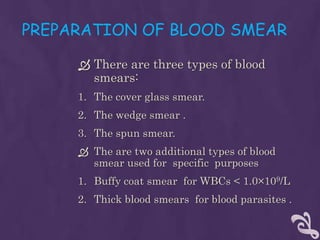
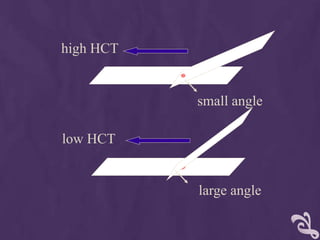
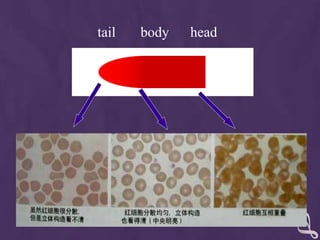
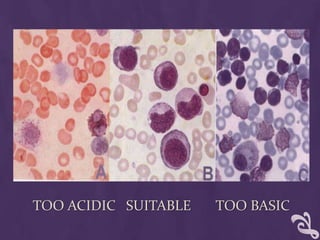
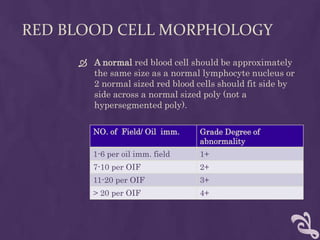
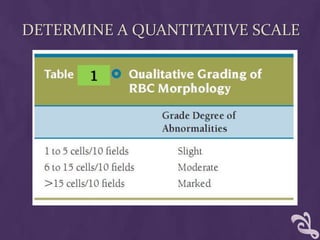
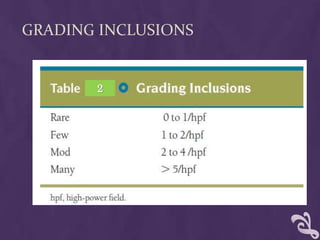
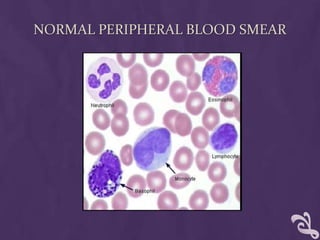
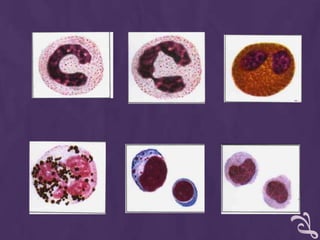
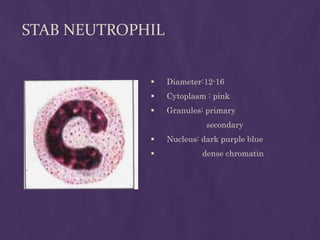
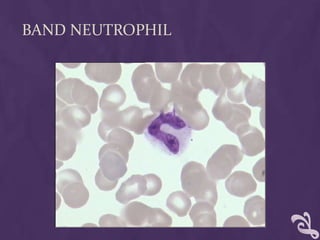
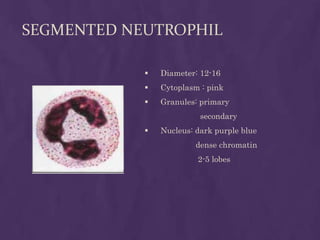
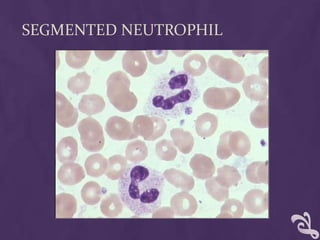
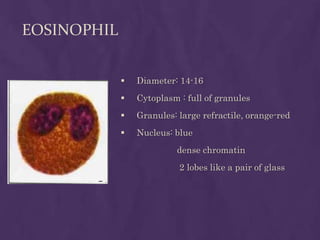
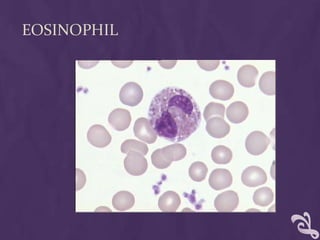
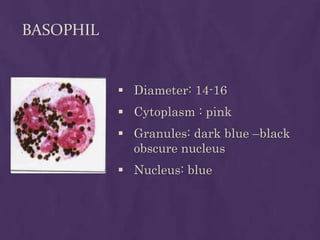
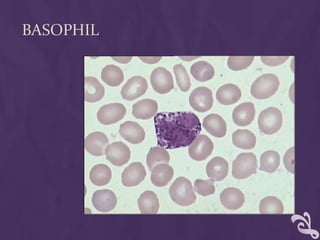
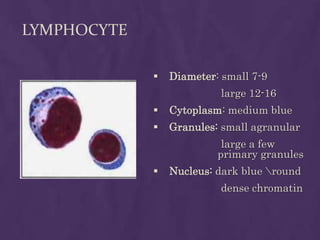
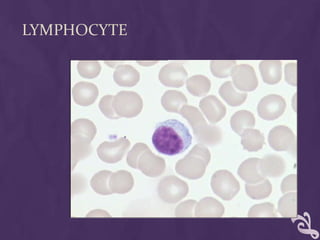
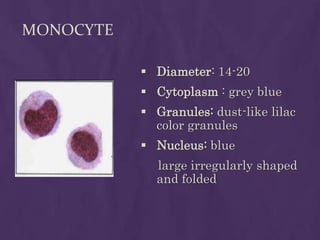
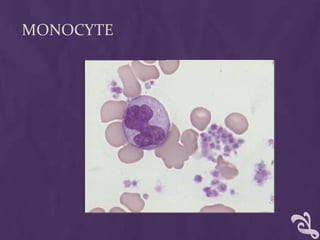
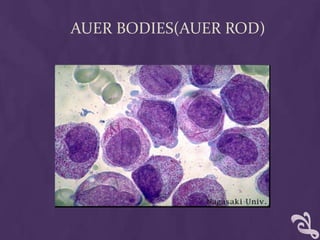
