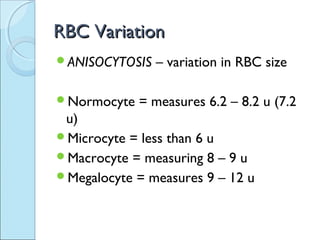
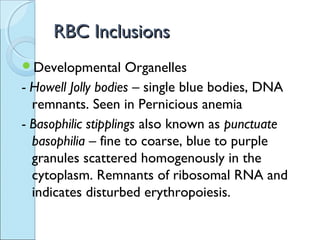
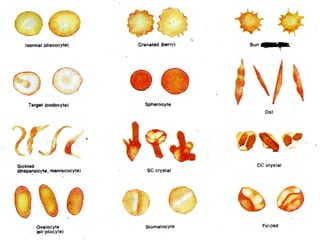
This document discusses red blood cell variation and pathology. It describes different types of red blood cell size variations including microcytes, normocytes and macrocytes. Variations in red blood cell color such as normochromic, hypochromic and hyperchromic cells are also outlined. Various abnormal red blood cell shapes caused by membrane abnormalities or trauma, including spherocytes, echinocytes and schistocytes, are defined. The document also lists intracellular inclusions and parasites that can be found within red blood cells.