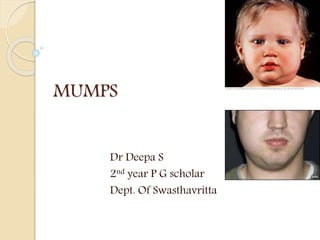
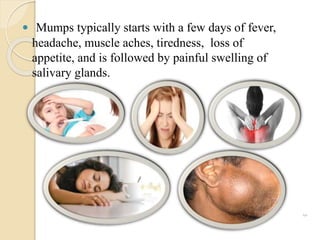
Mumps is a contagious viral infection that causes swelling of the salivary glands. It is caused by the mumps virus, an RNA virus of the paramyxovirus family. The virus is transmitted through droplets from the saliva or mucus of an infected person. Common symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, and swelling of the salivary glands. While usually self-limiting, complications can sometimes occur affecting organs like the testes, ovaries or brain. The mumps virus is most contagious in the days before and during the onset of swelling.