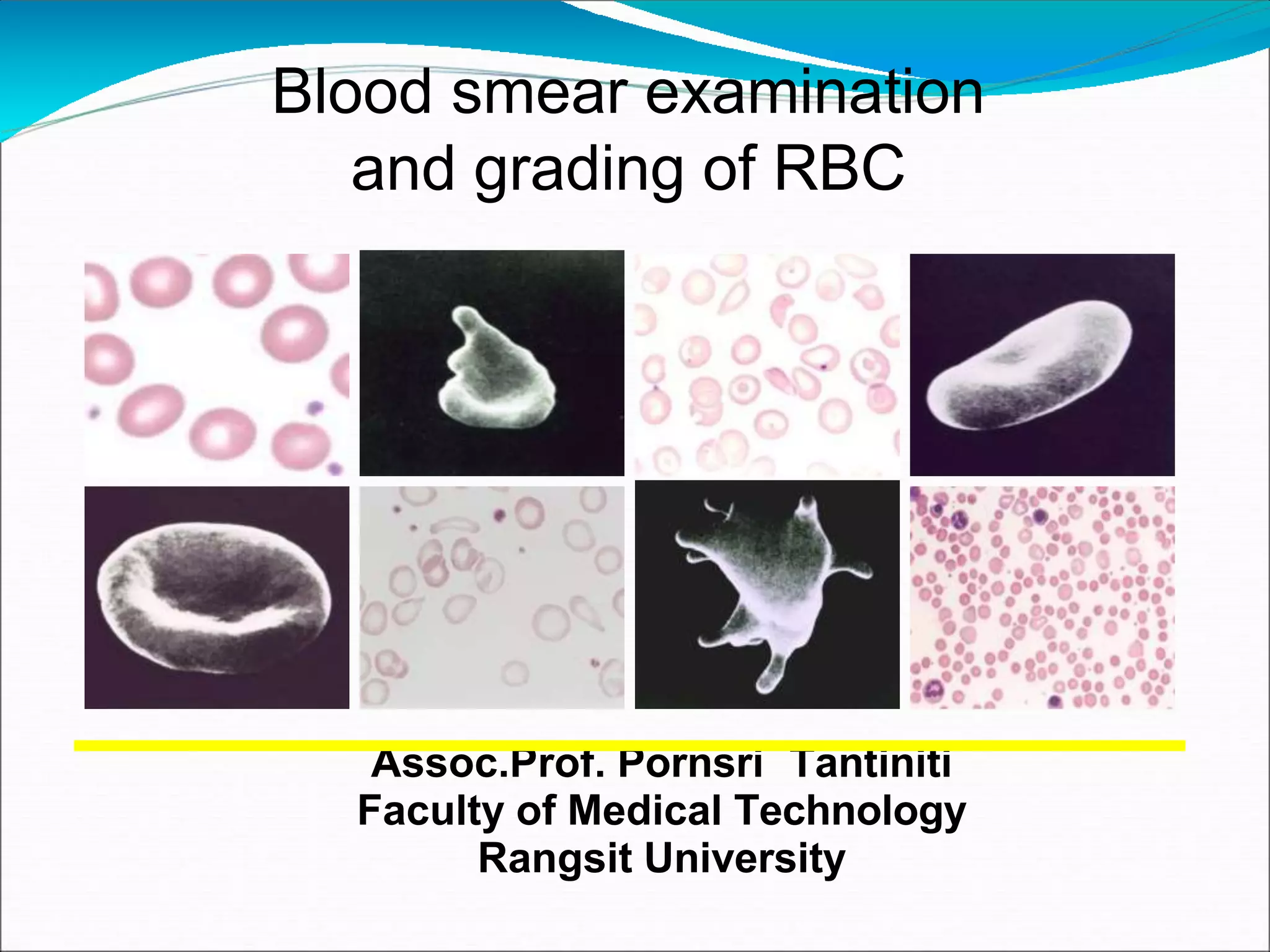
This document provides information on examining blood smears and grading abnormal red blood cells. It discusses red blood cell terminology and variations in size, shape, staining and inclusions. It describes different abnormal red blood cell morphologies including anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, hypochromia, polychromasia, and inclusions. Grading of abnormalities from few to 4+ is explained. Specific red blood cell changes seen in various hematological conditions are mentioned. Guidelines for examining blood smears under different microscope objectives and estimating white blood cell counts and platelets are provided. Key references on the topic are listed at the end.