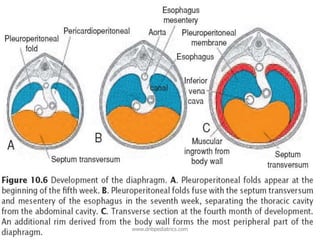
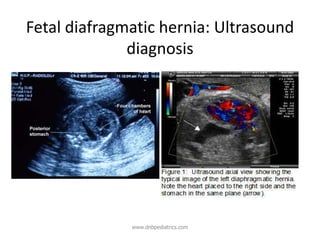
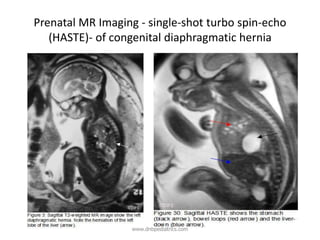
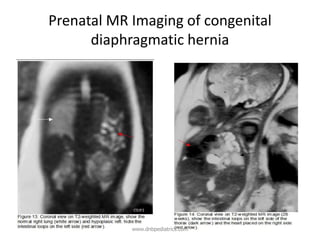
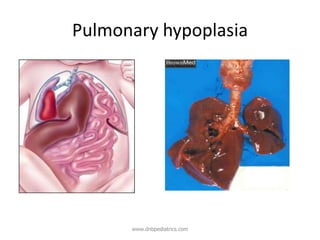
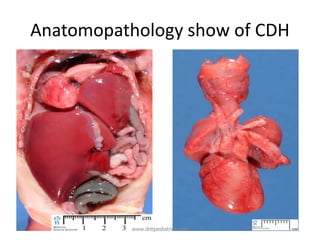
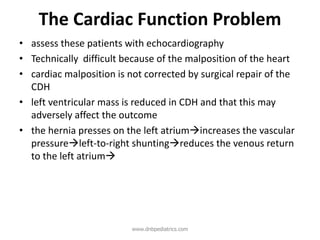
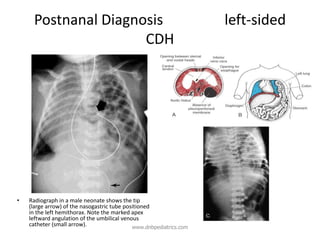
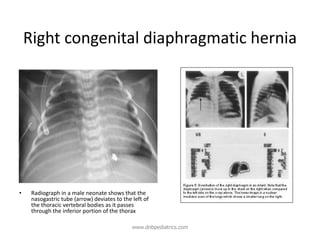
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect where the diaphragm fails to fully form, allowing abdominal organs to migrate into the chest cavity and compress the lungs during development. CDH occurs in approximately 1 in 2,000-5,000 live births. Prenatal ultrasound can detect CDH and allow for prenatal counseling. After birth, infants require immediate respiratory support, surgery to repair the diaphragmatic defect, and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. While survival has improved, CDH infants still face risks of chronic lung disease and long-term developmental issues. The prognosis depends on the severity of pulmonary hypoplasia assessed by measures like blood gas levels and ventilator