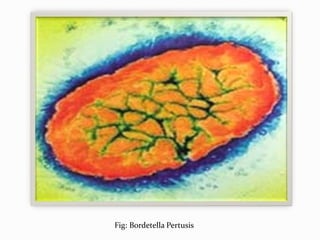
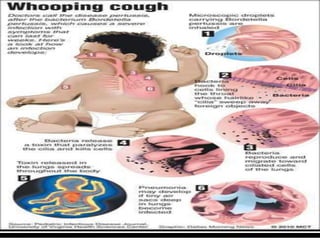
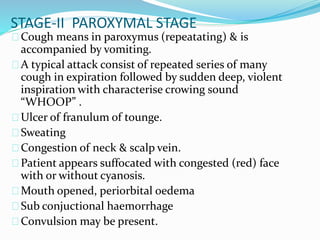
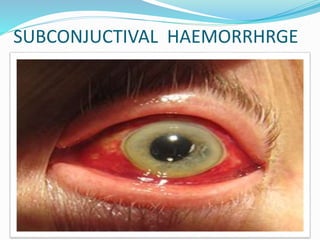
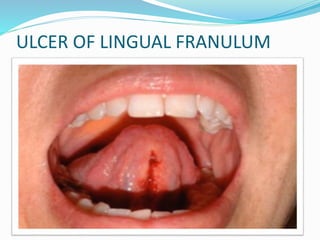
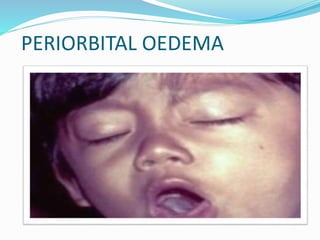
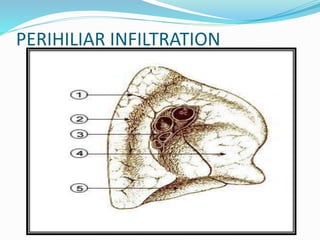
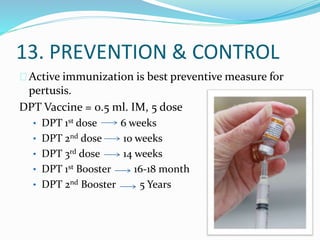
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It is characterized by severe coughing fits that can end in a "whooping" sound. It primarily affects children under 5 years old. The disease spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can be prevented through active immunization with the DPT vaccine, which is recommended in 5 doses for children up to age 6.