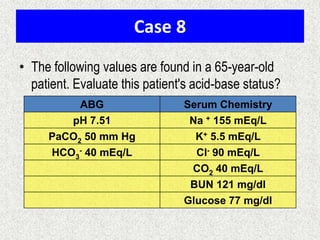
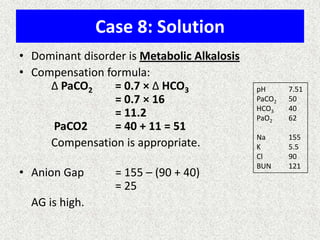
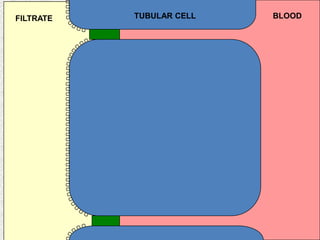
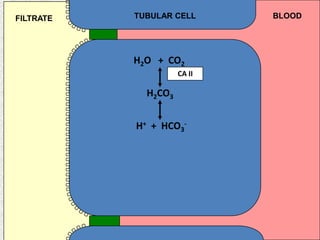
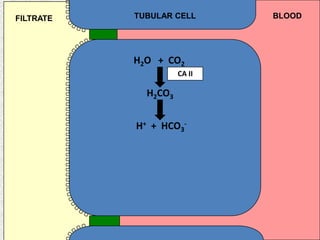
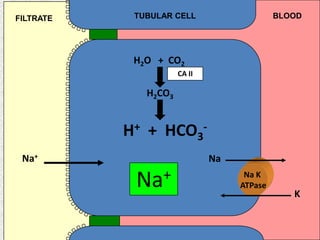
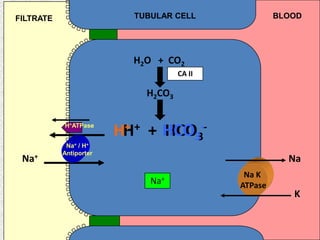
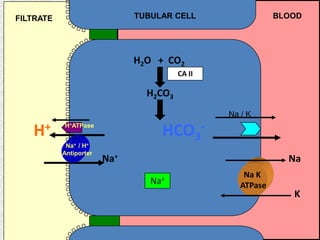
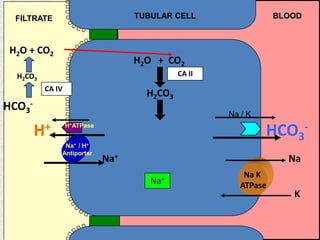
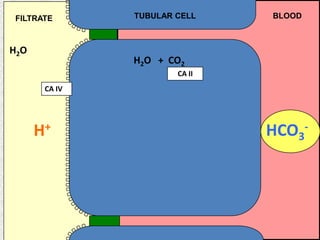
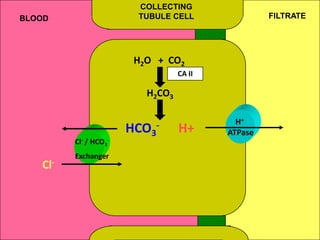
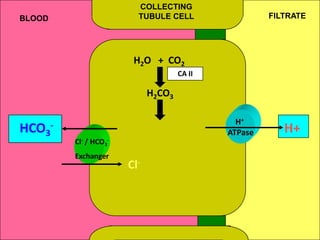
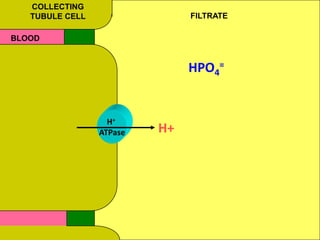
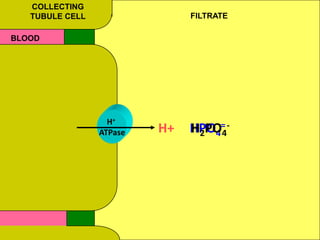
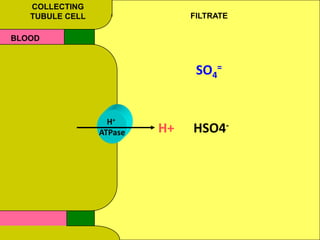
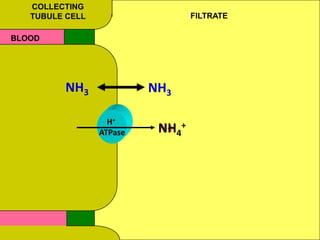
The document discusses acid-base regulation by the kidney. It does this through three main processes: 1) reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate in the proximal tubule, 2) secretion of hydrogen ions into the filtrate in the distal tubule, and 3) use of urinary buffers. It then provides detailed diagrams and explanations of the transport mechanisms involved in bicarbonate and hydrogen ion regulation throughout the renal tubular system. These include carbonic anhydrase, sodium-hydrogen antiporters, and the role of the collecting duct in final acid-base adjustments.




