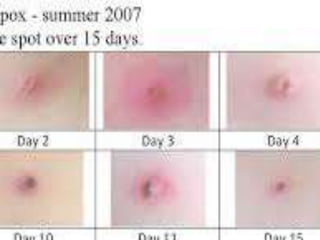
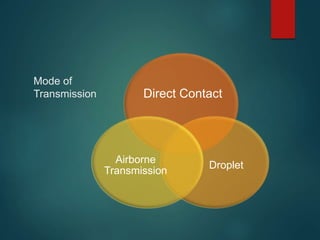
Varicella, commonly known as chickenpox, is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It presents with an itchy rash that goes through several phases from raised bumps to fluid-filled blisters to crusts and scabs. While usually mild and self-limiting, it can develop into more serious complications in babies, pregnant women, and those with weak immune systems. The virus is transmitted through direct contact or respiratory droplets. Vaccination with two doses is recommended to prevent infection. Complications may include bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, or inflammation of the brain or bloodstream. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and allowing the immune system to suppress the virus.