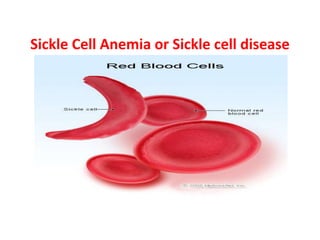
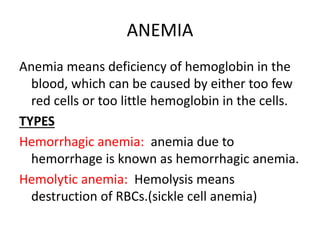
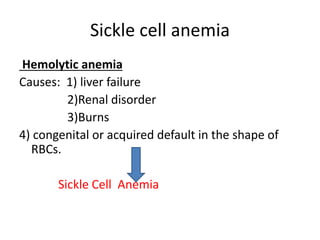
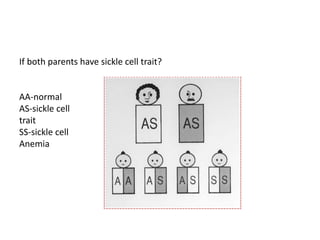
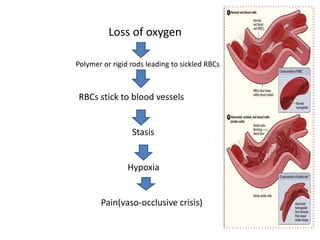
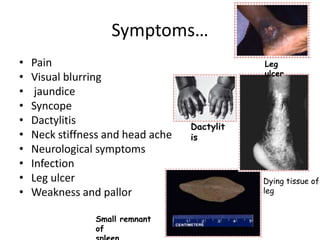
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary blood disorder caused by a genetic mutation that results in abnormal hemoglobin and sickle-shaped red blood cells. It affects approximately 90,000-100,000 people in the United States, primarily those of African descent. Symptoms include episodes of severe pain, organ damage, infections, and stroke due to sickled cells blocking blood flow. While there is no cure, treatment focuses on pain management, blood transfusions, medications, and in some cases stem cell transplants or gene therapy.