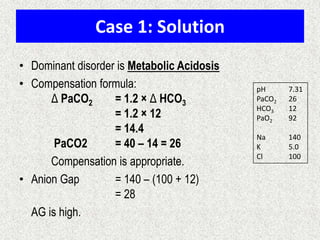
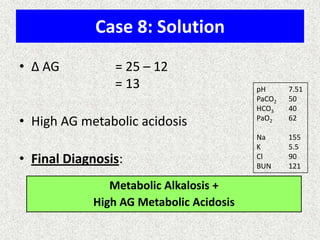
![Calculation of compensation
Mean "whole body" response equations for simple acid-base disturbances.
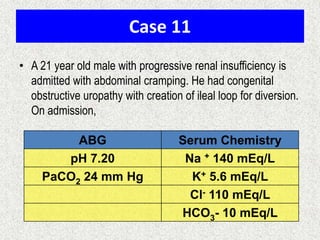
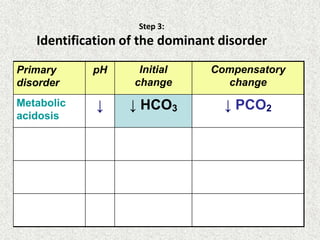
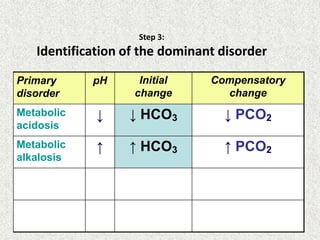
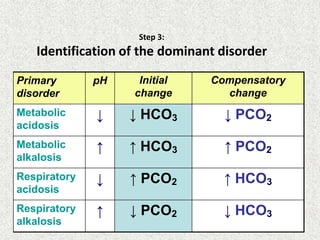
Disorder
pH
Primary
change
Compensatory
Response
Equation
Metabolic
Acidosis
[HCO3-]
PCO2
ΔPCO2 1.2 ΔHCO3
Metabolic
Alkalosis
[HCO3-]
PCO2
ΔPCO2 0.7 ΔHCO3
Respiratory
Acidosis
PCO2
[HCO3-]
Acute:
ΔHCO3- 0.1 ΔPCO2
Chronic:
ΔHCO3- 0.3 ΔPCO2
Respiratory
Alkalosis
PCO2
[HCO3-]
Acute:
ΔHCO3- 0.2 ΔPCO2
Chronic:
ΔHCO3- 0.5 ΔPCO2
Note: The formula calculates the change in the compensatory parameter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140306133952-phpapp02/85/Presentation1-23-320.jpg)
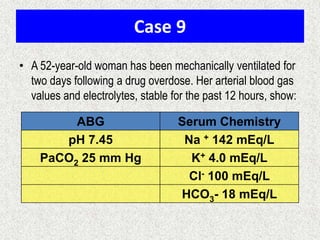
![Simple compensation
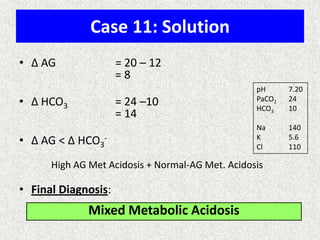
Disorder
pH
Primary problem
Compensation
Metabolic acidosis
↓
↓ in HCO3-
PaCO2
=1.5xHCO3+8(+/-2)
Metabolic alkalosis
↑
10↑ in HCO3-
7↑ in PaCO2
Respiratory acidosis
↓
ACUTE -10↑ in PaCO2
CHRONIC -10↑ in PaCO2
1↑ in [HCO3-]
3.5↑ in [HCO3-]
Respiratory alkalosis
↑
ACUTE-10↓ in PaCO2
CHRONIC-10↓ in PaCO2
2↓ in [HCO3-]
4↓ in [HCO3-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140306133952-phpapp02/85/Presentation1-24-320.jpg)
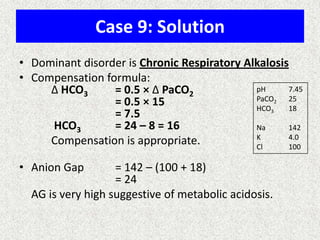
![Calculate the “gaps”
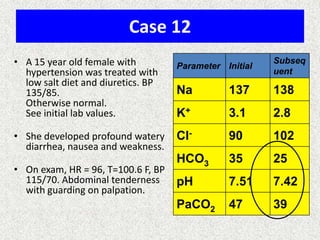
Anion gap
=
Na+ − [Cl− + HCO3−]
Δ AG
=
Anion gap − 12
Δ HCO3
=
24 − HCO3
Δ AG = Δ HCO3 −, then Pure high AG Met. Acidosis
Δ AG > Δ HCO3 −, then High AG Met Acidosis + Met. Alkalosis
Δ AG < Δ HCO3 −, then High AG Met Acidosis + Normal AG Met A
Note:
Add Δ AG to measured HCO3− to obtain bicarbonate level Delta _ AG
Pr e _ existing _ Bicarb
that would have existed IF the high AG metabolic acidosis
Current _ Bicarb
were to be absent, i.e., “Pre-existing Bicarbonate.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140306133952-phpapp02/85/Presentation1-25-320.jpg)

