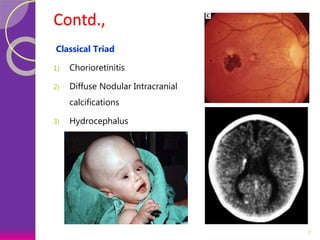
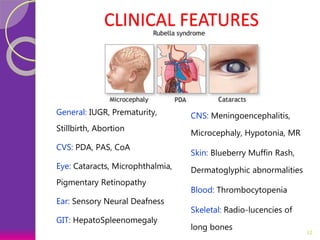
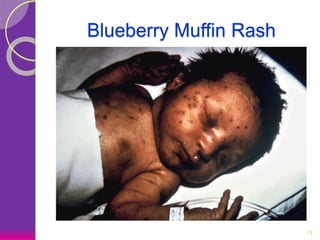
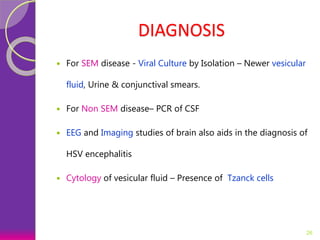
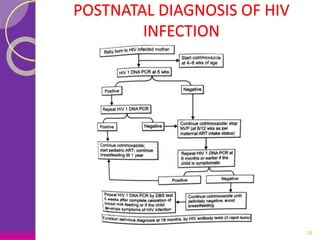
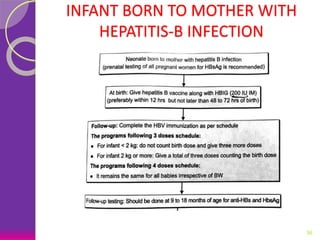
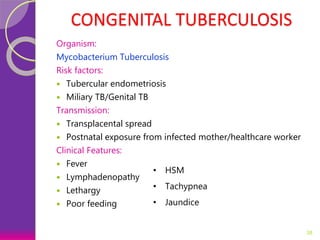
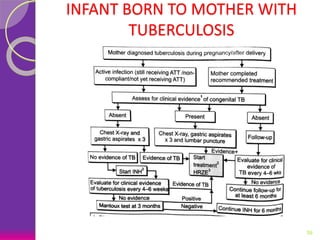
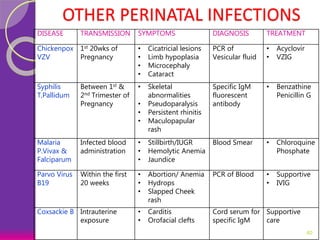
This document discusses various perinatal and congenital infections including TORCH infections. It provides details on the causative organisms, modes of transmission, clinical features, diagnosis, and management of toxoplasmosis, rubella, CMV, herpes, HIV, hepatitis B, tuberculosis, varicella zoster virus, syphilis, malaria, and parvovirus infections. Timely diagnosis and treatment of perinatally acquired infections is important. Prevention strategies include maternal screening, vaccination, treatment of infected mothers, and avoiding risk factors during pregnancy and delivery.