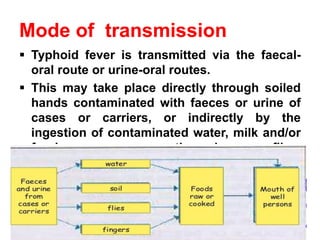
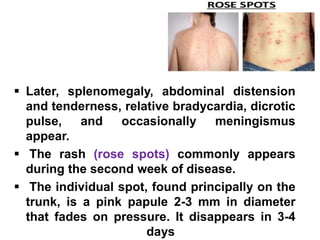
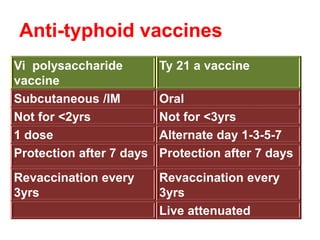
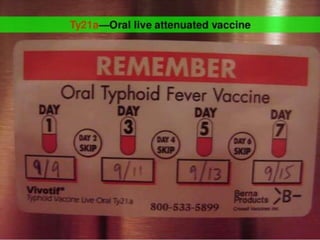
Typhoid fever is a systemic infection primarily caused by Salmonella typhi, characterized by prolonged fever, gastrointestinal symptoms, and potential complications such as intestinal hemorrhage. The disease spreads via the fecal-oral route, with humans as the sole reservoir of infection, and is particularly prevalent among individuals aged 5 to 19. Control measures include sanitation improvements, vaccination, and the treatment of infected individuals and carriers.