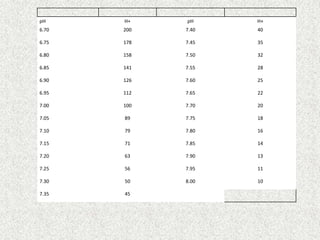
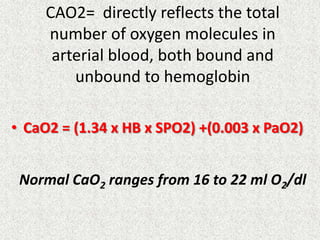
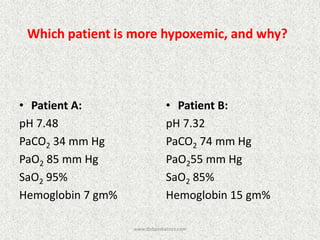





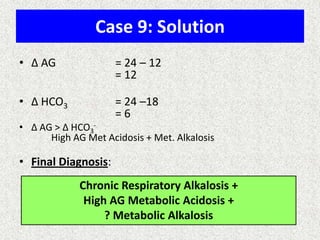
![A-a Gradient
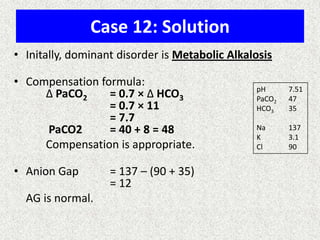
• [(713*FIO2)-(PaCO2/0.8)] – PaO2
INTERPRETATION
NORMAL – 10-20
(>30 is SINGNIFICANT)
Seen in – Shunt
Low V/Q
Hypoventilation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140306133952-phpapp02/85/Presentation1-36-320.jpg)

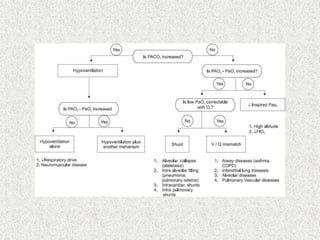





![RELATION OF ALBUMIN IN ABG
AG corrected = AG + 2.5[4 – albumin]
(AG= Anion gap)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140306133952-phpapp02/85/Presentation1-44-320.jpg)