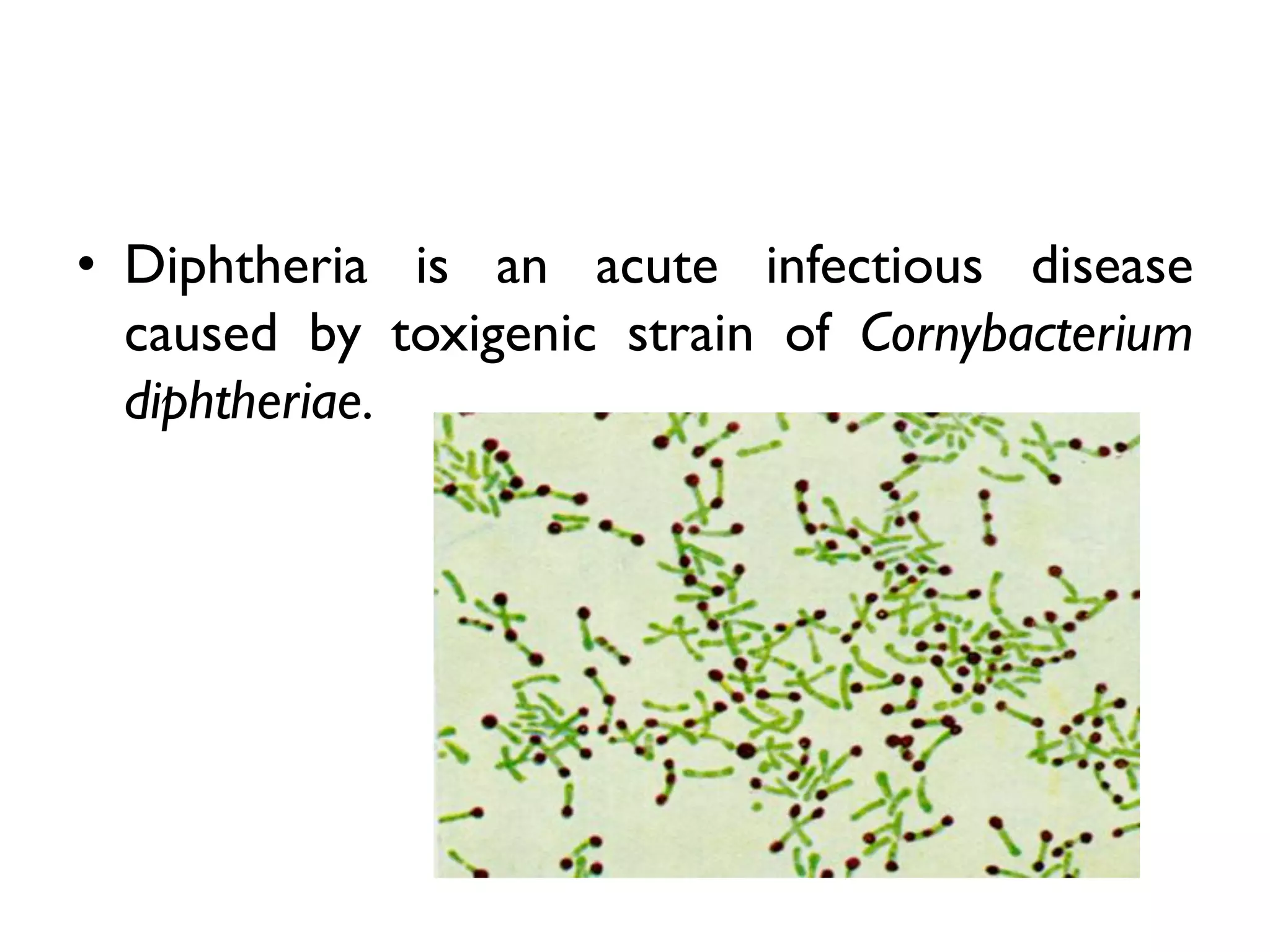
Diphtheria is an acute infectious disease caused by the toxigenic strain of Corynebacterium diphtheriae, characterized by the formation of a false membrane in the throat and severe symptoms from toxin absorption. It primarily affects children and spreads through droplet infection from carriers, with varying periods of infectivity. Control measures include early detection, isolation of cases, and immunization of infants with diphtheria toxoid.