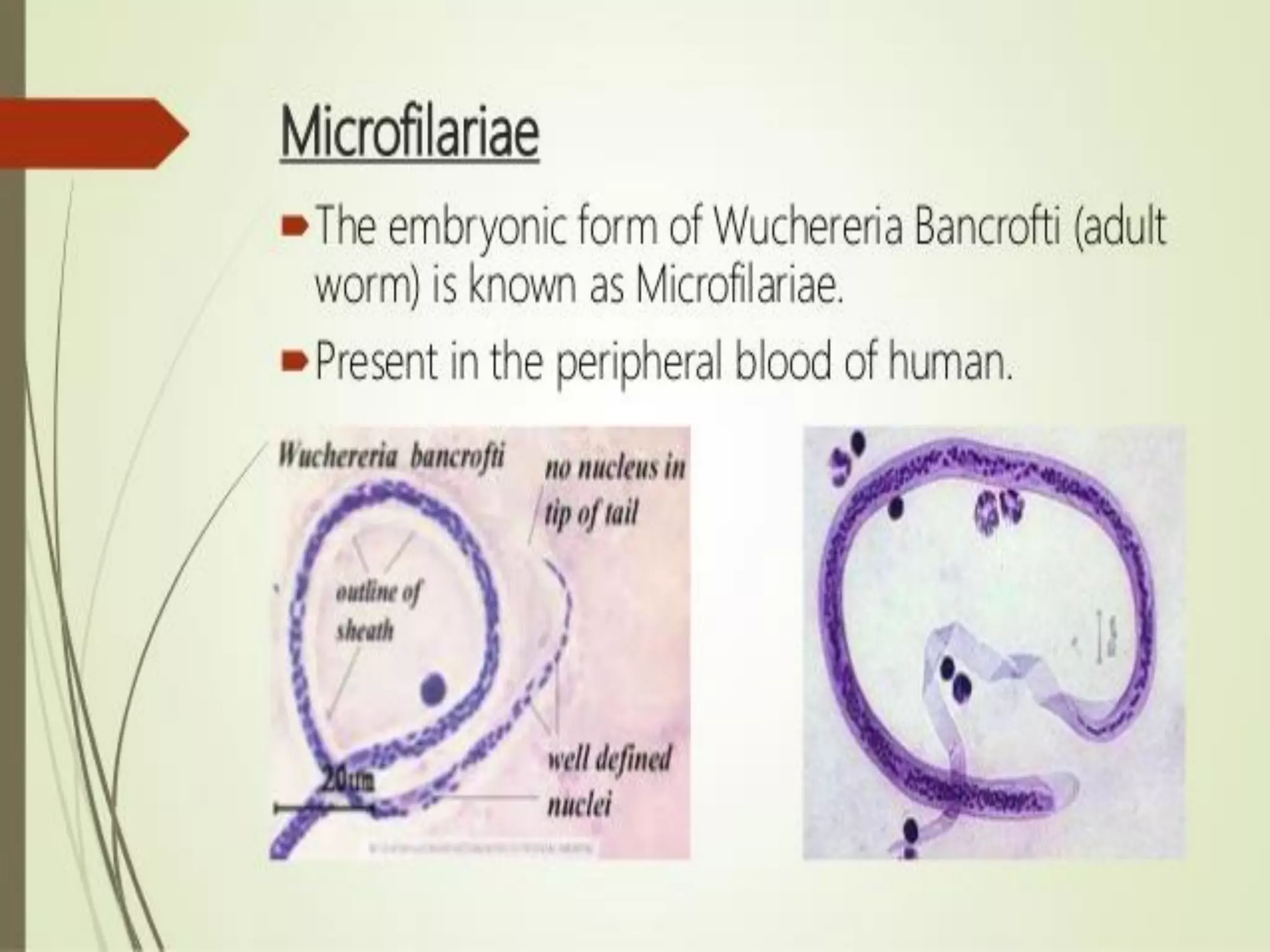
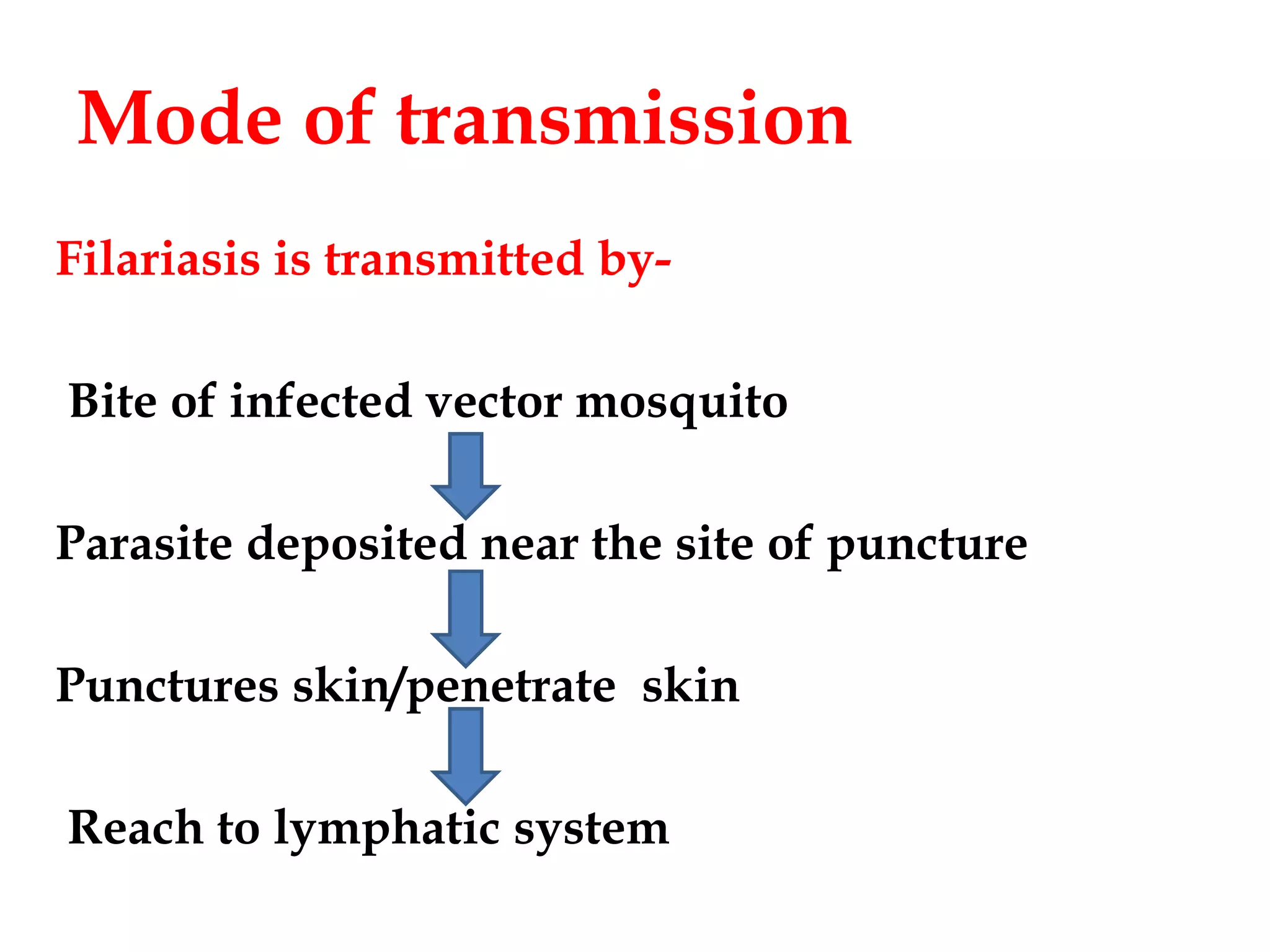
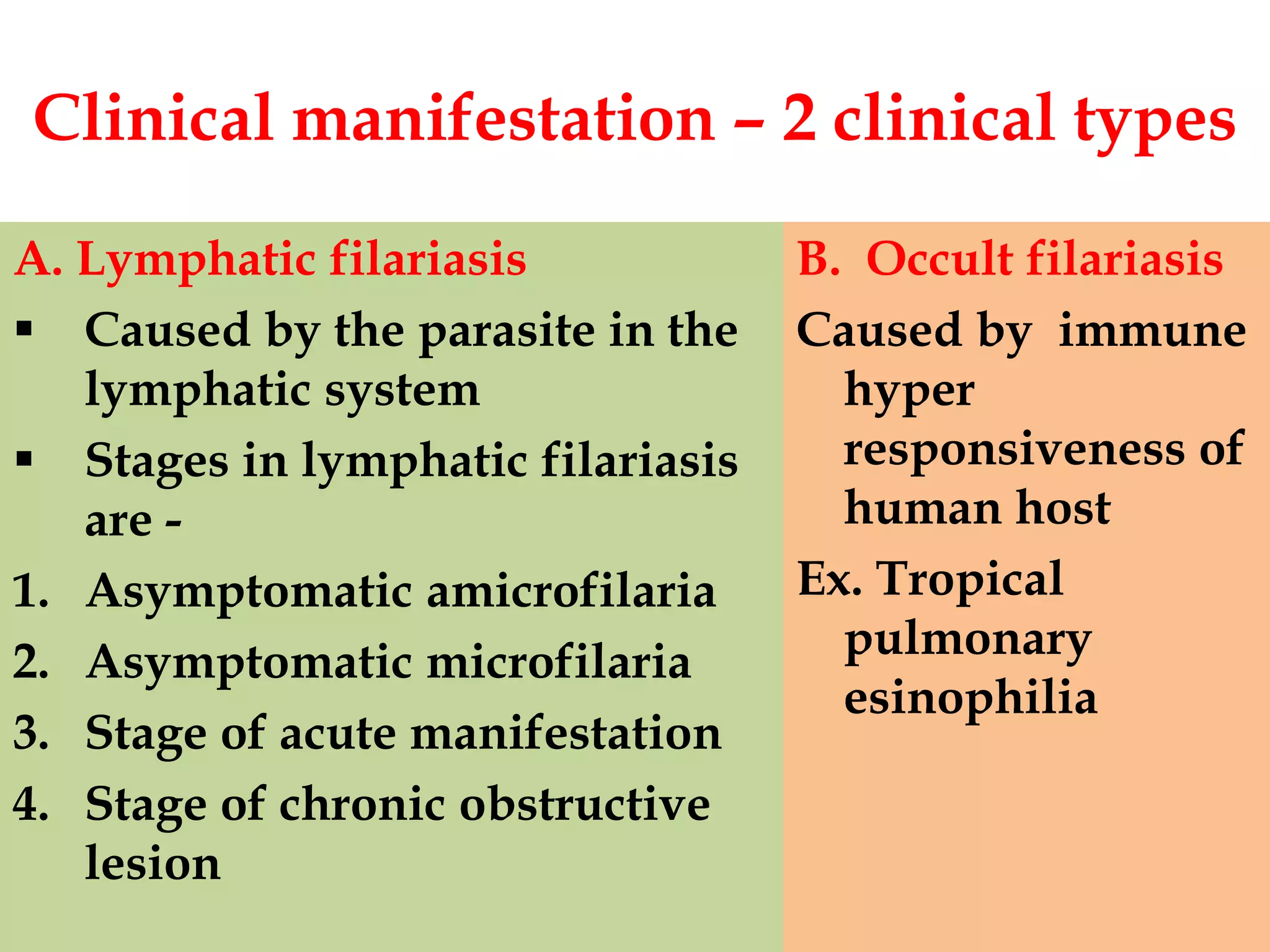
Lymphatic filariasis is caused by three nematode worms transmitted to humans through infected mosquito bites, leading to infections in the lymphatic system. It exhibits various manifestations ranging from asymptomatic microfilaria to severe chronic conditions like elephantiasis and requires both medication and vector control for effective management. The disease's epidemiology is influenced by factors including age, sex, climate, and social conditions, necessitating comprehensive community health strategies for prevention and treatment.