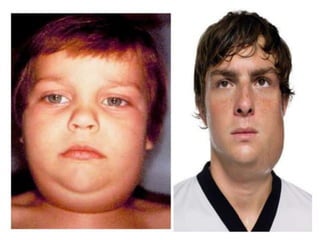
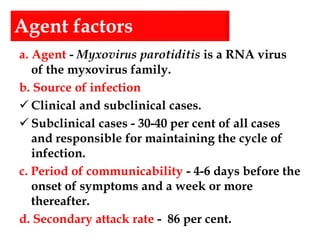
Mumps is an acute infectious disease caused by the Myxovirus parotiditis, characterized by swelling of the parotid glands. Transmission occurs via droplet infection or direct contact, with a communicability period of 4-6 days before symptoms appear. Prevention includes vaccination with live attenuated strains, and complications can involve various organs, including the testes and CNS.