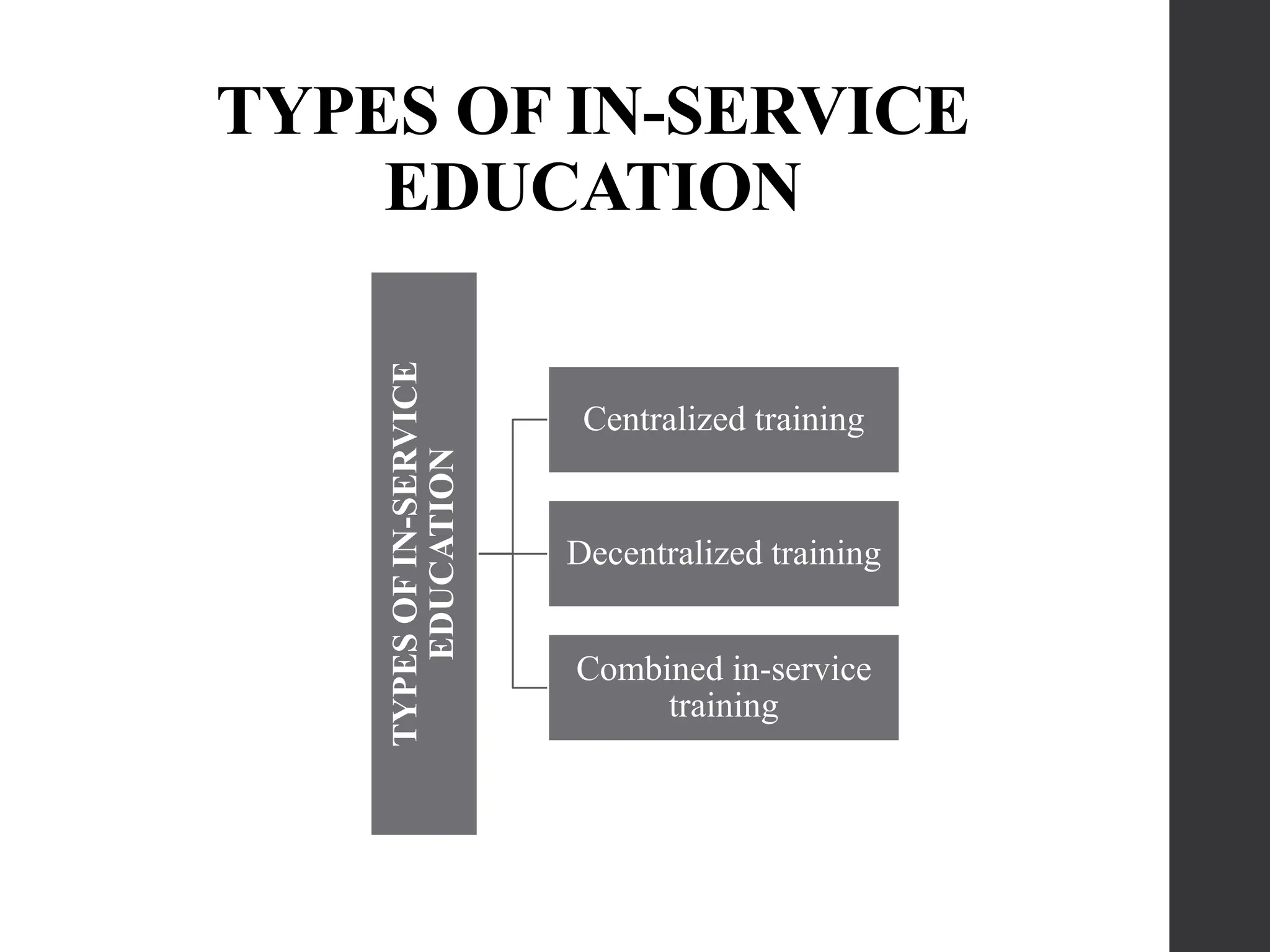
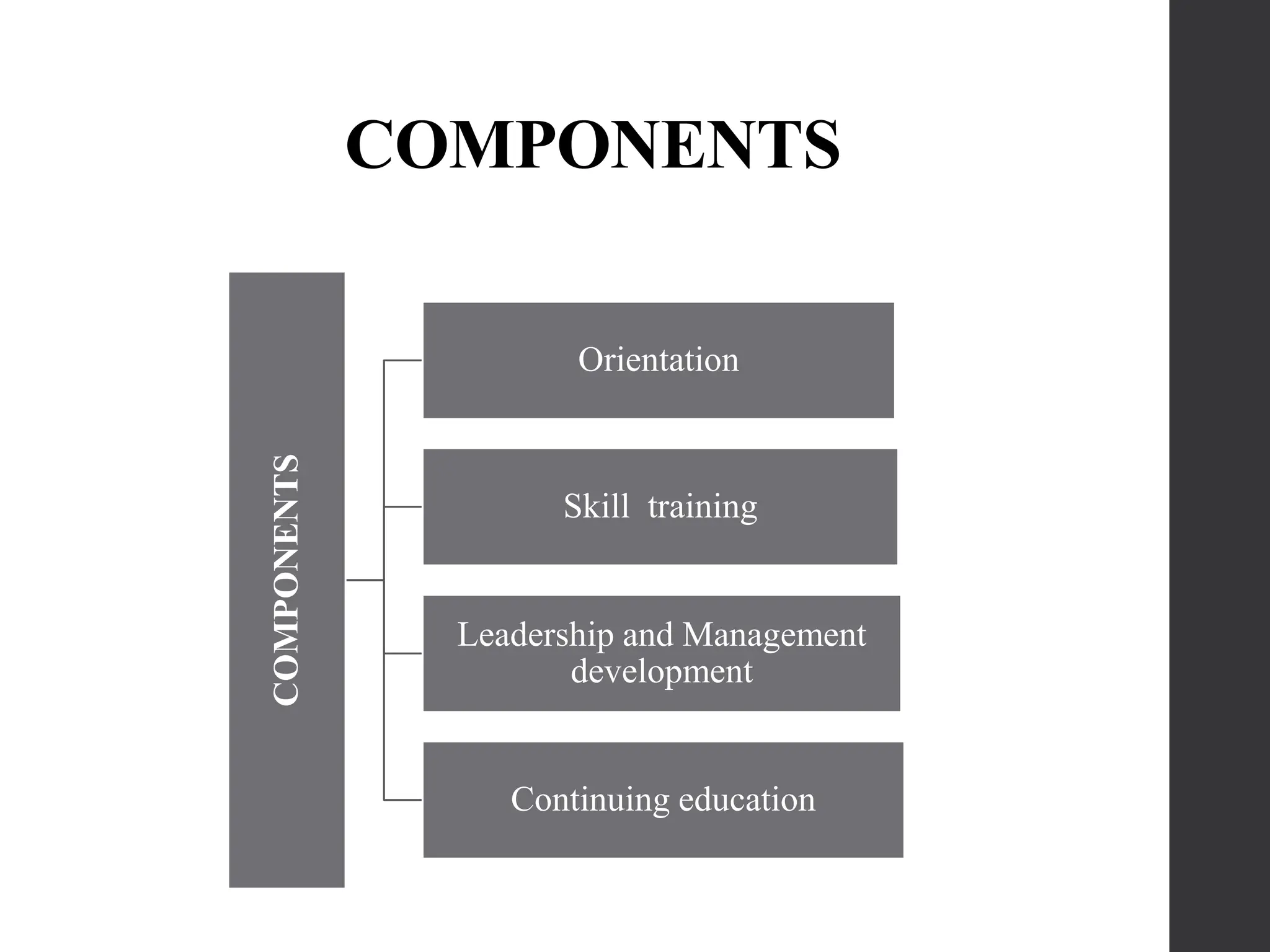
The document outlines the importance of in-service education for nursing staff as a critical component of staff development, aimed at enhancing professional competence and improving patient care. It details the program's definition, features, aims, and various planning and evaluation steps to ensure its effectiveness in meeting organizational goals. Additionally, it discusses adult learning principles and delivery methods to facilitate ongoing professional growth within the healthcare setting.