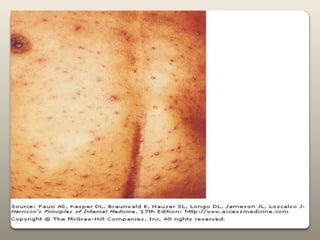
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella zoster virus. It presents as an itchy rash that starts on the torso and spreads outward. It is highly contagious but usually mild in children. Complications can include bacterial skin infections or pneumonia. Vaccination provides effective protection against chickenpox.