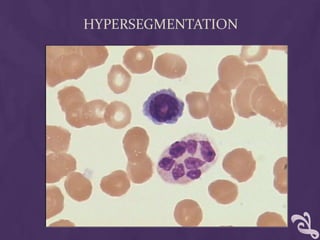
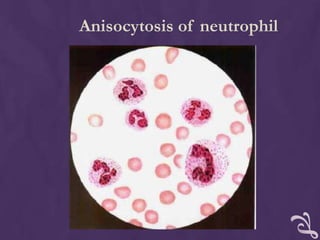
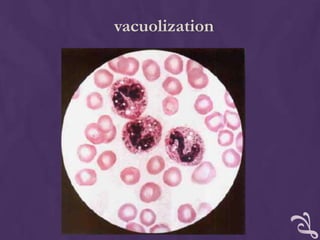
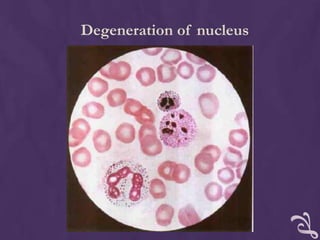
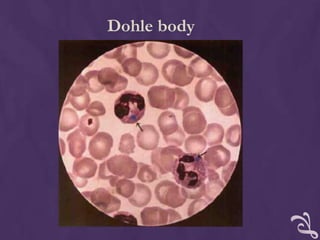
This document provides information about performing a peripheral blood smear examination, including the different types of blood smears, proper procedures for making blood smears, characteristics of a good smear, common causes of a poor smear, staining techniques, performing a manual differential count and assessing red blood cell morphology. Key steps include making wedge or spun smears from EDTA blood, allowing the smear to air dry before staining with Leishman's stain, examining under 10x, 40x and 100x magnification to perform white blood cell counts and differentials, and platelet and red blood cell morphology assessments. Causes of abnormal smears and signs of abnormal white blood cell morphology are also outlined.