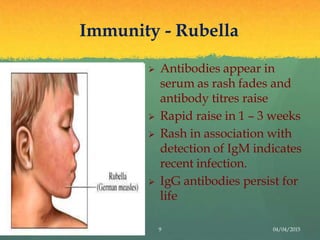
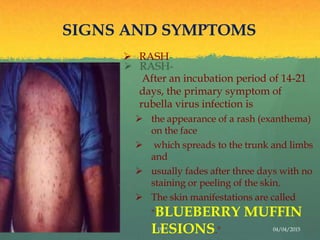
Rubella, also known as German measles, is a mild viral illness caused by the rubella virus. It was first described as a distinct clinical entity in the 18th century. In 1941, an Australian ophthalmologist documented the virus's ability to cause birth defects when a pregnant woman is infected. An attenuated vaccine was developed in 1967 that provides lifelong immunity. The virus is transmitted through respiratory droplets and causes a maculopapular rash. If a pregnant woman is infected it can lead to congenital rubella syndrome in the fetus, resulting in defects like deafness, cataracts and heart disease. Diagnosis involves virus isolation or serology to detect antibodies. There is no specific treatment but the live attenuated M