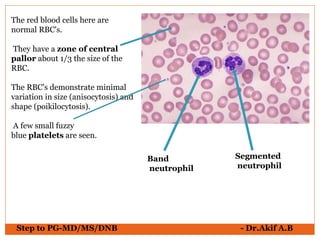
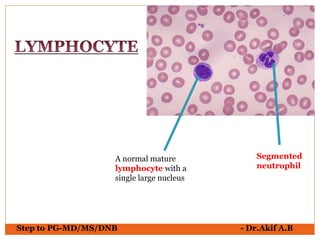
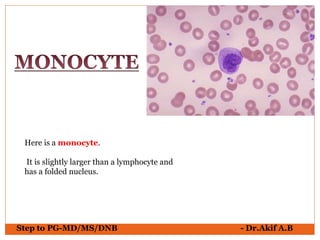
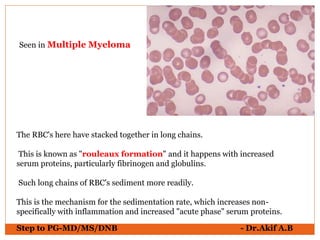
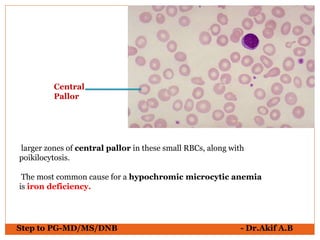
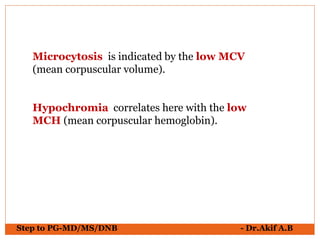
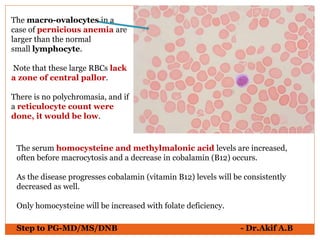
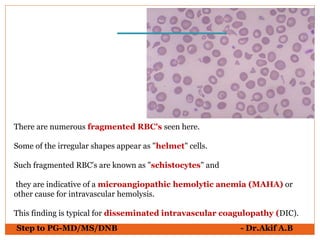
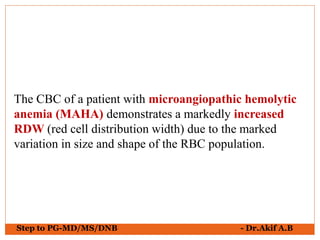
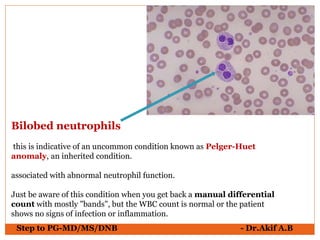
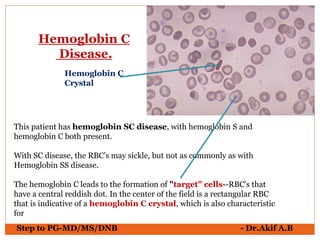
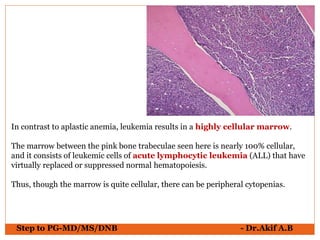
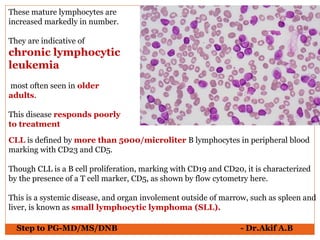
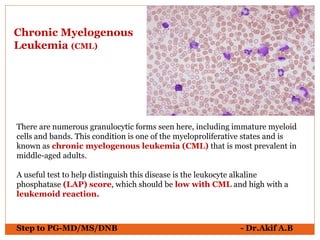
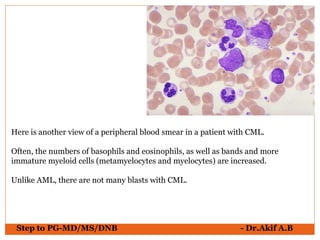
The document provides an overview of various hematological conditions, using peripheral blood smear analysis to illustrate key diagnostic features such as normal and abnormal red blood cell morphology, types of anemia, and the presence of specific white blood cells. It discusses conditions like sickle cell anemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and aplastic anemia, detailing their characteristics and clinical implications. Additionally, it highlights findings relevant to specific diseases, such as hypersegmented neutrophils in megaloblastic anemia and basophilic stippling in lead poisoning.